Ingen lysbildetittel
... population size. We show that there is a simple relation between the demographic variance and genetic drift in age-structured populations and how to use this to estimate effective population size and its agespecific components from individual data of age, survival and fecundity. Reproductive values ...
... population size. We show that there is a simple relation between the demographic variance and genetic drift in age-structured populations and how to use this to estimate effective population size and its agespecific components from individual data of age, survival and fecundity. Reproductive values ...
Genetics 2 - MaxSkyFan
... Test Cross • Test cross: When a single trait is being studied, a test cross is a cross between an individual with the dominant phenotype but of unknown genotype (homozygous or heterozygous) with a homozygous recessive individual. If the unknown is heterozygous, then approximately 50% of the ...
... Test Cross • Test cross: When a single trait is being studied, a test cross is a cross between an individual with the dominant phenotype but of unknown genotype (homozygous or heterozygous) with a homozygous recessive individual. If the unknown is heterozygous, then approximately 50% of the ...
the role of germline polymorphisms in the t-cell
... Other HLA-B genes, such as B60, have also been implicated in susceptibility to the disease [5]. The presence of susceptibility genes for AS outside the MHC is supported by family and twin studies which demonstrate that genetic susceptibility to AS is likely to be due to the effect of multiple loci a ...
... Other HLA-B genes, such as B60, have also been implicated in susceptibility to the disease [5]. The presence of susceptibility genes for AS outside the MHC is supported by family and twin studies which demonstrate that genetic susceptibility to AS is likely to be due to the effect of multiple loci a ...
P Cross
... • Extra X chromosome interferes with meiosis and usually prevents these individuals from reproducing • Most common sex chromosome disorder, second most common disorder due to the presence of an extra chromosome ...
... • Extra X chromosome interferes with meiosis and usually prevents these individuals from reproducing • Most common sex chromosome disorder, second most common disorder due to the presence of an extra chromosome ...
Name Period
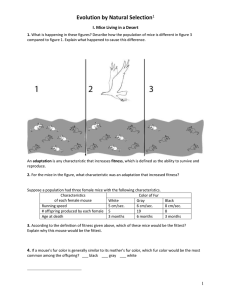
... where tree trunks and branches are lighter? ___black ___ speckled Which form of the peppered moth do you think had higher mortality in forests in areas where air pollution had resulted in dark tree trunks and branches? ___ black ___ speckled ...
... where tree trunks and branches are lighter? ___black ___ speckled Which form of the peppered moth do you think had higher mortality in forests in areas where air pollution had resulted in dark tree trunks and branches? ___ black ___ speckled ...
SERIES: ‘‘GENETICS OF ASTHMA AND COPD IN THE POSTGENOME ERA’’
... comparing the mathematical distribution of alleles in the population of interest and the population from which its founders are likely to have emigrated [1]. Genetic drift, however, is caused by the nature of sexual reproduction, in which each individual allele in a parent has a 50% chance of being ...
... comparing the mathematical distribution of alleles in the population of interest and the population from which its founders are likely to have emigrated [1]. Genetic drift, however, is caused by the nature of sexual reproduction, in which each individual allele in a parent has a 50% chance of being ...
Slightly beyond Turing`s computability for studying Genetic
... Not so many mathematical fundations in GP Not so many open problems in computability, in particular with applications ...
... Not so many mathematical fundations in GP Not so many open problems in computability, in particular with applications ...
Genetics
... the sex chromosomes, most commonly on the X chromosome. Genes on the X and Y chromosomes are often called sex-linked genes. Because males have only one X chromosome, males are more likely than females to have a sex linked trait that is controlled by a recessive allele. Females, however, tend to be c ...
... the sex chromosomes, most commonly on the X chromosome. Genes on the X and Y chromosomes are often called sex-linked genes. Because males have only one X chromosome, males are more likely than females to have a sex linked trait that is controlled by a recessive allele. Females, however, tend to be c ...
Regulatory region variability in the human presenilin-2
... effectively regulated by different inducible factors than the PSEN1 gene. For example, we have shown that there are multiple hypoxia inducible elements in the PSEN2 5-⬘ upstream promoter region and a sustained increase in PSEN2 gene expression in rat pup retina after induction by hypoxia.18,19 The f ...
... effectively regulated by different inducible factors than the PSEN1 gene. For example, we have shown that there are multiple hypoxia inducible elements in the PSEN2 5-⬘ upstream promoter region and a sustained increase in PSEN2 gene expression in rat pup retina after induction by hypoxia.18,19 The f ...
lecture 8 notes
... • The closer it is to 1, the more likely it is to reach 1 before it reaches 0. • Probability of fixing A: pA • Probability of fixing a: pa • With no other forces, eventually one or the other must fix. ...
... • The closer it is to 1, the more likely it is to reach 1 before it reaches 0. • Probability of fixing A: pA • Probability of fixing a: pa • With no other forces, eventually one or the other must fix. ...
Genetic Drift
... • The closer it is to 1, the more likely it is to reach 1 before it reaches 0. • Probability of fixing A: pA • Probability of fixing a: pa • With no other forces, eventually one or the other must fix. ...
... • The closer it is to 1, the more likely it is to reach 1 before it reaches 0. • Probability of fixing A: pA • Probability of fixing a: pa • With no other forces, eventually one or the other must fix. ...
Ch. 11 ppt
... PowerPoint® Lecture Slides are prepared by Dr. Isaac Barjis, Biology Instructor Copyright © The McGraw Hill Companies Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display ...
... PowerPoint® Lecture Slides are prepared by Dr. Isaac Barjis, Biology Instructor Copyright © The McGraw Hill Companies Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display ...
Partha - IIT Kanpur
... Choose n individuals randomly Pick the one with highest fitness Place n copies of this individual in the mating pool Choose n different individuals and repeat the process till all in the original population have been chosen ...
... Choose n individuals randomly Pick the one with highest fitness Place n copies of this individual in the mating pool Choose n different individuals and repeat the process till all in the original population have been chosen ...
Evolution of Genes and Genes in Evolution
... times as much as a sea urchin, five to six times as much as a limpet, and some fifty times as much as a sponge. So far so good; but the frog exceeds man by a factor of more than two, the lungfish Protopterus by at least sixteen, and the urodele amphidian, Amphiuma, by more than twenty five. The D N ...
... times as much as a sea urchin, five to six times as much as a limpet, and some fifty times as much as a sponge. So far so good; but the frog exceeds man by a factor of more than two, the lungfish Protopterus by at least sixteen, and the urodele amphidian, Amphiuma, by more than twenty five. The D N ...
Algorithms for Selecting a Mate
... Has no effect on the genetic content, just the way the information is stored. Requires additional meta-information to be stored that describes the location of each bit. ...
... Has no effect on the genetic content, just the way the information is stored. Requires additional meta-information to be stored that describes the location of each bit. ...
Genetics Study Guide
... • Short growing period/Easy to Grow • 7 traits in 2 distinct forms • Produces many offspring ...
... • Short growing period/Easy to Grow • 7 traits in 2 distinct forms • Produces many offspring ...
Document
... So, very clearly, delta p depends on allele frequencies, the strength of selection, and dominance. If allele 1 is a favored dominant (h=0), what is delta p? If allele 1 is a favored recessive (h=1), what is delta p? If allele 1 is “co-dominant” (h=1/2), what is delta p? Assuming allele 1 is rare (p ...
... So, very clearly, delta p depends on allele frequencies, the strength of selection, and dominance. If allele 1 is a favored dominant (h=0), what is delta p? If allele 1 is a favored recessive (h=1), what is delta p? If allele 1 is “co-dominant” (h=1/2), what is delta p? Assuming allele 1 is rare (p ...
CHP12ABIOH - willisworldbio
... be expressed because he does not inherit on the __ chromosome from his father a dominant allele that would ____ the expression of the recessive allele. • Two traits that are governed by X-linked recessive inheritance in humans are ______________________and __________. ...
... be expressed because he does not inherit on the __ chromosome from his father a dominant allele that would ____ the expression of the recessive allele. • Two traits that are governed by X-linked recessive inheritance in humans are ______________________and __________. ...
Finch Lab
... some of the finches on the island. Within this population, there is variation in beak size. Some individual birds have large beaks and some have small beaks. Assume that the allele for a large beak is “B” and the allele for a small beak is “b’. Large beaks are dominant. Recently, a La Nina event occ ...
... some of the finches on the island. Within this population, there is variation in beak size. Some individual birds have large beaks and some have small beaks. Assume that the allele for a large beak is “B” and the allele for a small beak is “b’. Large beaks are dominant. Recently, a La Nina event occ ...
Hello, and thank you for your enquiry about the horse genetics
... little degree level study. Do not let this frighten you - I always think of first year degree level as being the time when students of disparate backgrounds are brought up to a similar level of knowledge in their degree subject, as far as that is possible. (I taught genetics at university for quite ...
... little degree level study. Do not let this frighten you - I always think of first year degree level as being the time when students of disparate backgrounds are brought up to a similar level of knowledge in their degree subject, as far as that is possible. (I taught genetics at university for quite ...
Polymorphism (biology)

Polymorphism in biology is said to occur when two or more clearly different phenotypes exist in the same population of a species—in other words, the occurrence of more than one form or morph. In order to be classified as such, morphs must occupy the same habitat at the same time and belong to a panmictic population (one with random mating).Polymorphism as described here involves morphs of the phenotype. The term is also used somewhat differently by molecular biologists to describe certain point mutations in the genotype, such as SNPs (see also RFLPs). This usage is not discussed in this article.Polymorphism is common in nature; it is related to biodiversity, genetic variation and adaptation; it usually functions to retain variety of form in a population living in a varied environment. The most common example is sexual dimorphism, which occurs in many organisms. Other examples are mimetic forms of butterflies (see mimicry), and human hemoglobin and blood types.According to the theory of evolution, polymorphism results from evolutionary processes, as does any aspect of a species. It is heritable and is modified by natural selection. In polyphenism, an individual's genetic make-up allows for different morphs, and the switch mechanism that determines which morph is shown is environmental. In genetic polymorphism, the genetic make-up determines the morph. Ants exhibit both types in a single population.Polymorphism also refers to the occurrence of structurally and functionally more than two different types of individuals, called zooids within the same organism. It is a characteristic feature of Cnidarians.For example, in Obelia there are feeding individuals, the gastrozooids; the individuals capable of asexual reproduction only, the gonozooids, blastostyles and free-living or sexually reproducing individuals, the medusae.