GeneticsProtocol Lab student hand out
... We all know that children tend to resemble their parents in appearance. Parents and children generally have similar eye color, hair texture, height and other characteristics because children inherit genes that control specific characteristics from their parents. Where are genes found in our bodies? ...
... We all know that children tend to resemble their parents in appearance. Parents and children generally have similar eye color, hair texture, height and other characteristics because children inherit genes that control specific characteristics from their parents. Where are genes found in our bodies? ...
Phenotype
... from the female’s nucleus and place them in the offspring nucleus. 3. Record the genotype and phenotype on your handout. ...
... from the female’s nucleus and place them in the offspring nucleus. 3. Record the genotype and phenotype on your handout. ...
Chapter 9: Introduction to Genetics
... • Person B is blonde, because they are shaded in. They are thus homozygous recessive (hh). • Persons C through F must have at least dominant allele (H). Without more information, this would make them HH or Hh. • Person B can only provide the h alleles to its eggs, so persons C-F must be heterozygous ...
... • Person B is blonde, because they are shaded in. They are thus homozygous recessive (hh). • Persons C through F must have at least dominant allele (H). Without more information, this would make them HH or Hh. • Person B can only provide the h alleles to its eggs, so persons C-F must be heterozygous ...
B. Genetic Drift - HCC Learning Web
... The conditions that are required to maintain a non-evolving population are: Mutations do not occur The population size is large There is no gene flow, that is, no immigration or emigration within the localized area Mating is totally random. No natural selection occurs, that is all genotype ...
... The conditions that are required to maintain a non-evolving population are: Mutations do not occur The population size is large There is no gene flow, that is, no immigration or emigration within the localized area Mating is totally random. No natural selection occurs, that is all genotype ...
11-2
... quantities follow the laws of probability. Predict If you crossed dominant allele. About 1/4 showed the trait a TT plant with a Tt plant, would the offspring be tall or short? controlled by the recessive allele. Segregation did occur according to Mendel’s model. As you can see in the F2 generation, ...
... quantities follow the laws of probability. Predict If you crossed dominant allele. About 1/4 showed the trait a TT plant with a Tt plant, would the offspring be tall or short? controlled by the recessive allele. Segregation did occur according to Mendel’s model. As you can see in the F2 generation, ...
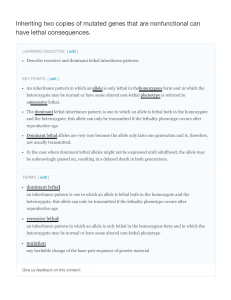
Inheriting two copies of mutated genes that are
... essential, these individuals might fail to develop past fertilization, die in utero, or die later in life, depending on what life stage requires this gene. An inheritance pattern in which an allele is only lethal in the homozygous form and in which the heterozygote may be normal or have some altered ...
... essential, these individuals might fail to develop past fertilization, die in utero, or die later in life, depending on what life stage requires this gene. An inheritance pattern in which an allele is only lethal in the homozygous form and in which the heterozygote may be normal or have some altered ...
4b. Pedigree Analysis in Humans
... dominating over any affected allele - If it were X-linked dominant, I1 could not have an unaffected daughter (II4) as an affected father will always pass on the disease to his daughter – occurs because she must inherit the only X-chromosome that her father has, which carries the trait (b) Autosomal ...
... dominating over any affected allele - If it were X-linked dominant, I1 could not have an unaffected daughter (II4) as an affected father will always pass on the disease to his daughter – occurs because she must inherit the only X-chromosome that her father has, which carries the trait (b) Autosomal ...
Methods of Analysis and Resources Available for Genetic Trait
... was assumed. For intermarker distances of x cM and given heterozygosities H, the expected number of meioses M for a maximum LOD score of 3 was calculated. Results may be represented approximately by the relationship M 5 10 1 x(1 2 H). Clearly it is easier to map a new locus into an interval of lengt ...
... was assumed. For intermarker distances of x cM and given heterozygosities H, the expected number of meioses M for a maximum LOD score of 3 was calculated. Results may be represented approximately by the relationship M 5 10 1 x(1 2 H). Clearly it is easier to map a new locus into an interval of lengt ...
Lecture PDF - Carol Eunmi LEE
... Expected Allele Frequencies at 2nd Generation p = AA + Aa/2 = 0.64 + (0.32/2) = 0.8 q = aa + Aa/2 = 0.04 + (0.32/2) = 0.2 ...
... Expected Allele Frequencies at 2nd Generation p = AA + Aa/2 = 0.64 + (0.32/2) = 0.8 q = aa + Aa/2 = 0.04 + (0.32/2) = 0.2 ...
Lecture PPT - Carol Eunmi LEE
... Testing for Deviaton from HardyWeinberg Expectations • A c2 goodness-of-fit test can be used to determine if a population is significantly different from the expections of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. • If we have a series of genotype counts from a population, then we can compare these counts to the ...
... Testing for Deviaton from HardyWeinberg Expectations • A c2 goodness-of-fit test can be used to determine if a population is significantly different from the expections of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. • If we have a series of genotype counts from a population, then we can compare these counts to the ...
LECTURE 2: MENDEL`S LAWS and EXTENSIONS TO MENDEL
... is a very important tool for the geneticist; this is especially true when analyzing inheritance in organisms that cannot self-fertilize! If Y-R- is YYRR, then all test cross progeny will be yellow; round. If Y-R- is YYRr, then half will be yellow; round and half will be yellow; wrinkled. If Y-R- is ...
... is a very important tool for the geneticist; this is especially true when analyzing inheritance in organisms that cannot self-fertilize! If Y-R- is YYRR, then all test cross progeny will be yellow; round. If Y-R- is YYRr, then half will be yellow; round and half will be yellow; wrinkled. If Y-R- is ...
REINDEER HEREDITY SUMMARY SHEET
... 6. Draw a single stranded chromosome with one gene labeled on the chromosome….like we drew in our activity. This was a useful drawing for us….but is it very accurate drawing? _________ EXPLAIN ...
... 6. Draw a single stranded chromosome with one gene labeled on the chromosome….like we drew in our activity. This was a useful drawing for us….but is it very accurate drawing? _________ EXPLAIN ...
Mendelian Inheritance | Principles of Biology from Nature Education
... monohybrid cross between two heterozygotes gives four offspring. The probability of event A is one-quarter, and the probability of event B is one-quarter. Applying the addition rule to this situation, we would add one-quarter to one-quarter to conclude that there is a 50% chance (¼ + ¼ = ½ ) that on ...
... monohybrid cross between two heterozygotes gives four offspring. The probability of event A is one-quarter, and the probability of event B is one-quarter. Applying the addition rule to this situation, we would add one-quarter to one-quarter to conclude that there is a 50% chance (¼ + ¼ = ½ ) that on ...
Biology Lab
... offspring of organisms have a mixture of both parents’ genes. The offspring receive one set of chromosomes and genes from its mother in the egg and one set from its father in the sperm. This variety allows for natural selection to occur. In this lab, you will simulate meiosis and fertilization and e ...
... offspring of organisms have a mixture of both parents’ genes. The offspring receive one set of chromosomes and genes from its mother in the egg and one set from its father in the sperm. This variety allows for natural selection to occur. In this lab, you will simulate meiosis and fertilization and e ...
DOUBLE TRAIT INHERITANCE Dihybrid cross: a type of cross that
... Each gamete produced by the yellow-round seed will either be YR or YR (same) Each gamete produced by the green-wrinkle seed will be yr or yr (same) The F1 offspring are shown below. possible gamete combinations for each parent ...
... Each gamete produced by the yellow-round seed will either be YR or YR (same) Each gamete produced by the green-wrinkle seed will be yr or yr (same) The F1 offspring are shown below. possible gamete combinations for each parent ...
116 study guide ch5
... If your total number puts you in the diseased category, you have crossed the threshold for that disorder. The greater the number of dominant alleles, the more severely the disease will be expressed. Some diseases can be helped by altering the body’s environment. For ...
... If your total number puts you in the diseased category, you have crossed the threshold for that disorder. The greater the number of dominant alleles, the more severely the disease will be expressed. Some diseases can be helped by altering the body’s environment. For ...
Genetics Case Study: The Royal Family
... assassinated) •Alexei’s body missing from mass grave found in 1990’s. ...
... assassinated) •Alexei’s body missing from mass grave found in 1990’s. ...
1 Lecture 6 Mendelian Genetics in Populations: Selection and
... 3. Do thought experiment: imagine population with two alleles A and a; selection acts against heterozygoes (assume no heterozygotes survive to adulthood) 4. Note that fixation only depends on initial frequency, not on dominance or recessiveness: a. The classic textbook examples demonstrate that a st ...
... 3. Do thought experiment: imagine population with two alleles A and a; selection acts against heterozygoes (assume no heterozygotes survive to adulthood) 4. Note that fixation only depends on initial frequency, not on dominance or recessiveness: a. The classic textbook examples demonstrate that a st ...
Genetics Case Study: The Royal Family
... assassinated) •Alexei’s body missing from mass grave found in 1990’s. ...
... assassinated) •Alexei’s body missing from mass grave found in 1990’s. ...
Population Genetics (EXERCISE)
... frequency may change in a population. Two important factors are genetic drift, and gene flow. Genetic drift is the fluctuation of genotypic and allelic frequency that occurs in small populations and is due to chance, rather than natural selection. The bottleneck effect is a type of genetic drift tha ...
... frequency may change in a population. Two important factors are genetic drift, and gene flow. Genetic drift is the fluctuation of genotypic and allelic frequency that occurs in small populations and is due to chance, rather than natural selection. The bottleneck effect is a type of genetic drift tha ...
Untitled
... Mendel’s discoveries provide the basis for all ideas surrounding modern genetics. Charles Darwin. Charles Darwin, a naturalist who studied plants, also performed experiments with self-fertilization and cross-fertilization. Darwin concluded that cross-fertilization allows for greater genetic variatio ...
... Mendel’s discoveries provide the basis for all ideas surrounding modern genetics. Charles Darwin. Charles Darwin, a naturalist who studied plants, also performed experiments with self-fertilization and cross-fertilization. Darwin concluded that cross-fertilization allows for greater genetic variatio ...