heredity
... carried by insects to a flower on a different plant. Pollen can also be carried by the wind from one flower to another. ...
... carried by insects to a flower on a different plant. Pollen can also be carried by the wind from one flower to another. ...
Introduction to Genetics using Punnett Squares
... flowers his pea plants were either violet or white, Mendel began to study the segregation of heritable traits. ...
... flowers his pea plants were either violet or white, Mendel began to study the segregation of heritable traits. ...
File
... Sexual reproduction leads to variety – this is critical for a species survival as the greater the variety within the individuals the more likely that at least a few of them will have the ability to survive difficult conditions ...
... Sexual reproduction leads to variety – this is critical for a species survival as the greater the variety within the individuals the more likely that at least a few of them will have the ability to survive difficult conditions ...
Challenges of integrating conventional breeding and biotechnology
... way to go for a complete tool-kit, these tools can already be applied for large-scale QTL analysis of yield and yield components to provide targets for marker-assisted selection and gene cloning for transgenic modification. In parallel, there are studies of the underlying physiological consequences ...
... way to go for a complete tool-kit, these tools can already be applied for large-scale QTL analysis of yield and yield components to provide targets for marker-assisted selection and gene cloning for transgenic modification. In parallel, there are studies of the underlying physiological consequences ...
Quiz2 Answers - biology tech support page
... During gamete formation the segregation of one gene pair is independent of all other gene pairs Two members of a gene pair segregate from each other into the gametes, whereby one half of the gametes carries one of the traits, the other half carries the other The union of one gamete from each parent ...
... During gamete formation the segregation of one gene pair is independent of all other gene pairs Two members of a gene pair segregate from each other into the gametes, whereby one half of the gametes carries one of the traits, the other half carries the other The union of one gamete from each parent ...
26. Genetics Intro Notes
... Mendel’s Pea Plant Experiments 2. Mendel cross-pollinated 2 varieties (1 true breeding tall and 1 true breeding short plant) from the P1 generation 3. This produced the F1 (“filial” or zygote/kid possibilities) generation *It was amazing to Mendel that all of the kids were tall and none of them ...
... Mendel’s Pea Plant Experiments 2. Mendel cross-pollinated 2 varieties (1 true breeding tall and 1 true breeding short plant) from the P1 generation 3. This produced the F1 (“filial” or zygote/kid possibilities) generation *It was amazing to Mendel that all of the kids were tall and none of them ...
11-3: exploring mendelian genetics
... TWO FACTOR CROSS: F 1 Following two different genes from one generation to the next. Mendel crossed true-breeding plants that produced only round yellow peas (RRYY) with plants that produced with wrinkled green peas ...
... TWO FACTOR CROSS: F 1 Following two different genes from one generation to the next. Mendel crossed true-breeding plants that produced only round yellow peas (RRYY) with plants that produced with wrinkled green peas ...
10.2-Heredity (Mendel)
... to offspring was 1st to predict how traits are transferred from one generation to the next ...
... to offspring was 1st to predict how traits are transferred from one generation to the next ...
Application No. DIR 115 - Office of the Gene Technology Regulator
... cotton into the environment on a limited scale and under controlled conditions. The GM cotton plants have been genetically modified for enhanced fibre yield. The applicant proposes to conduct the trial between August 2012 and August 2015 at one site per growing season at the local government area of ...
... cotton into the environment on a limited scale and under controlled conditions. The GM cotton plants have been genetically modified for enhanced fibre yield. The applicant proposes to conduct the trial between August 2012 and August 2015 at one site per growing season at the local government area of ...
Mendelian Genetics
... • Each gene is found at a fixed position on a particular chromosome. Making a map of their locations allows us to identify and study them better. The basis of linkage mapping is that since crossing over occurs at random locations, the closer two genes are to each other, the less likely it is that a ...
... • Each gene is found at a fixed position on a particular chromosome. Making a map of their locations allows us to identify and study them better. The basis of linkage mapping is that since crossing over occurs at random locations, the closer two genes are to each other, the less likely it is that a ...
File
... • Enzymes are used to cut up and join together parts of the DNA of one organism, and insert them into the DNA of another organism • In the resulting new organism the inserted genes will code for one or more new characteristics - for example producing a new substance, or performing a new function • T ...
... • Enzymes are used to cut up and join together parts of the DNA of one organism, and insert them into the DNA of another organism • In the resulting new organism the inserted genes will code for one or more new characteristics - for example producing a new substance, or performing a new function • T ...
3 Intro to Genetic Crosses
... • A gene is a small section of chromosome that determines a specific trait • Genes are arranged on a chromosome • Each chromosome carries specific genes ...
... • A gene is a small section of chromosome that determines a specific trait • Genes are arranged on a chromosome • Each chromosome carries specific genes ...
Model plants, with special emphasis on Arabidopsis
... those crops that have received the most R&D attention. Crop breeding as practiced to date is a time-consuming process being based on generating large numbers of gene combinations and evaluating the progeny in many locations and environments to find the plants that are superior and capable of improvi ...
... those crops that have received the most R&D attention. Crop breeding as practiced to date is a time-consuming process being based on generating large numbers of gene combinations and evaluating the progeny in many locations and environments to find the plants that are superior and capable of improvi ...
Overview - University of Missouri
... genetics, high through-put robotics and bioinformatics to derive large amounts of high quality biological information that will allow a greater understanding of the organism being studied. ...
... genetics, high through-put robotics and bioinformatics to derive large amounts of high quality biological information that will allow a greater understanding of the organism being studied. ...
Abstract
... •Hem2B is plasmid DNA containing the bla gene (positive control). E. coli is negative control. •No hybridization with this probe was seen with any ampicillin resistant laboratory strains. ...
... •Hem2B is plasmid DNA containing the bla gene (positive control). E. coli is negative control. •No hybridization with this probe was seen with any ampicillin resistant laboratory strains. ...
Chapter 9: Introduction to Genetics
... During the formation of the reproductive cells, the tall and short alleles in the F1 plants were segregated from each other ...
... During the formation of the reproductive cells, the tall and short alleles in the F1 plants were segregated from each other ...
UNIT II GENETIC ENGINEERING OF PLANTS AND APPLICATIONS
... The scientific challenge in utilizing the B. thuringiensis protoxin is to create a transgenic plant that expresses and synthesizes the functional form of this prokaryotic insecticide at sufficient levels to prevent the damage by insect predation. In initial experiments, the B.thuringiensis subsp .ku ...
... The scientific challenge in utilizing the B. thuringiensis protoxin is to create a transgenic plant that expresses and synthesizes the functional form of this prokaryotic insecticide at sufficient levels to prevent the damage by insect predation. In initial experiments, the B.thuringiensis subsp .ku ...
Unit 9(Heredity and Evolution)
... 11. Two pea plants one with round green seeds (RRyy) and another with wrinkled yellow (rrYY) seeds produce F1 progeny that have round, yellow (RrYy) seeds. When F1 plants are selfed, the F2 progeny will have new combination of characters. Choose the new combination from the following ...
... 11. Two pea plants one with round green seeds (RRyy) and another with wrinkled yellow (rrYY) seeds produce F1 progeny that have round, yellow (RrYy) seeds. When F1 plants are selfed, the F2 progeny will have new combination of characters. Choose the new combination from the following ...
Microsoft Word - AgMemo insert #1 harvest weed management
... that would normally kill this species. Genetic variation may alter physiological traits that enable herbicide uptake, translocation and activation at the site of action (target-site resistance). Alternatively, changes may influence the plant’s ability to detoxify herbicides, or enable transport to a ...
... that would normally kill this species. Genetic variation may alter physiological traits that enable herbicide uptake, translocation and activation at the site of action (target-site resistance). Alternatively, changes may influence the plant’s ability to detoxify herbicides, or enable transport to a ...
Genetics and Mendel
... • One allele is not dominant over another. • The result of these crosses produce heterozygous offspring showing traits between both homozygous parents. • Example: snapdragon ...
... • One allele is not dominant over another. • The result of these crosses produce heterozygous offspring showing traits between both homozygous parents. • Example: snapdragon ...
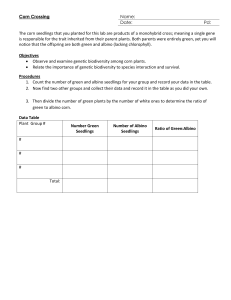
Corn Crossing Handout
... The corn seedlings that you planted for this lab are products of a monohybrid cross; meaning a single gene is responsible for the trait inherited from their parent plants. Both parents were entirely green, yet you will notice that the offspring are both green and albino (lacking chlorophyll). Object ...
... The corn seedlings that you planted for this lab are products of a monohybrid cross; meaning a single gene is responsible for the trait inherited from their parent plants. Both parents were entirely green, yet you will notice that the offspring are both green and albino (lacking chlorophyll). Object ...
Agenda 06/12/06 1. Notes - Genetics 2. Practice Problems 3
... • Dominant Allele prevents other Dominant genes from showing their traits. • These are written ...
... • Dominant Allele prevents other Dominant genes from showing their traits. • These are written ...
Non-Mendelian Genetics
... (Classical) Genetics? What are Alleles? • Developed by Gregor Mendel (1822-1884): studied heredity in pea plants (mainly texture and color of seeds); based solely on observations (no knowledge of DNA or meiosis) – see cartoon – Law of Segregation: there are two sets of genes for a particular trait ( ...
... (Classical) Genetics? What are Alleles? • Developed by Gregor Mendel (1822-1884): studied heredity in pea plants (mainly texture and color of seeds); based solely on observations (no knowledge of DNA or meiosis) – see cartoon – Law of Segregation: there are two sets of genes for a particular trait ( ...
NOTES: CH 14, part 1 - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... ● Gregor Mendel, an Austrian monk, applied mathematics to his study of genetics. He chose to study the garden pea plant to investigate how traits were passed from generation to generation. Mendel’s Experimental, Quantitative Approach ● Mendel chose to work with peas: -Because they are -Because he co ...
... ● Gregor Mendel, an Austrian monk, applied mathematics to his study of genetics. He chose to study the garden pea plant to investigate how traits were passed from generation to generation. Mendel’s Experimental, Quantitative Approach ● Mendel chose to work with peas: -Because they are -Because he co ...