Populations: Survivorship Curves
... likelihood that at least some members of a species will survive under gradually changing environmental conditions. • Relate how distribution and abundance of organisms and populations in ecosystems are limited by the ability of the ecosystem to recycle materials and the availability of matter, space ...
... likelihood that at least some members of a species will survive under gradually changing environmental conditions. • Relate how distribution and abundance of organisms and populations in ecosystems are limited by the ability of the ecosystem to recycle materials and the availability of matter, space ...
Cornell Notes: Dividing Decimals
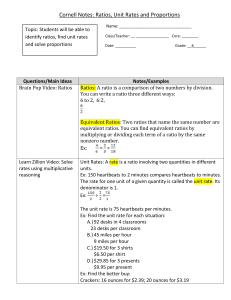
... Ratios: A ratio is a comparison of two numbers by division. You can write a ratio three different ways: 6 to 2, 6:2, ...
... Ratios: A ratio is a comparison of two numbers by division. You can write a ratio three different ways: 6 to 2, 6:2, ...
Chapter 5 Review
... happening with the birthrate and the deathrate (two different things)? If a population increases, this means births would be higher than deaths, so the population could either have A) an increase of birthrate over deathrate, or B) a decrease of deathrate to below birth rate. 12) Assuming immigration ...
... happening with the birthrate and the deathrate (two different things)? If a population increases, this means births would be higher than deaths, so the population could either have A) an increase of birthrate over deathrate, or B) a decrease of deathrate to below birth rate. 12) Assuming immigration ...
Response of sexual behaviour and desired family size to the HIV
... (Abstinence, Be faithful, use Condoms) 2. Number attending Voluntary Counselling and Testing has increased (1,000 in 2000; 400,000 in 2004) 3. Many respondents indicated that sexual behaviour had changed little (among unmarried young people, higher income men and lower income women) ...
... (Abstinence, Be faithful, use Condoms) 2. Number attending Voluntary Counselling and Testing has increased (1,000 in 2000; 400,000 in 2004) 3. Many respondents indicated that sexual behaviour had changed little (among unmarried young people, higher income men and lower income women) ...
Chapter 8 & 9 Review
... • A) the most developed countries • B) the least developed countries • C) countries in the second stage of demographic transition ...
... • A) the most developed countries • B) the least developed countries • C) countries in the second stage of demographic transition ...
AP Chap 53 Population Ecology
... • Demography is the study of the vital statistics (death and birth rates) of a population and how they change over time • Death rates and birth rates are of particular interest to demographers • A life table is an age-specific summary of the survival pattern of a population • It is best made by foll ...
... • Demography is the study of the vital statistics (death and birth rates) of a population and how they change over time • Death rates and birth rates are of particular interest to demographers • A life table is an age-specific summary of the survival pattern of a population • It is best made by foll ...
“Trade-offs” and Life Histories
... No population can grow indefinitely, and humans are no exception.The human population increased relatively slowly until about 1650 and then began to grow exponentially. Though the global population is still growing, the rate of growth began to slow during the 1960s Regional Patterns of Population Ch ...
... No population can grow indefinitely, and humans are no exception.The human population increased relatively slowly until about 1650 and then began to grow exponentially. Though the global population is still growing, the rate of growth began to slow during the 1960s Regional Patterns of Population Ch ...
6.247Mb Microsoft PowerPoint
... Many students have participated in the project since it began nearly three years ago. In addition to the six involved in the production of this poster, they include Rachel Schoen, Rachel Haazert, Carissa Pannell, Patrick Murack, Bill Hintz, Kristine Funk, Rebecca Kitzman, Kristine Dahlheimer and Nal ...
... Many students have participated in the project since it began nearly three years ago. In addition to the six involved in the production of this poster, they include Rachel Schoen, Rachel Haazert, Carissa Pannell, Patrick Murack, Bill Hintz, Kristine Funk, Rebecca Kitzman, Kristine Dahlheimer and Nal ...
Chapter 5 Exam: DO NOT WRITE ON THIS EXAM 1. Which of the
... 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the factors that play a role in population growth rate? a. immigration c. emigration b. death rate d. demography 2. One of the main characteristics of a population is its a. change over time c. dynamics b. geographic distribution d. habitat 3. There are 150 Sa ...
... 1. Which of the following is NOT one of the factors that play a role in population growth rate? a. immigration c. emigration b. death rate d. demography 2. One of the main characteristics of a population is its a. change over time c. dynamics b. geographic distribution d. habitat 3. There are 150 Sa ...
Chapter 53 Notes - Rogue Community College
... • long life expectancies • high GNI PPP: –GNI PPP per capita is the gross national income in purchasing power parity divided by mid-year population. ...
... • long life expectancies • high GNI PPP: –GNI PPP per capita is the gross national income in purchasing power parity divided by mid-year population. ...
14 investigating Population growth rates
... b. Describe what would happen if the bacteria continued to reproduce for 24 hours (do not calculate an exact number). c. Suggest at least two limiting factors that will ultimately stop the increase of a bacteria population. 6. Scientists and policy makers often have to work together to set catch ...
... b. Describe what would happen if the bacteria continued to reproduce for 24 hours (do not calculate an exact number). c. Suggest at least two limiting factors that will ultimately stop the increase of a bacteria population. 6. Scientists and policy makers often have to work together to set catch ...
Population Ecology - mshsRebeccaMazoff
... rate, the potential life-span, the average life expectancy, and the average age of reproduction are important determinants of the makeup of a population. ...
... rate, the potential life-span, the average life expectancy, and the average age of reproduction are important determinants of the makeup of a population. ...
07_PopBio
... Understand the three types of survivorship curves. What factors influence population growth rates? What are some life history traits? Know the difference between K- and r- strategists and what kind of limiting factors each has. ...
... Understand the three types of survivorship curves. What factors influence population growth rates? What are some life history traits? Know the difference between K- and r- strategists and what kind of limiting factors each has. ...
SilentSpring-EcologySlideShow-APBio
... Competition for Resources- in crowded populations, increasing population density intensifies Interspecific competition for declining resources, resulting in a lower birth rate. Territoriality- when territory space becomes the resource for which individuals compete. The presence of non-breeding indiv ...
... Competition for Resources- in crowded populations, increasing population density intensifies Interspecific competition for declining resources, resulting in a lower birth rate. Territoriality- when territory space becomes the resource for which individuals compete. The presence of non-breeding indiv ...
Population Ecology
... Population Dynamics • Theoretically, if reproduction and mortality rates in a non-mobile population are equal and constant, the number of individuals in the population would remain constant • Natural population are not static – Constantly subject to change and motion because of many variable factor ...
... Population Dynamics • Theoretically, if reproduction and mortality rates in a non-mobile population are equal and constant, the number of individuals in the population would remain constant • Natural population are not static – Constantly subject to change and motion because of many variable factor ...
video slide
... rate of increase declines as carrying capacity is reached We construct the logistic model by starting with the exponential model and adding an expression that reduces per capita rate of increase as N increases The logistic growth equation includes K, the carrying capacity ...
... rate of increase declines as carrying capacity is reached We construct the logistic model by starting with the exponential model and adding an expression that reduces per capita rate of increase as N increases The logistic growth equation includes K, the carrying capacity ...
How Do Populations Change in Size?
... Female rabbits can have between 1-7 litters per year (average 3-4/year). 1) Theoretically, how many babies could 1 female rabbit birth in one year? 2) If half of the babies from #1 are female, how many more baby rabbits could be born the next season? 3) What would happen to the population if these b ...
... Female rabbits can have between 1-7 litters per year (average 3-4/year). 1) Theoretically, how many babies could 1 female rabbit birth in one year? 2) If half of the babies from #1 are female, how many more baby rabbits could be born the next season? 3) What would happen to the population if these b ...
version
... given age that are breeding and the number of female offspring of those breeding females. Belding’s Ground Squirrel reproduction peaks at age 4 years and falls off in older age classes. Reproductive tables differ greatly from species to species. Humans, squirrels and oysters all produce very differe ...
... given age that are breeding and the number of female offspring of those breeding females. Belding’s Ground Squirrel reproduction peaks at age 4 years and falls off in older age classes. Reproductive tables differ greatly from species to species. Humans, squirrels and oysters all produce very differe ...
Population Ecology
... i) ΔN = change in population size ii) Δ t = time interval iii) B = number of births iv) D = number of deaths IV) Per Capita (Per individual0 Growth Rate a) Now express B as average birth (bN) per capita (per individual) per year → i) b= per capita birth rate → number offspring produced per year by a ...
... i) ΔN = change in population size ii) Δ t = time interval iii) B = number of births iv) D = number of deaths IV) Per Capita (Per individual0 Growth Rate a) Now express B as average birth (bN) per capita (per individual) per year → i) b= per capita birth rate → number offspring produced per year by a ...
BLY 303 Lecture Notes, 2012 (O`Brien) III. Population Growth
... Following the development of the Germ Theory of Disease, child mortality decreased significantly ...
... Following the development of the Germ Theory of Disease, child mortality decreased significantly ...
Factors Affecting Human Population Size
... The economic cost of raising and educating children determines their numbers. the more children cost, the less children people tend to have. ...
... The economic cost of raising and educating children determines their numbers. the more children cost, the less children people tend to have. ...
Biotic Potential
... but then stops increasing. • The reason for this is that the environment can no longer support the vast number of new cells being produced. • A food shortage may result. • Bacteria also produce waste products which may be toxic to themselves. ...
... but then stops increasing. • The reason for this is that the environment can no longer support the vast number of new cells being produced. • A food shortage may result. • Bacteria also produce waste products which may be toxic to themselves. ...
Birth rate
The birth rate (technically, births/population rate) is the total number of live births per 1,000 of a population in a year. The rate of births in a population is calculated in several ways: live births from a universal registration system for births, deaths, and marriages; population counts from a census, and estimation through specialized demographic techniques. The birth rate (along with mortality and migration rate) are used to calculate population growth.The crude birth rate is the number of live births per 1,000 people per year. Another term used interchangeably with birth rate is natality. When the crude death rate is subtracted from the crude birth rate, the result is the rate of natural increase (RNI). This is equal to the rate of population change (excluding migration).The total (crude) birth rate (which includes all births)—typically indicated as births per 1,000 population—is distinguished from an age-specific rate (the number of births per 1,000 persons in an age group). The first known use of the term ""birth rate"" in English occurred in 1859.In 2012 the average global birth rate was 19.15 births per 1,000 total population, compared to 20.09 per 1,000 total population in 2007.The raw birth rate (not births/population rate) is 4.3 births/second for the world (2014 est.).