DNA Functions
... the ribosome, the proper amino acid is brought into the ribosome by tRNA. In the ribosome, the amino acid is transferred to the growing polypeptide chain [protein]. Each tRNA molecule carries only one kind of amino acid. In addition to an amino acid, each tRNA molecule has three upaired bases ...
... the ribosome, the proper amino acid is brought into the ribosome by tRNA. In the ribosome, the amino acid is transferred to the growing polypeptide chain [protein]. Each tRNA molecule carries only one kind of amino acid. In addition to an amino acid, each tRNA molecule has three upaired bases ...
6.4 Traits, Genes, and Alleles KEY CONCEPT of traits.
... 6.4 Traits, Genes, and Alleles • An allele is any alternative form of a gene occurring at a specific locus on a chromosome. – Each parent donates one allele for every gene. – Homozygous describes two alleles that are the same at a specific locus. – Heterozygous describes two alleles that are differ ...
... 6.4 Traits, Genes, and Alleles • An allele is any alternative form of a gene occurring at a specific locus on a chromosome. – Each parent donates one allele for every gene. – Homozygous describes two alleles that are the same at a specific locus. – Heterozygous describes two alleles that are differ ...
6.4 Traits, Genes, and Alleles
... 6.4 Traits, Genes, and Alleles • An allele is any alternative form of a gene occurring at a specific locus on a chromosome. – Each parent donates one allele for every gene. – Homozygous describes two alleles that are the same at a specific locus. – Heterozygous describes two alleles that are differ ...
... 6.4 Traits, Genes, and Alleles • An allele is any alternative form of a gene occurring at a specific locus on a chromosome. – Each parent donates one allele for every gene. – Homozygous describes two alleles that are the same at a specific locus. – Heterozygous describes two alleles that are differ ...
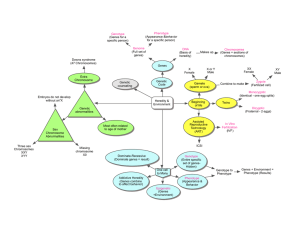
coding and non-coding functions of the genome
... “Until recently, we had a dogmatic view that established a very simple relationship: one gene equals one protein,” explained Luciano Di Croce, ICREA professor, group leader at the Center for Genomic Regulation in Barcelona and scientific leader of this B·Debate. “That made research very easy, becaus ...
... “Until recently, we had a dogmatic view that established a very simple relationship: one gene equals one protein,” explained Luciano Di Croce, ICREA professor, group leader at the Center for Genomic Regulation in Barcelona and scientific leader of this B·Debate. “That made research very easy, becaus ...
chapter10_all
... • Differentiation occurs as different cell lineages begin to express different subsets of their genes • Which genes a cell uses determines the molecules it will produce, which in turn determines what kind of cell it will be • differentiation • Process by which cells become specialized ...
... • Differentiation occurs as different cell lineages begin to express different subsets of their genes • Which genes a cell uses determines the molecules it will produce, which in turn determines what kind of cell it will be • differentiation • Process by which cells become specialized ...
Vocabulary Quiz Key Terms
... An enzyme that breaks the hydrogen bonds holding the base pairs together as it unwinds and unzips the double helix, allowing new nucleotides to bind to the 2 single strands by base pairing. An enzyme that adds complementary nucleotides to the template strand of the unzipped double helix until the en ...
... An enzyme that breaks the hydrogen bonds holding the base pairs together as it unwinds and unzips the double helix, allowing new nucleotides to bind to the 2 single strands by base pairing. An enzyme that adds complementary nucleotides to the template strand of the unzipped double helix until the en ...
Protein synthesis
... 12. The second step is called _______________________________ and links _____________________________________ together to form a chain, which folds into a 3D structure to form a ______________________. Be sure to click through Transcription and Translation, too, not just the overview. What three reg ...
... 12. The second step is called _______________________________ and links _____________________________________ together to form a chain, which folds into a 3D structure to form a ______________________. Be sure to click through Transcription and Translation, too, not just the overview. What three reg ...
How Environmental Factors Influence Transcription (PowerPoint)
... • Students will know how environmental factors influence transcription. ...
... • Students will know how environmental factors influence transcription. ...
Predicting Mitochondrial tRNA Modification - CS 229
... Central Dogma of Biology [1]. Essentially, this Dogma states that DNA sequence (which serves as data storage) is transcribed to messenger RNA (mRNA transcripts) and later translated into proteins, which are nano-scale machines that do most of the functional work in the cell. This flow of information ...
... Central Dogma of Biology [1]. Essentially, this Dogma states that DNA sequence (which serves as data storage) is transcribed to messenger RNA (mRNA transcripts) and later translated into proteins, which are nano-scale machines that do most of the functional work in the cell. This flow of information ...
Plasmids are fragments of double-stranded DNA that can replicate
... Short segment of DNA which contains several restriction sites allowing for the easy insertion of DNA. In expression plasmids, the MCS is often downstream from a promoter. Gene, promoter or other DNA fragment cloned into the MCS for further study. Drives transcription of the target gene. Vital compon ...
... Short segment of DNA which contains several restriction sites allowing for the easy insertion of DNA. In expression plasmids, the MCS is often downstream from a promoter. Gene, promoter or other DNA fragment cloned into the MCS for further study. Drives transcription of the target gene. Vital compon ...
Genetic Terminology
... discovering that a gene is linked to another gene (which can serve as a marker for it), assigning genes to particular chromosomes, assigning genes to specific regions on chromosomes, and determining nucleotide sequences on chromosomes. Meiosis: The type of cell division that occurs in sex cells by ...
... discovering that a gene is linked to another gene (which can serve as a marker for it), assigning genes to particular chromosomes, assigning genes to specific regions on chromosomes, and determining nucleotide sequences on chromosomes. Meiosis: The type of cell division that occurs in sex cells by ...
Gene expression (central dogma)
... A DNA molecule consists of functional units called genes. Each gene provides instructions for a functional product (a molecule needed to perform a job in the cell). In many cases, the functional product of a gene is a protein. The functional products of most known genes are proteins, or, more accura ...
... A DNA molecule consists of functional units called genes. Each gene provides instructions for a functional product (a molecule needed to perform a job in the cell). In many cases, the functional product of a gene is a protein. The functional products of most known genes are proteins, or, more accura ...
Sodium Channel Mutations and Susceptibility to Heart
... A, Heteroduplex mutation scans of exons comprising the entire codingregion of SCN5A were performed by denaturing highperformanceliquid chromatography (DHPLC). Heterozygous variation in DNA sequence wasdetected in exons 6, 16, 17, 21, and 27 for the 5 family probands in Figure 1 and Figure 3. In cont ...
... A, Heteroduplex mutation scans of exons comprising the entire codingregion of SCN5A were performed by denaturing highperformanceliquid chromatography (DHPLC). Heterozygous variation in DNA sequence wasdetected in exons 6, 16, 17, 21, and 27 for the 5 family probands in Figure 1 and Figure 3. In cont ...
drug
... … but resistant strains of M.t. are appearing • Of ~ 4400 ORFs in 4.4 Mbp genome, large number for fatty acid metabolism (lipid biosynthesis & degradation) - complex membranes for defense? and enzymes to degrade lipids in host cell membranes? • Large families of novel, glycine-rich protein genes ...
... … but resistant strains of M.t. are appearing • Of ~ 4400 ORFs in 4.4 Mbp genome, large number for fatty acid metabolism (lipid biosynthesis & degradation) - complex membranes for defense? and enzymes to degrade lipids in host cell membranes? • Large families of novel, glycine-rich protein genes ...
Ch 18
... assistance of proteins called transcription factors (TFs) – General TFs are essential for the transcription of all protein-coding genes – In eukaryotes, high levels of transcription of particular genes depend on control elements interacting with specific TFs proximal control elementsare located cl ...
... assistance of proteins called transcription factors (TFs) – General TFs are essential for the transcription of all protein-coding genes – In eukaryotes, high levels of transcription of particular genes depend on control elements interacting with specific TFs proximal control elementsare located cl ...
Section 6: Information Flow
... 2. Both strains possess the genes for pigment biosynthesis but expression patterns differ. Students need not report back at this point. The goal is to stimulate interest and thought regarding this observable difference. ...
... 2. Both strains possess the genes for pigment biosynthesis but expression patterns differ. Students need not report back at this point. The goal is to stimulate interest and thought regarding this observable difference. ...
Section 6-1
... • Traits controlled by single genes with only two alleles – Height in pea plants – Widow’s peak – Stuff from last unit • Multiple Alleles – Some traits controlled by a single gene with more than two alleles • Blood type – controlled by three alleles – Type A – IAIA or IAi – Type B – IBIB or IBi – Ty ...
... • Traits controlled by single genes with only two alleles – Height in pea plants – Widow’s peak – Stuff from last unit • Multiple Alleles – Some traits controlled by a single gene with more than two alleles • Blood type – controlled by three alleles – Type A – IAIA or IAi – Type B – IBIB or IBi – Ty ...
dna methylation
... maintenance • They are coordinated with DNA methylation • Catch 22: The histone structure and everything around them is coded in DNA ...
... maintenance • They are coordinated with DNA methylation • Catch 22: The histone structure and everything around them is coded in DNA ...
dna methylation
... maintenance • They are coordinated with DNA methylation • Catch 22: The histone structure and everything around them is coded in DNA ...
... maintenance • They are coordinated with DNA methylation • Catch 22: The histone structure and everything around them is coded in DNA ...
Lecture 17 - The Eukaryotic Genome
... thought there was going to be one gene for each human trait. And if you want to cure greed, you change the greed gene, right? Or the envy gene, which is probably far more dangerous. But it turns out that we're pretty complex. If you want to find out why someone gets Alzheimer's or cancer, then it is ...
... thought there was going to be one gene for each human trait. And if you want to cure greed, you change the greed gene, right? Or the envy gene, which is probably far more dangerous. But it turns out that we're pretty complex. If you want to find out why someone gets Alzheimer's or cancer, then it is ...
RNA-Seq

RNA-seq (RNA sequencing), also called whole transcriptome shotgun sequencing (WTSS), is a technology that uses the capabilities of next-generation sequencing to reveal a snapshot of RNA presence and quantity from a genome at a given moment in time.