Creating a Karyotype: A Chromosome Study
... An examination of the chromosomes of a cell under high magnification can give a lot of information about an organism. If the cells are from an unborn human, its sex can be determined before it is born. It can also be determined if the unborn may have certain birth defects or problems caused by impro ...
... An examination of the chromosomes of a cell under high magnification can give a lot of information about an organism. If the cells are from an unborn human, its sex can be determined before it is born. It can also be determined if the unborn may have certain birth defects or problems caused by impro ...
Infection elevates diversity - Aneil Agrawal
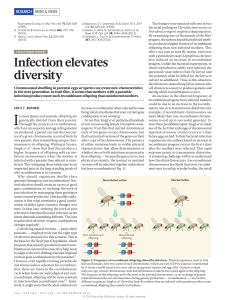
... use of the fact that exchange of chromosomal material (crossover events) occurs 4–5 days before eggs are laid. In their bacterial-infection experiments, the authors found an increase in recombinant progeny even in the first 4 days after the mothers were infected. This rapid response points to transm ...
... use of the fact that exchange of chromosomal material (crossover events) occurs 4–5 days before eggs are laid. In their bacterial-infection experiments, the authors found an increase in recombinant progeny even in the first 4 days after the mothers were infected. This rapid response points to transm ...
Final Concepts for Chapter 9 Mendelian Genetics
... All offspring produced should show the dominant characteristics if the dominant parent is pure (GG) for the trait. ...
... All offspring produced should show the dominant characteristics if the dominant parent is pure (GG) for the trait. ...
REVISION QUESTIONS
... The different species of finches (A, B, C and D) below are found on different Galapagos Islands and are thought to have originated from a seed-eating ancestral species from the mainland of South America. They resemble each other with respect to their internal body structure but differ with respect t ...
... The different species of finches (A, B, C and D) below are found on different Galapagos Islands and are thought to have originated from a seed-eating ancestral species from the mainland of South America. They resemble each other with respect to their internal body structure but differ with respect t ...
English
... chromosomes is called the genome of the organism. When animals mate, the genome of the offspring is a combination of the traits from the mother and the father. All of the cells within the animal are genetically identical. Each cell contains identical numbers of chromosomes. The number found in a cel ...
... chromosomes is called the genome of the organism. When animals mate, the genome of the offspring is a combination of the traits from the mother and the father. All of the cells within the animal are genetically identical. Each cell contains identical numbers of chromosomes. The number found in a cel ...
Genetics notes
... IF THE ALLELES ARE THE SAME, THEY ARE HOMOZYGOUS (PP, pp) ii IF THEY ARE DIFFERENT, THEY ARE HETEROZYGOUS (Pp) ...
... IF THE ALLELES ARE THE SAME, THEY ARE HOMOZYGOUS (PP, pp) ii IF THEY ARE DIFFERENT, THEY ARE HETEROZYGOUS (Pp) ...
Ch6Sec3 Reinforce Mendel Hered
... with pollen from a plant of his choosing, which produced offspring referred to as the F1 generation. • Observation of “either-or” traits: Mendel studied seven traits that appeared in only two forms. For example, flowers were white or purple; peas were wrinkled or round. Mendel observed that when he ...
... with pollen from a plant of his choosing, which produced offspring referred to as the F1 generation. • Observation of “either-or” traits: Mendel studied seven traits that appeared in only two forms. For example, flowers were white or purple; peas were wrinkled or round. Mendel observed that when he ...
Honors Biology - Genetics Study Guide
... Very Important Note: I have already tested your ability to complete and interpret Punnett squares with the quiz we recently took. This test is mostly conceptual. In other words, there will only be a few questions requiring the completion of Punnett squares. In order to have success on this test, you ...
... Very Important Note: I have already tested your ability to complete and interpret Punnett squares with the quiz we recently took. This test is mostly conceptual. In other words, there will only be a few questions requiring the completion of Punnett squares. In order to have success on this test, you ...
12.1 notes CD
... The first group of parents that are crossed in a breeding experiment are called the ________________________ or P generation. The offspring of the P generation is called the first filial generation, or ______________________. ...
... The first group of parents that are crossed in a breeding experiment are called the ________________________ or P generation. The offspring of the P generation is called the first filial generation, or ______________________. ...
Ch. 7: Presentation Slides
... genetic segments between non-homologous (unrelated) chromosomes • There is no loss of genetic information but the functions of specific genes may be altered • Reciprocal translocation may affect one or both pairs of chromosomes ...
... genetic segments between non-homologous (unrelated) chromosomes • There is no loss of genetic information but the functions of specific genes may be altered • Reciprocal translocation may affect one or both pairs of chromosomes ...
File
... a. Also has 3 different alleles- trait also considered a multiple-allele trait b. When alleles are neither dominant of recessive (in both incomplete and codominance) use upper case letters with either subscripts or superscripts) ...
... a. Also has 3 different alleles- trait also considered a multiple-allele trait b. When alleles are neither dominant of recessive (in both incomplete and codominance) use upper case letters with either subscripts or superscripts) ...
Genetics and Inheritance
... in 2 chances of landing heads up…BUT if you were to toss a coin 20 times you might expect it to be 10 heads and 10 tails but that might not be the case. ...
... in 2 chances of landing heads up…BUT if you were to toss a coin 20 times you might expect it to be 10 heads and 10 tails but that might not be the case. ...
Lesson 12: Single Trait Inheritance student notes
... http://www.johnkyrk.com/meiosis.html . The cell here started with ONE PAIR of REPLICATED chromosomes. A chromosome looks like a rod until it receives a signal that the cell needs to divide. Then the chromosome duplicates to resemble an X. Thus XX refers to a PAIR of REPLICATED chromosomes. A cell th ...
... http://www.johnkyrk.com/meiosis.html . The cell here started with ONE PAIR of REPLICATED chromosomes. A chromosome looks like a rod until it receives a signal that the cell needs to divide. Then the chromosome duplicates to resemble an X. Thus XX refers to a PAIR of REPLICATED chromosomes. A cell th ...
Ch - Ranger College
... - Eugenics – 1920-1930’s – science misused - “pseudoscience” - “biodeterminism” - genetically superior groups - Structure of DNA described 1950’s ...
... - Eugenics – 1920-1930’s – science misused - “pseudoscience” - “biodeterminism” - genetically superior groups - Structure of DNA described 1950’s ...
Document
... Alterations of chromosome number or structure cause some genetic disorders. • So far we’ve seen that the phenotype can be affected by small scale changes involving individual genes • Random mutations are the source of all new alleles, which can lead to a new phenotype. ...
... Alterations of chromosome number or structure cause some genetic disorders. • So far we’ve seen that the phenotype can be affected by small scale changes involving individual genes • Random mutations are the source of all new alleles, which can lead to a new phenotype. ...
Partial Linkage
... Alterations of chromosome number or structure cause some genetic disorders. • So far we’ve seen that the phenotype can be affected by small scale changes involving individual genes • Random mutations are the source of all new alleles, which can lead to a new phenotype. ...
... Alterations of chromosome number or structure cause some genetic disorders. • So far we’ve seen that the phenotype can be affected by small scale changes involving individual genes • Random mutations are the source of all new alleles, which can lead to a new phenotype. ...
PPT File
... Mendel laid the groundwork for genetics. • Traits are distinguishing characteristics that are inherited. • Genetics is the study of biological inheritance patterns and variation. • Gregor Mendel showed that traits are inherited as discrete units. • Many in Mendel’s day thought traits were blended. ...
... Mendel laid the groundwork for genetics. • Traits are distinguishing characteristics that are inherited. • Genetics is the study of biological inheritance patterns and variation. • Gregor Mendel showed that traits are inherited as discrete units. • Many in Mendel’s day thought traits were blended. ...
Ch 15b
... mice grow to normal size. But when a mutant allele is inherited from the father, heterozygous mice have the dwarf phenotype. ...
... mice grow to normal size. But when a mutant allele is inherited from the father, heterozygous mice have the dwarf phenotype. ...
Chapter 13 Practice Multiple Choice
... ____ 16. Which sample of DNA might be from a nerve cell arrested in G0 of the cell cycle? a. I b. II c. III d. Either I or II e. Either II or III ____ 17. Which sample might represent an animal cell in G2 phase of the cell cycle? a. I b. II c. III d. Both I and II e. Both II and III ____ 18. Which s ...
... ____ 16. Which sample of DNA might be from a nerve cell arrested in G0 of the cell cycle? a. I b. II c. III d. Either I or II e. Either II or III ____ 17. Which sample might represent an animal cell in G2 phase of the cell cycle? a. I b. II c. III d. Both I and II e. Both II and III ____ 18. Which s ...
WARM UP - Ms. Chambers' Biology
... – Trait: a characteristic based on heredity • i.e. hair color, plant flower color, number of wings on a fly… ...
... – Trait: a characteristic based on heredity • i.e. hair color, plant flower color, number of wings on a fly… ...
slides
... a. The same as when it happens in meiosis I b. In meiosis II, all gametes are abnormal, while in meiosis I only ½ the gametes are abnormal c. In meiosis II, only ½ the gametes are abnormal, ...
... a. The same as when it happens in meiosis I b. In meiosis II, all gametes are abnormal, while in meiosis I only ½ the gametes are abnormal c. In meiosis II, only ½ the gametes are abnormal, ...
Name Monohybrid Cross Homework Problems Answer the following
... 2. The gene for black coat color is dominant in guinea pigs. How is homozygous black different from heterozygous black, even though the guinea pigs look alike? 3. When two hybrid animals are crossed, there appear among the offspring homozygous dominant, heterozygous and homozygous recessive individu ...
... 2. The gene for black coat color is dominant in guinea pigs. How is homozygous black different from heterozygous black, even though the guinea pigs look alike? 3. When two hybrid animals are crossed, there appear among the offspring homozygous dominant, heterozygous and homozygous recessive individu ...
Meiosis - My Haiku
... genes in sexual reproduction results in a great variety of possible gene combinations from the offspring of any two parents. Recognize that genetic variation can occur from such processes as crossing over, jumping genes, and deletion and duplication of genes. ...
... genes in sexual reproduction results in a great variety of possible gene combinations from the offspring of any two parents. Recognize that genetic variation can occur from such processes as crossing over, jumping genes, and deletion and duplication of genes. ...
Hybrid (biology)

In biology a hybrid, also known as cross breed, is the result of mixing, through sexual reproduction, two animals or plants of different breeds, varieties, species or genera. Using genetic terminology, it may be defined as follows. Hybrid generally refers to any offspring resulting from the breeding of two genetically distinct individuals, which usually will result in a high degree of heterozygosity, though hybrid and heterozygous are not, strictly speaking, synonymous. a genetic hybrid carries two different alleles of the same gene a structural hybrid results from the fusion of gametes that have differing structure in at least one chromosome, as a result of structural abnormalities a numerical hybrid results from the fusion of gametes having different haploid numbers of chromosomes a permanent hybrid is a situation where only the heterozygous genotype occurs, because all homozygous combinations are lethal.From a taxonomic perspective, hybrid refers to: Offspring resulting from the interbreeding between two animal species or plant species. See also hybrid speciation. Hybrids between different subspecies within a species (such as between the Bengal tiger and Siberian tiger) are known as intra-specific hybrids. Hybrids between different species within the same genus (such as between lions and tigers) are sometimes known as interspecific hybrids or crosses. Hybrids between different genera (such as between sheep and goats) are known as intergeneric hybrids. Extremely rare interfamilial hybrids have been known to occur (such as the guineafowl hybrids). No interordinal (between different orders) animal hybrids are known. The third type of hybrid consists of crosses between populations, breeds or cultivars within a single species. This meaning is often used in plant and animal breeding, where hybrids are commonly produced and selected, because they have desirable characteristics not found or inconsistently present in the parent individuals or populations.↑ ↑ ↑ ↑