Topic 7: Mendelian and Human Genetics Uncover Inheritance
... CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITIES Chromosomal abnormalities, in the form of nondisjunction, are very common among humans. It's estimated that up to half of all miscarriages are due to some form of chromosome disorder. Sex chromosome disorders are the most commonly observed type of aneuploidy in humans, beca ...
... CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITIES Chromosomal abnormalities, in the form of nondisjunction, are very common among humans. It's estimated that up to half of all miscarriages are due to some form of chromosome disorder. Sex chromosome disorders are the most commonly observed type of aneuploidy in humans, beca ...
Human Pedigrees
... chance mating of carriers is extremely rare – For example ~20% of albinos are born of unions between cousins – And first cousin marriages account for ~40% of TaySachs kids – Also true of disease-causing recessive alleles eg. cystic fibrosis and PK4 phenylketonuria ...
... chance mating of carriers is extremely rare – For example ~20% of albinos are born of unions between cousins – And first cousin marriages account for ~40% of TaySachs kids – Also true of disease-causing recessive alleles eg. cystic fibrosis and PK4 phenylketonuria ...
Natural Selection - The Science Queen
... The individuals that survive are not always the strongest, fastest, or smartest. Therefore, "survival of the fittest" ...
... The individuals that survive are not always the strongest, fastest, or smartest. Therefore, "survival of the fittest" ...
Chapter 2 - Test Bank 1
... 9. Some alleles mask another and are dominant, while the other is recessive. 10. Co-dominance is also possible. 11. The A-B-O blood type system provides examples for this discussion, with hemoglobin cited an example of a protein with over a hundred alleles. D. Polygenetic Inheritance 1. Many physica ...
... 9. Some alleles mask another and are dominant, while the other is recessive. 10. Co-dominance is also possible. 11. The A-B-O blood type system provides examples for this discussion, with hemoglobin cited an example of a protein with over a hundred alleles. D. Polygenetic Inheritance 1. Many physica ...
Change in moth population over 80 years, 630-631
... d) Do you think that the change was a result of a change in reproductive capacity of the two kinds of moths? Do you think the change was a result of the survival of the moth best fit for the environment (selection pressure)? e) What has happened to the frequency of the gene for speckled white color ...
... d) Do you think that the change was a result of a change in reproductive capacity of the two kinds of moths? Do you think the change was a result of the survival of the moth best fit for the environment (selection pressure)? e) What has happened to the frequency of the gene for speckled white color ...
Chapter 23
... • Natural selection increases the frequencies of alleles that enhance survival and reproduction • Adaptive evolution occurs as the match between an organism and its environment increases • Because the environment can change, adaptive evolution is a continuous process ...
... • Natural selection increases the frequencies of alleles that enhance survival and reproduction • Adaptive evolution occurs as the match between an organism and its environment increases • Because the environment can change, adaptive evolution is a continuous process ...
Random Allelic Variation
... alone because they become fixed for different alleles or different combinations of alleles at unlinked loci The probability that an allele will ultimately become fixed is equal to its frequency in the population in any given generation Rate of fixation (or loss) is greater in small populations ...
... alone because they become fixed for different alleles or different combinations of alleles at unlinked loci The probability that an allele will ultimately become fixed is equal to its frequency in the population in any given generation Rate of fixation (or loss) is greater in small populations ...
File
... Different versions of the same gene are called alleles (uh-LEELZ) Alleles are important because they account for the differences in inherited characteristics from one individual to another. Homologous chromosomes often contain different alleles because one comes from the mother and the other c ...
... Different versions of the same gene are called alleles (uh-LEELZ) Alleles are important because they account for the differences in inherited characteristics from one individual to another. Homologous chromosomes often contain different alleles because one comes from the mother and the other c ...
Document
... Determining the order of genes can be done with a three-point testcross the frequency of double crossovers is the product of the probabilities of each ...
... Determining the order of genes can be done with a three-point testcross the frequency of double crossovers is the product of the probabilities of each ...
Document
... Lake Victoria -- more than 500 species of haplochromine cichlids morphological, ecological, and behavioral diversity ...
... Lake Victoria -- more than 500 species of haplochromine cichlids morphological, ecological, and behavioral diversity ...
APOC3 rs2854116 single nucleotide polymorphism
... polymorphism and frequencies of alleles and genotypic of this polymorphism. The demand for APOC3-rs2854116 genotype analysis will therefore increase, making a fast, reliable assay for APOC3 genotyping essential. Methods for determining APOC3 genotypes were known along time ago. Methods for genotypin ...
... polymorphism and frequencies of alleles and genotypic of this polymorphism. The demand for APOC3-rs2854116 genotype analysis will therefore increase, making a fast, reliable assay for APOC3 genotyping essential. Methods for determining APOC3 genotypes were known along time ago. Methods for genotypin ...
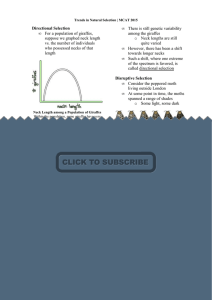
Directional Selection • For a population of giraffes, suppose we
... So, the most fit robins would lay a few eggs o There will be an evolutionary trend towards laying a few eggs ...
... So, the most fit robins would lay a few eggs o There will be an evolutionary trend towards laying a few eggs ...
Words in text: 1,591 Group Selection Kathryn Demps and Peter
... are often distinct entities within a population of competing cultural groups. Culturally, group selection applies to the increase in frequency of traits in the larger population that contribute to the comparative success of a cultural group against other groups. One example of a behavior that contri ...
... are often distinct entities within a population of competing cultural groups. Culturally, group selection applies to the increase in frequency of traits in the larger population that contribute to the comparative success of a cultural group against other groups. One example of a behavior that contri ...
Principles of Inheritance
... depending upon whether they are expressed (dominant) or hidden (recessive) in heterozygotes –In the ABO system, A and B alleles are dominant over O, and co-dominant with each other (Blood type AB) –O is recessive to both A and B ...
... depending upon whether they are expressed (dominant) or hidden (recessive) in heterozygotes –In the ABO system, A and B alleles are dominant over O, and co-dominant with each other (Blood type AB) –O is recessive to both A and B ...
Unit VIII Evolution - Elizabethtown Area School District
... evolution is a foundational scientific truth, one that has stood up to rigorous scrutiny and upon which much of human knowledge and achievement rests. To reject this truth or to treat it as “one theory among others” is to deliberately embrace scientific ignorance and transmit such ignorance to our c ...
... evolution is a foundational scientific truth, one that has stood up to rigorous scrutiny and upon which much of human knowledge and achievement rests. To reject this truth or to treat it as “one theory among others” is to deliberately embrace scientific ignorance and transmit such ignorance to our c ...
Document
... Knew that there is great variation among species, but didn’t know that variation originates by mutation. Knew that variation is inherited, but didn’t know about genes, had poor theory of inheritance. Knew that natural selection acts on variation to cause adaptation in organisms, but didn’t kno ...
... Knew that there is great variation among species, but didn’t know that variation originates by mutation. Knew that variation is inherited, but didn’t know about genes, had poor theory of inheritance. Knew that natural selection acts on variation to cause adaptation in organisms, but didn’t kno ...
Plant Genetic Diversity and the Struggle to
... selection, and as a consequence, recent thinking has emphasized the role of mutation and genetic random drift as the primary determinants of genetic diversity. The resulting neutral theory of molecular evolution has dominated population genetic thought for more than 20 years. Nonadaptlve theories ha ...
... selection, and as a consequence, recent thinking has emphasized the role of mutation and genetic random drift as the primary determinants of genetic diversity. The resulting neutral theory of molecular evolution has dominated population genetic thought for more than 20 years. Nonadaptlve theories ha ...
Слайд 1 - SvitPPT
... • Polymorphism: A genetic variation that is observed at a frequency of >1% in a population ...
... • Polymorphism: A genetic variation that is observed at a frequency of >1% in a population ...
Evolution of Populations
... 1. If a trait made an organism less likely to survive and reproduce, what would happen to the allele for that trait? Fewer copies of the allele would pass to future generations and the allele could even disappear from the gene pool completely. ...
... 1. If a trait made an organism less likely to survive and reproduce, what would happen to the allele for that trait? Fewer copies of the allele would pass to future generations and the allele could even disappear from the gene pool completely. ...
Slide - UBC Botany
... • Selection affects the distribution of alleles within populations • Method examines site frequency spectrum and compares to neutral expectations • Could be applied to a single locus. Now used often for genomic scans for selective sweeps ...
... • Selection affects the distribution of alleles within populations • Method examines site frequency spectrum and compares to neutral expectations • Could be applied to a single locus. Now used often for genomic scans for selective sweeps ...
Polymorphism (biology)

Polymorphism in biology is said to occur when two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species—in other words, the occurrence of more than one form or morph. In order to be classified as such, morphs must occupy the same habitat at the same time and belong to a panmictic population (one with random mating).Polymorphism as described here involves morphs of the phenotype. The term is also used somewhat differently by molecular biologists to describe certain point mutations in the genotype, such as SNPs (see also RFLPs). This usage is not discussed in this article.Polymorphism is common in nature; it is related to biodiversity, genetic variation and adaptation; it usually functions to retain variety of form in a population living in a varied environment. The most common example is sexual dimorphism, which occurs in many organisms. Other examples are mimetic forms of butterflies (see mimicry), and human hemoglobin and blood types.According to the theory of evolution, polymorphism results from evolutionary processes, as does any aspect of a species. It is heritable and is modified by natural selection. In polyphenism, an individual's genetic make-up allows for different morphs, and the switch mechanism that determines which morph is shown is environmental. In genetic polymorphism, the genetic make-up determines the morph. Ants exhibit both types in a single population.Polymorphism also refers to the occurrence of structurally and functionally more than two different types of individuals, called zooids within the same organism. It is a characteristic feature of Cnidarians.For example, in Obelia there are feeding individuals, the gastrozooids; the individuals capable of asexual reproduction only, the gonozooids, blastostyles and free-living or sexually reproducing individuals, the medusae.