Post-mortem SNP analysis of CYP2D6 gene reveals correlation
... Furthermore, post-mortem pharmacokinetic determinations are inevitably limited to one-time sampling instead of measuring the area under the curve, which may complicate interpretation. In case of tramadol, the elimination half lives of the parent compound and O-demethyltramadol are fairly similar (6 ...
... Furthermore, post-mortem pharmacokinetic determinations are inevitably limited to one-time sampling instead of measuring the area under the curve, which may complicate interpretation. In case of tramadol, the elimination half lives of the parent compound and O-demethyltramadol are fairly similar (6 ...
Revisiting the Impact of Inversions in Evolution
... where the interacting loci reside (Nei 1967, Pepper 2003). Because inversion polymorphisms generate low recombination rates among the standard (noninverted) and inverted arrangements, they facilitate the spread of the coadapted alleles. Inversions carrying favorable alleles then spread to fixation un ...
... where the interacting loci reside (Nei 1967, Pepper 2003). Because inversion polymorphisms generate low recombination rates among the standard (noninverted) and inverted arrangements, they facilitate the spread of the coadapted alleles. Inversions carrying favorable alleles then spread to fixation un ...
Pleiotropy and the evolution of floral integration
... QTL on linkage group 4 in Penstemon affects both petal reflexing and nectar concentration, and the additive effect of substituting the P. barbatus allele (the parent with more reflexed petals and more dilute nectar) is an increase in reflexing and decrease in nectar concentration (Wessinger et al., ...
... QTL on linkage group 4 in Penstemon affects both petal reflexing and nectar concentration, and the additive effect of substituting the P. barbatus allele (the parent with more reflexed petals and more dilute nectar) is an increase in reflexing and decrease in nectar concentration (Wessinger et al., ...
Genetics Study Guide
... 20. The diagram below shows the first part of Mendel’s experiment. Label the parent (P) generation and the F1 generation. Also label the hybrid plants. ...
... 20. The diagram below shows the first part of Mendel’s experiment. Label the parent (P) generation and the F1 generation. Also label the hybrid plants. ...
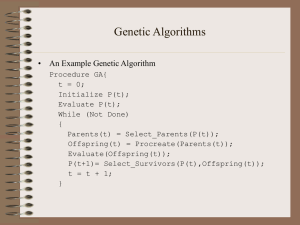
GAs
... • Crossover is usually the primary operator with mutation serving only as a mechanism to introduce diversity in the population. • However, when designing a GA to solve a problem it is not uncommon that one will have to develop unique crossover and mutation operators that take advantage of the struct ...
... • Crossover is usually the primary operator with mutation serving only as a mechanism to introduce diversity in the population. • However, when designing a GA to solve a problem it is not uncommon that one will have to develop unique crossover and mutation operators that take advantage of the struct ...
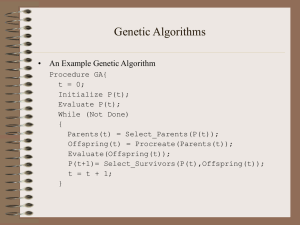
Genetic Algorithms
... • Crossover is usually the primary operator with mutation serving only as a mechanism to introduce diversity in the population. • However, when designing a GA to solve a problem it is not uncommon that one will have to develop unique crossover and mutation operators that take advantage of the struct ...
... • Crossover is usually the primary operator with mutation serving only as a mechanism to introduce diversity in the population. • However, when designing a GA to solve a problem it is not uncommon that one will have to develop unique crossover and mutation operators that take advantage of the struct ...
Questions - Vanier College
... Two prospective parents are meeting with a genetic counsellor because of the presence of factor VIII deficiency hemophilia in both of their families. Factor VIII is a protein that helps the blood to clot, and when a person’s factor VIII level is very low, even the smallest cuts can be troublesome, a ...
... Two prospective parents are meeting with a genetic counsellor because of the presence of factor VIII deficiency hemophilia in both of their families. Factor VIII is a protein that helps the blood to clot, and when a person’s factor VIII level is very low, even the smallest cuts can be troublesome, a ...
Laboratory 4 Patterns of Inheritance (human)
... expression is sex-limited, meaning their expression is limited to one sex or another. Other traits are not determined by a single gene, but by many genes with various alleles for each gene; these traits are called polygenic. Some genes influence genes at another locus; this phenomenon is called epis ...
... expression is sex-limited, meaning their expression is limited to one sex or another. Other traits are not determined by a single gene, but by many genes with various alleles for each gene; these traits are called polygenic. Some genes influence genes at another locus; this phenomenon is called epis ...
Virtual Lab - Ants
... Modeling Natural Selection- Virtual Lab -Ants and abiotic Factors How does Natural Selection affect allele frequency? In this exploration you will investigate a simulated model of natural selection of an organism in different environments. The simulation represents the effect of predation on natural ...
... Modeling Natural Selection- Virtual Lab -Ants and abiotic Factors How does Natural Selection affect allele frequency? In this exploration you will investigate a simulated model of natural selection of an organism in different environments. The simulation represents the effect of predation on natural ...
1 Direct evidence that genetic variation in glycerol-3
... fermentation products including alcohols. In particular, it is believed that the high tolerance of D. melanogaster to alcohols is an evolved phenotype because other members of the melanogaster subgroup, such as D. simulans, show lower tolerance and avoid alcohol exposure (Mckenzie and Parsons 1972; ...
... fermentation products including alcohols. In particular, it is believed that the high tolerance of D. melanogaster to alcohols is an evolved phenotype because other members of the melanogaster subgroup, such as D. simulans, show lower tolerance and avoid alcohol exposure (Mckenzie and Parsons 1972; ...
The Rat Gene Map
... fewer) conserved segments. Thus, the number of apparently conserved autosomal chromosome segments is only 33. Of the 20 singletons, 8 appear to be located inside existing segments. The maximal number of conserved segments indicated by the present data set is 61—about half the number of segments fou ...
... fewer) conserved segments. Thus, the number of apparently conserved autosomal chromosome segments is only 33. Of the 20 singletons, 8 appear to be located inside existing segments. The maximal number of conserved segments indicated by the present data set is 61—about half the number of segments fou ...
Traits and Families
... A gene is a recipe for a protein. It is used by the cell to make that protein. In achondroplasia, the normal allele (FGRF3) codes for a protein (fibroblast growth factor) that is part of the structure of normal bones, including those of the arms and legs. The achondroplasia allele produces a protein ...
... A gene is a recipe for a protein. It is used by the cell to make that protein. In achondroplasia, the normal allele (FGRF3) codes for a protein (fibroblast growth factor) that is part of the structure of normal bones, including those of the arms and legs. The achondroplasia allele produces a protein ...
Recombination and epistasis facilitate introgressive hybridization
... two types of hazard to the endemic species. One is hybrid sterility, which inhibits normal reproduction, and the other is introgressive hybridization, which does not completely retard mating and reproduction by hybridization but instead allows exotic species or local varieties to genetically admix w ...
... two types of hazard to the endemic species. One is hybrid sterility, which inhibits normal reproduction, and the other is introgressive hybridization, which does not completely retard mating and reproduction by hybridization but instead allows exotic species or local varieties to genetically admix w ...
The Promises and Pitfalls of Genoeconomics
... These advances in genetics are in turn transforming medical research. Some diseases have been linked to single genetic mutations in specific genes (e.g., Huntington’s disease and Fragile X syndrome), which can be assayed to diagnose the disease, predict the age of onset and/or severity, and better u ...
... These advances in genetics are in turn transforming medical research. Some diseases have been linked to single genetic mutations in specific genes (e.g., Huntington’s disease and Fragile X syndrome), which can be assayed to diagnose the disease, predict the age of onset and/or severity, and better u ...
Heterozygote Advantage: The Effect of Artificial Selection in
... fitness in mutant homozygotes because of low survival, mating, and/or reproduction. Here when artificial selection or another fitness component besides survival results in zero fitness, we will indicate this using quotes as “lethal.” Typically such recessive lethals would generally be at a very low ...
... fitness in mutant homozygotes because of low survival, mating, and/or reproduction. Here when artificial selection or another fitness component besides survival results in zero fitness, we will indicate this using quotes as “lethal.” Typically such recessive lethals would generally be at a very low ...
1. True or False? The standard human karotype consists of 23 pairs
... 4. True or False? Genetically unbalanced chromosomal complements due to an extra or missing chromosome often have more severe effects on phenotype than does addition of genetically balanced set of chromosomes. True ...
... 4. True or False? Genetically unbalanced chromosomal complements due to an extra or missing chromosome often have more severe effects on phenotype than does addition of genetically balanced set of chromosomes. True ...
Document
... caused by loci at which heterozygotes are more fit than both homozygotes. Inbreeding decreases the frequency of heterozygotes, increases the frequency of homozygotes, so fitness is reduced. Dominance Hypothesis: Genetic variance for fitness is caused by rare deleterious alleles that are recessive or ...
... caused by loci at which heterozygotes are more fit than both homozygotes. Inbreeding decreases the frequency of heterozygotes, increases the frequency of homozygotes, so fitness is reduced. Dominance Hypothesis: Genetic variance for fitness is caused by rare deleterious alleles that are recessive or ...
video slide - CARNES AP BIO
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Mutant Mice and Neuroscience: Viewpoint Recommendations
... commonly used ES cell lines are polymorphic at a number of loci, showing that they were not derived from inbred strains (Simpson et al., 1997). This raises the possibility that random segregation of these polymorphic loci to either mutants or controls could affect the phenotypes of the resulting ani ...
... commonly used ES cell lines are polymorphic at a number of loci, showing that they were not derived from inbred strains (Simpson et al., 1997). This raises the possibility that random segregation of these polymorphic loci to either mutants or controls could affect the phenotypes of the resulting ani ...
Maximum likelihood methods for detecting adaptive evolution after
... are the single-copy genes that predate the duplication event. Paralogs 1 and 2 refer to the two sets of genes that derived from the duplication event. The one-ratio model (R1) assumes all branches have the same parameter. The R2 model assumes one is for all branches that predate the duplication ...
... are the single-copy genes that predate the duplication event. Paralogs 1 and 2 refer to the two sets of genes that derived from the duplication event. The one-ratio model (R1) assumes all branches have the same parameter. The R2 model assumes one is for all branches that predate the duplication ...
Linkage Analysis of Endogenous Viral Element 1, Blue Eggshell
... in this family. Selfed progeny of the vigorous mutant selected in 1993 expressed the mutant phenotype in the greenhouse in the winter greenhouse cycle of 1993-1994, indicating that the expression of the trait was not sensitive to environmental conditions. Panicle characteristics segregated in a 1:1 ...
... in this family. Selfed progeny of the vigorous mutant selected in 1993 expressed the mutant phenotype in the greenhouse in the winter greenhouse cycle of 1993-1994, indicating that the expression of the trait was not sensitive to environmental conditions. Panicle characteristics segregated in a 1:1 ...
Permutation Representation
... new individuals through recombination and mutation • The new individuals have their fitness evaluated and compete (possibly also with parents) for survival. • Over time Natural selection causes a rise in the fitness of the population ...
... new individuals through recombination and mutation • The new individuals have their fitness evaluated and compete (possibly also with parents) for survival. • Over time Natural selection causes a rise in the fitness of the population ...
Lab #7
... Females are homozygous X (XX), while males are heterozygous (XY). The terms usually used are homogametic for females (because they can only give Xs to their gametes) and heterogametic for males (because they can give gametes with either Xs or Ys). In addition to determining the sex of the individual ...
... Females are homozygous X (XX), while males are heterozygous (XY). The terms usually used are homogametic for females (because they can only give Xs to their gametes) and heterogametic for males (because they can give gametes with either Xs or Ys). In addition to determining the sex of the individual ...
Polymorphism (biology)

Polymorphism in biology is said to occur when two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species—in other words, the occurrence of more than one form or morph. In order to be classified as such, morphs must occupy the same habitat at the same time and belong to a panmictic population (one with random mating).Polymorphism as described here involves morphs of the phenotype. The term is also used somewhat differently by molecular biologists to describe certain point mutations in the genotype, such as SNPs (see also RFLPs). This usage is not discussed in this article.Polymorphism is common in nature; it is related to biodiversity, genetic variation and adaptation; it usually functions to retain variety of form in a population living in a varied environment. The most common example is sexual dimorphism, which occurs in many organisms. Other examples are mimetic forms of butterflies (see mimicry), and human hemoglobin and blood types.According to the theory of evolution, polymorphism results from evolutionary processes, as does any aspect of a species. It is heritable and is modified by natural selection. In polyphenism, an individual's genetic make-up allows for different morphs, and the switch mechanism that determines which morph is shown is environmental. In genetic polymorphism, the genetic make-up determines the morph. Ants exhibit both types in a single population.Polymorphism also refers to the occurrence of structurally and functionally more than two different types of individuals, called zooids within the same organism. It is a characteristic feature of Cnidarians.For example, in Obelia there are feeding individuals, the gastrozooids; the individuals capable of asexual reproduction only, the gonozooids, blastostyles and free-living or sexually reproducing individuals, the medusae.