Mendelian Genetics
... not affect the inheritance of alleles for another trait • New combinations of alleles that are not present in either parent ...
... not affect the inheritance of alleles for another trait • New combinations of alleles that are not present in either parent ...
fundamentals of genetics - Doral Academy Preparatory
... Mendel crossed traits – one of the P traits failed to appear in the F1 plants. An every case, the trait reappeared in the F2 generation at a ratio of 3:1. This pattern lead Mendel to hypothesize that one factor in the pair may prevent the other from having an effect. • Dominant Trait masks or domina ...
... Mendel crossed traits – one of the P traits failed to appear in the F1 plants. An every case, the trait reappeared in the F2 generation at a ratio of 3:1. This pattern lead Mendel to hypothesize that one factor in the pair may prevent the other from having an effect. • Dominant Trait masks or domina ...
Biology 30 Patterns and Probabilities
... curved wings/black body colour flies are crossed with straight wings/normal body colour, instead of 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio, there is the 3:1 ratio found when only a monohybrid cross is done ** genes on the same chromosome tend to segregate together – Linked genes BUT! Crossing-over will sometimes ...
... curved wings/black body colour flies are crossed with straight wings/normal body colour, instead of 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio, there is the 3:1 ratio found when only a monohybrid cross is done ** genes on the same chromosome tend to segregate together – Linked genes BUT! Crossing-over will sometimes ...
Unit 1 Topic 3 - Holy Cross Collegiate
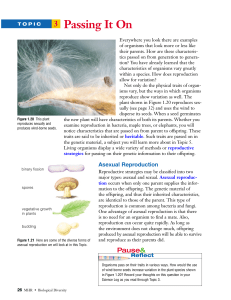
... Plants have developed diverse adaptations and structures for reproduction. Ferns and mosses reproduce by forming spores. Angiosperms and gymnosperms reproduce sexually by forming seeds. As you may recall from your earlier work, angiosperms are flowering plants. Over half of all known plant species ar ...
... Plants have developed diverse adaptations and structures for reproduction. Ferns and mosses reproduce by forming spores. Angiosperms and gymnosperms reproduce sexually by forming seeds. As you may recall from your earlier work, angiosperms are flowering plants. Over half of all known plant species ar ...
Topic 3 - Science 9 Jones
... Plants have developed diverse adaptations and structures for reproduction. Ferns and mosses reproduce by forming spores. Angiosperms and gymnosperms reproduce sexually by forming seeds. As you may recall from your earlier work, angiosperms are flowering plants. Over half of all known plant species ar ...
... Plants have developed diverse adaptations and structures for reproduction. Ferns and mosses reproduce by forming spores. Angiosperms and gymnosperms reproduce sexually by forming seeds. As you may recall from your earlier work, angiosperms are flowering plants. Over half of all known plant species ar ...
Sexyloop: Self-Reproduction, Evolution, and Sex in Cellular Automata
... disappear (die) in their environment allowing a continuous self-reproduction and turn-over of generations in a finite space. He named this model the structurally dissolvable selfreproducing loop (SDSR loop). Then, Sayama created the evoloop based on the SDSR loop using also nine states [9]. The very ...
... disappear (die) in their environment allowing a continuous self-reproduction and turn-over of generations in a finite space. He named this model the structurally dissolvable selfreproducing loop (SDSR loop). Then, Sayama created the evoloop based on the SDSR loop using also nine states [9]. The very ...
Notes to Instructors Answers
... Campbell Biology, 9th edition, defines natural selection as “differential success in the reproduction of different phenotypes resulting from the interaction of organisms with their environment.” The text goes on to state that “evolution occurs when natural selection causes changes in relative freque ...
... Campbell Biology, 9th edition, defines natural selection as “differential success in the reproduction of different phenotypes resulting from the interaction of organisms with their environment.” The text goes on to state that “evolution occurs when natural selection causes changes in relative freque ...
Reproduction of Living Organisms
... • Requires BOTH male and female gametes. • Gametes = sex cells ...
... • Requires BOTH male and female gametes. • Gametes = sex cells ...
Dragon Genetics
... To test whether baby dragons with wings and baby dragons without wings will be equally likely to have big horns, you will carry out a simulation of the simultaneous inheritance of the genes for wings and horns. Since the father is homozygous (wwhh), you know that all of the father's sperm will be wh ...
... To test whether baby dragons with wings and baby dragons without wings will be equally likely to have big horns, you will carry out a simulation of the simultaneous inheritance of the genes for wings and horns. Since the father is homozygous (wwhh), you know that all of the father's sperm will be wh ...
Chapter 8 Study Guide test 2015-16
... 18. (True or False) The one thing that Gregor Mendel realized could explain the results of his experiments was that each trait had two sets of instructions, one from each parent. (rewrite the sen ...
... 18. (True or False) The one thing that Gregor Mendel realized could explain the results of his experiments was that each trait had two sets of instructions, one from each parent. (rewrite the sen ...
Dragon Genetics 1 Teacher Prep
... This activity is designed for students who already understand mitosis, meiosis, fertilization, and basic genetics. Useful activities for introducing these topics are "Mitosis, Meiosis and Fertilization" and "Genetics", both available on this web site. Preparation of Popsicle Stick Chromosomes Each p ...
... This activity is designed for students who already understand mitosis, meiosis, fertilization, and basic genetics. Useful activities for introducing these topics are "Mitosis, Meiosis and Fertilization" and "Genetics", both available on this web site. Preparation of Popsicle Stick Chromosomes Each p ...
Reassignment of the Human CSFl Gene to Chromosome lp13-p21
... kb and contains 10 exons'.'; differential splicing generates multiple CSF-1 messenger RNA (mRNA) species with different coding and 3' untranslated sequences.'-" Shortly after human CSFl cDNA and genomic clones were isolated: the gene was mapped by isotopic in situ chromosomal hybridization, together ...
... kb and contains 10 exons'.'; differential splicing generates multiple CSF-1 messenger RNA (mRNA) species with different coding and 3' untranslated sequences.'-" Shortly after human CSFl cDNA and genomic clones were isolated: the gene was mapped by isotopic in situ chromosomal hybridization, together ...
Mechanisms of Nucleolar Dominance in Animals and Plants
... were crossed, however, the D chromosomes of only one parent would form a secondary constriction in the hybrid. Heitz (32), among others, had shown that such secondary constrictions are the site at which the nucleolus forms during interphase and that constrictions only form when nucleoli are present. ...
... were crossed, however, the D chromosomes of only one parent would form a secondary constriction in the hybrid. Heitz (32), among others, had shown that such secondary constrictions are the site at which the nucleolus forms during interphase and that constrictions only form when nucleoli are present. ...
chapter12_Sections 1-3 - (per 3) and wed 4/24 (per 2,6)
... • The two genes of a pair are often not identical: Maternal and paternal genes can encode slightly different forms (alleles) of the same gene’s product • alleles • Forms of a gene that encode slightly different versions of the gene’s product (ex: gene for rat eye color: one allele from mom encodes f ...
... • The two genes of a pair are often not identical: Maternal and paternal genes can encode slightly different forms (alleles) of the same gene’s product • alleles • Forms of a gene that encode slightly different versions of the gene’s product (ex: gene for rat eye color: one allele from mom encodes f ...
chapter12_Meiosis and Sexual Reproduction(1
... • Sex mixes up the genes of two parents, so offspring of sexual reproducers have unique combinations of traits • Diversity offers sexual reproducers as a group a better chance of surviving environmental change than clones • sexual reproduction • Reproductive mode by which offspring arise from two pa ...
... • Sex mixes up the genes of two parents, so offspring of sexual reproducers have unique combinations of traits • Diversity offers sexual reproducers as a group a better chance of surviving environmental change than clones • sexual reproduction • Reproductive mode by which offspring arise from two pa ...
RRYY
... The tall pea plants he worked with were from populations of plants that had been tall for many generations and had always produced tall offspring. Such plants are said to be true breeding for tallness. Likewise, the short plants he worked with were true breeding for shortness ...
... The tall pea plants he worked with were from populations of plants that had been tall for many generations and had always produced tall offspring. Such plants are said to be true breeding for tallness. Likewise, the short plants he worked with were true breeding for shortness ...
The Biological Species Concept
... 14.10 The tempo of speciation can appear steady or jumpy • According to the gradualism model – New species evolve by the gradual accumulation of changes brought about by natural selection ...
... 14.10 The tempo of speciation can appear steady or jumpy • According to the gradualism model – New species evolve by the gradual accumulation of changes brought about by natural selection ...
Genetics Quiz Wiz
... 1. In white fish, light grey coloring of the scales can mask over the allele of dark grey scales. So when a white fish with light grey scales has offspring with a fish with dark grey scales, all the offspring have light grey scales. Which of Mendel’s Laws best explains this? ...
... 1. In white fish, light grey coloring of the scales can mask over the allele of dark grey scales. So when a white fish with light grey scales has offspring with a fish with dark grey scales, all the offspring have light grey scales. Which of Mendel’s Laws best explains this? ...
Document
... F1 cross to produce the F2 generation Ex RRYY x rryy Round yellow mated with wrinkled green • Offspring would all be hybrid for both traits (RrYy) ...
... F1 cross to produce the F2 generation Ex RRYY x rryy Round yellow mated with wrinkled green • Offspring would all be hybrid for both traits (RrYy) ...
Comparative Phylogeography: Designing Studies
... Evolutionary significant unit (ESU). A population (or populations) of a species that is genetically distinct from other populations; in phylogeography, an evolutionarily distinct phylogroup can be considered an ESU. ESUs have many applications in conservation. Gene genealogies. The pattern of simila ...
... Evolutionary significant unit (ESU). A population (or populations) of a species that is genetically distinct from other populations; in phylogeography, an evolutionarily distinct phylogroup can be considered an ESU. ESUs have many applications in conservation. Gene genealogies. The pattern of simila ...
Reconstitution of gametes for assisted reproduction U.Eichenlaub
... in the debate article by Tesarik (2002). There is no adequate discussion on the mechanisms providing for high ®delity of chromosome segregation in mitosis and meiosis, and for proper imprinting in construction of `reconstituted gametes'. The debate article is uncritical with respect to the currently ...
... in the debate article by Tesarik (2002). There is no adequate discussion on the mechanisms providing for high ®delity of chromosome segregation in mitosis and meiosis, and for proper imprinting in construction of `reconstituted gametes'. The debate article is uncritical with respect to the currently ...
X w
... Downs Syndrome Staining and specific banding pattern allows you to line up and identify various chromosomes Down's syndrome results from an individual possessing three copies of chromosome 21 rather than the normal two. It is the most common of all human defects and occurs in 1/200 conceptions and ...
... Downs Syndrome Staining and specific banding pattern allows you to line up and identify various chromosomes Down's syndrome results from an individual possessing three copies of chromosome 21 rather than the normal two. It is the most common of all human defects and occurs in 1/200 conceptions and ...
Problem Set 1A Due August 31 1. A diploid somatic cell from a rat
... normal skin pigmentation have two children. The man has one albino parent; the woman has parents with normal pigmentation, but an albino brother. a. What is the probability that at least one of the children is albino? Using alleles A and a, since one of the man’s parents is albino, he must be a carr ...
... normal skin pigmentation have two children. The man has one albino parent; the woman has parents with normal pigmentation, but an albino brother. a. What is the probability that at least one of the children is albino? Using alleles A and a, since one of the man’s parents is albino, he must be a carr ...
Cytology of Genetics
... divisions to produce one egg nucleus, two polar nuclei, 2 synergid nuclei and 3 antipodal nuclei. ...
... divisions to produce one egg nucleus, two polar nuclei, 2 synergid nuclei and 3 antipodal nuclei. ...
Hybrid (biology)

In biology a hybrid, also known as cross breed, is the result of mixing, through sexual reproduction, two animals or plants of different breeds, varieties, species or genera. Using genetic terminology, it may be defined as follows. Hybrid generally refers to any offspring resulting from the breeding of two genetically distinct individuals, which usually will result in a high degree of heterozygosity, though hybrid and heterozygous are not, strictly speaking, synonymous. a genetic hybrid carries two different alleles of the same gene a structural hybrid results from the fusion of gametes that have differing structure in at least one chromosome, as a result of structural abnormalities a numerical hybrid results from the fusion of gametes having different haploid numbers of chromosomes a permanent hybrid is a situation where only the heterozygous genotype occurs, because all homozygous combinations are lethal.From a taxonomic perspective, hybrid refers to: Offspring resulting from the interbreeding between two animal species or plant species. See also hybrid speciation. Hybrids between different subspecies within a species (such as between the Bengal tiger and Siberian tiger) are known as intra-specific hybrids. Hybrids between different species within the same genus (such as between lions and tigers) are sometimes known as interspecific hybrids or crosses. Hybrids between different genera (such as between sheep and goats) are known as intergeneric hybrids. Extremely rare interfamilial hybrids have been known to occur (such as the guineafowl hybrids). No interordinal (between different orders) animal hybrids are known. The third type of hybrid consists of crosses between populations, breeds or cultivars within a single species. This meaning is often used in plant and animal breeding, where hybrids are commonly produced and selected, because they have desirable characteristics not found or inconsistently present in the parent individuals or populations.↑ ↑ ↑ ↑