Changes to the Earth`s rocks and atmosphere
... other gases, including carbon dioxide, water vapour and noble gases. During the first billion years of the Earth’s existence there was intense volcanic activity. This activity released the gases (called outgassing) that formed the early atmosphere and water vapour that condensed to form the oceans. ...
... other gases, including carbon dioxide, water vapour and noble gases. During the first billion years of the Earth’s existence there was intense volcanic activity. This activity released the gases (called outgassing) that formed the early atmosphere and water vapour that condensed to form the oceans. ...
Comparison of the rocky planets
... The plates are defined based on rheology (behavior of material ), not composition. The tectonic plates reflect the lithosphere (lithos=rock)-rigid, nonflowing -the lithosphere consists of the crust plus uppermost mantle beneath it lies the asthenosphere (mantle which is soft and flowable on geologic ...
... The plates are defined based on rheology (behavior of material ), not composition. The tectonic plates reflect the lithosphere (lithos=rock)-rigid, nonflowing -the lithosphere consists of the crust plus uppermost mantle beneath it lies the asthenosphere (mantle which is soft and flowable on geologic ...
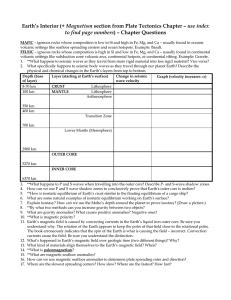
Earth`s Structure notes 5/26/15 • Crust
... – Oceanic crust is younger, thinner, denser and made of basalt • Mantle- 80 % 0f the volume of the earth. – Upper mantle is rigid, below is the asthenosphere which is a plastic like layer on which the tectonic plates float. – There is a huge difference in temperature between the outer mantle and the ...
... – Oceanic crust is younger, thinner, denser and made of basalt • Mantle- 80 % 0f the volume of the earth. – Upper mantle is rigid, below is the asthenosphere which is a plastic like layer on which the tectonic plates float. – There is a huge difference in temperature between the outer mantle and the ...
Jianna Tameta October 30, 2014 The Earth`s Layers There are four
... The Earth’s Layers There are four layers of the Earth. They are the crust, mantle, outer core, and the inner core. Scientists study earthquakes to find out what the inside of the Earth looks like. Scientists use a tool called a seismograph to study earthquakes. The first outer most layer is the crus ...
... The Earth’s Layers There are four layers of the Earth. They are the crust, mantle, outer core, and the inner core. Scientists study earthquakes to find out what the inside of the Earth looks like. Scientists use a tool called a seismograph to study earthquakes. The first outer most layer is the crus ...
Chapter 2 – A Living Planet - smallworldbigthoughts-eub-geo
... • Continental Drift – The theory that the continents have shifted over time into new positions on the face of the Earth – Began with Pangaea ...
... • Continental Drift – The theory that the continents have shifted over time into new positions on the face of the Earth – Began with Pangaea ...
Notes: Earth/Moon Formation 3/11
... #9. How do scientists know about the interior layering of the moon? Seismographs have recorded moonquakes. #10. How is the interior layering of the moon similar to that of Earth? Different? They are similar because the moon also has a crust, mantle and core. The core is both liquid and solid. They ...
... #9. How do scientists know about the interior layering of the moon? Seismographs have recorded moonquakes. #10. How is the interior layering of the moon similar to that of Earth? Different? They are similar because the moon also has a crust, mantle and core. The core is both liquid and solid. They ...
Name:
... 5. The core (of the Earth) is composed mostly of ___________ and _____________. 6. In the ______________ core, the iron and nickel are ______________. 7. Although the inner core is very hot, intense pressure from the weight of the rest of the ____________ prevents the material of the inner core from ...
... 5. The core (of the Earth) is composed mostly of ___________ and _____________. 6. In the ______________ core, the iron and nickel are ______________. 7. Although the inner core is very hot, intense pressure from the weight of the rest of the ____________ prevents the material of the inner core from ...
Earth`s Interior (+ Magnetism section from Plate Tectonics Chapter
... 5. **How is isostatic equilibrium of Earth’s crust similar to the floating equilibrium of a cargo ship? 6. What are some natural examples of isostatic equilibrium working on Earth’s surface? 7. Explain isostasy? How can we use the Moho’s depth around the planet to prove isostasy? (Draw a picture.) 8 ...
... 5. **How is isostatic equilibrium of Earth’s crust similar to the floating equilibrium of a cargo ship? 6. What are some natural examples of isostatic equilibrium working on Earth’s surface? 7. Explain isostasy? How can we use the Moho’s depth around the planet to prove isostasy? (Draw a picture.) 8 ...
Earth Surfaces Chapter 1 Study Guide The inner core is . A. layers
... surface._________________________________________________________________ 6. Geologists have used indirect evidence from seismic waves to learn more E. convection About the Earth’s interior _______________________. 7. Transfer of heat in fluid is ______________________________. F. gas 8. When you to ...
... surface._________________________________________________________________ 6. Geologists have used indirect evidence from seismic waves to learn more E. convection About the Earth’s interior _______________________. 7. Transfer of heat in fluid is ______________________________. F. gas 8. When you to ...
7-1 Inside the Earth RG
... 16. Large pieces of the lithosphere that move around on the asthenosphere are called ________________________________________ 17. Why are tectonic plates like the pieces of a jigsaw puzzle? ...
... 16. Large pieces of the lithosphere that move around on the asthenosphere are called ________________________________________ 17. Why are tectonic plates like the pieces of a jigsaw puzzle? ...
01 - Middletown Public Schools
... 23. Will a seismic wave traveling through a solid go faster or slower than a seismic wave traveling through ...
... 23. Will a seismic wave traveling through a solid go faster or slower than a seismic wave traveling through ...
CH 5 Earth`s Phys Enviro
... Alters ocean and atmospheric circulation patterns Normal conditions- westward blowing tradewinds keep warmest water in western Pacific ENSO conditions- trade winds weaken and warm water expands eastward to South America ...
... Alters ocean and atmospheric circulation patterns Normal conditions- westward blowing tradewinds keep warmest water in western Pacific ENSO conditions- trade winds weaken and warm water expands eastward to South America ...
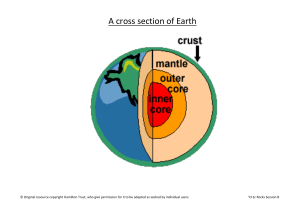
Cross section of the Earth
... We live on this outer layer. It is made of hard rocks that have been wrinkled & bent to make mountains and valleys. The thinnest parts of the crust are under the oceans; the thickest parts are in mountainous regions on the continents. The Mantle is the layer under the crust. It is a very thick lay ...
... We live on this outer layer. It is made of hard rocks that have been wrinkled & bent to make mountains and valleys. The thinnest parts of the crust are under the oceans; the thickest parts are in mountainous regions on the continents. The Mantle is the layer under the crust. It is a very thick lay ...
Ch. 5 Lecture Power Pt
... Alters ocean and atmospheric circulation patterns Normal conditions- westward blowing tradewinds keep warmest water in western Pacific ENSO conditions- trade winds weaken and warm water expands eastward to South America ...
... Alters ocean and atmospheric circulation patterns Normal conditions- westward blowing tradewinds keep warmest water in western Pacific ENSO conditions- trade winds weaken and warm water expands eastward to South America ...
Earth`s Interior
... Earth: The Unfinished Planet Earth continues to lose heat Volcanism brings material to Earth’s surface Other processes (subduction) return more dense material to interior Conclusion: Earth is still under construction! ...
... Earth: The Unfinished Planet Earth continues to lose heat Volcanism brings material to Earth’s surface Other processes (subduction) return more dense material to interior Conclusion: Earth is still under construction! ...
Earth and Space Science Review
... a. Solar = Sun blocked out (caused by shadow of moon on Earth), only seen from certain places on Earth http://www.mreclipse.com/Special/SEprimer.html b. Lunar = moon blocked out (caused by shadow of Earth on moon) Seen from everywhere on Earth http://www.mreclipse.com/Special/LEprimer.html ...
... a. Solar = Sun blocked out (caused by shadow of moon on Earth), only seen from certain places on Earth http://www.mreclipse.com/Special/SEprimer.html b. Lunar = moon blocked out (caused by shadow of Earth on moon) Seen from everywhere on Earth http://www.mreclipse.com/Special/LEprimer.html ...
Earthlike planets
... a. molten metallic core. b.solid central core. c.plastic mantle. d.the crust. e.aurora. 5. The oxygen in Earth's atmosphere a.was manufactured inside stars. b.was added to the atmosphere by plant life. c.has grown more abundant since the origin of Earth. d.all of these e.none of these ...
... a. molten metallic core. b.solid central core. c.plastic mantle. d.the crust. e.aurora. 5. The oxygen in Earth's atmosphere a.was manufactured inside stars. b.was added to the atmosphere by plant life. c.has grown more abundant since the origin of Earth. d.all of these e.none of these ...
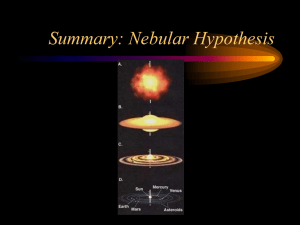
EarthFormationPwrPT
... Much of the CO2 dissolved into the oceans. Eventually, a simple form of bacteria developed that could live on energy from the Sun and carbon dioxide in the water, producing oxygen as a waste product. Thus, oxygen began to build up in the atmosphere, while the carbon dioxide levels continued to drop. ...
... Much of the CO2 dissolved into the oceans. Eventually, a simple form of bacteria developed that could live on energy from the Sun and carbon dioxide in the water, producing oxygen as a waste product. Thus, oxygen began to build up in the atmosphere, while the carbon dioxide levels continued to drop. ...
The Four Spheres of the Earth
... The atmosphere is the body of air which surrounds our planet. Most of our atmosphere is located close to the earth's surface where it is most dense. The air of our planet is 79% nitrogen and just under 21% oxygen; the small amount remaining is composed of carbon dioxide and other gasses. It also inc ...
... The atmosphere is the body of air which surrounds our planet. Most of our atmosphere is located close to the earth's surface where it is most dense. The air of our planet is 79% nitrogen and just under 21% oxygen; the small amount remaining is composed of carbon dioxide and other gasses. It also inc ...
Chapter 3
... Warm air rises into the atmosphere, cools, and sinks back down toward earth. The process repeats causing a ...
... Warm air rises into the atmosphere, cools, and sinks back down toward earth. The process repeats causing a ...
Physics 127 Descriptive Astronomy Homework #11 Key (Website
... B-2. Rocks found on the moon are between 3.1 and 4.47 billion years old. By contrast, the majority of the earth's surface is made of oceanic crust that is less than 200 million years old, and the very oldest earth rocks are about 4 billion years old. If the earth and moon are essentially the same ag ...
... B-2. Rocks found on the moon are between 3.1 and 4.47 billion years old. By contrast, the majority of the earth's surface is made of oceanic crust that is less than 200 million years old, and the very oldest earth rocks are about 4 billion years old. If the earth and moon are essentially the same ag ...
Color and Lenses - Thomas C. Cario Middle School
... rock that is under stress breaks. 11.________: The point on the surface of the Earth directly above the focus. ...
... rock that is under stress breaks. 11.________: The point on the surface of the Earth directly above the focus. ...
Timeline for Core Geology
... 1830 - Sir Charles Lyell publishes Principles of Geology, which describes the world as being several hundred million years old 1837 - Louis Agassiz begins his glaciation studies which eventually demonstrate that the Earth has had at least one ice age 1862 - Lord Kelvin attempts to find the age of th ...
... 1830 - Sir Charles Lyell publishes Principles of Geology, which describes the world as being several hundred million years old 1837 - Louis Agassiz begins his glaciation studies which eventually demonstrate that the Earth has had at least one ice age 1862 - Lord Kelvin attempts to find the age of th ...
2.2 Notes
... layers: the core, the mantle, and the crust. - The inner core is about 4,000 miles (about 6,430 km) below the surface. - The outer core is about 1,400 miles (about 2,250 km) thick. - Both are made of iron and nickel. - The mantle is made of hot, dense rock. - It releases 80 percent of the heat gener ...
... layers: the core, the mantle, and the crust. - The inner core is about 4,000 miles (about 6,430 km) below the surface. - The outer core is about 1,400 miles (about 2,250 km) thick. - Both are made of iron and nickel. - The mantle is made of hot, dense rock. - It releases 80 percent of the heat gener ...
File
... The Earth orbits around the Sun - One complete revolution every 365.24 days due to the Sun’s gravitational pull As Earth orbits around the Sun, it rotates (spins on its rotational axis) - One complete rotation every 24 hours ...
... The Earth orbits around the Sun - One complete revolution every 365.24 days due to the Sun’s gravitational pull As Earth orbits around the Sun, it rotates (spins on its rotational axis) - One complete rotation every 24 hours ...