class 2-III - apbtechstudent
... •The problem is solved by quantum mechanically to find the possible values of energy possessed by the electron. •To find the how the electrons are distributed among the different possible energy levels, For this purpose Sommerfeld employed Fermi – Dirac Statics instead of Maxwell – Bolzmann statics ...
... •The problem is solved by quantum mechanically to find the possible values of energy possessed by the electron. •To find the how the electrons are distributed among the different possible energy levels, For this purpose Sommerfeld employed Fermi – Dirac Statics instead of Maxwell – Bolzmann statics ...
Word document - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... I will announce office hours in class. Feel free to check to see if I am in at other times as well. Goals: 1. To gain some insight to the behavior of solids, in particular the behavior of crystals and of electrons traveling in solids. 2. To understand the basic principles of physics used in modeling ...
... I will announce office hours in class. Feel free to check to see if I am in at other times as well. Goals: 1. To gain some insight to the behavior of solids, in particular the behavior of crystals and of electrons traveling in solids. 2. To understand the basic principles of physics used in modeling ...
입자이론물리 연구실 소개
... Particles with integer spin: Bosons Particles with half-integer spin: Fermions Fermions should obey Pauli’s exclusion principle. No two identical particles can be at the same quantum state, while ...
... Particles with integer spin: Bosons Particles with half-integer spin: Fermions Fermions should obey Pauli’s exclusion principle. No two identical particles can be at the same quantum state, while ...
Lecture 19
... completely we need all four quantum numbers (n, l, m, ms ). Indeed, when higher-order effects are considered, or perturbations from external fields such as magnetic fields, the degeneracy in energy is broken. What do you do if you have more than one electron? In that case the main new effects come f ...
... completely we need all four quantum numbers (n, l, m, ms ). Indeed, when higher-order effects are considered, or perturbations from external fields such as magnetic fields, the degeneracy in energy is broken. What do you do if you have more than one electron? In that case the main new effects come f ...
Lecture (pdf)
... Black hole cosmology in gravity with torsion The conservation law for angular momentum of elementary particles in curved spacetime, consistent with relativistic quantum mechanics, extends general relativity to the Einstein-Cartan theory of gravity. In this theory, spacetime has a geometric structure ...
... Black hole cosmology in gravity with torsion The conservation law for angular momentum of elementary particles in curved spacetime, consistent with relativistic quantum mechanics, extends general relativity to the Einstein-Cartan theory of gravity. In this theory, spacetime has a geometric structure ...
Chapter 1. The Birth of Modern Physics
... φ is the angle between planet’s linear momentum vector p and r (see Figure 1). Since the orbital motion takes place in a plane, we can use ...
... φ is the angle between planet’s linear momentum vector p and r (see Figure 1). Since the orbital motion takes place in a plane, we can use ...
TD2 Statistical Physics (M1)
... We want to see if this isolated system can be described within the ergodicity hypothesis, or not. I.1) Qualitative discussion. Compare the trajectory of the oscillator in the phase space (x,p), as obtained from the equations of motion, with the surface of energy E defined by Hx, p E . I.2) Quant ...
... We want to see if this isolated system can be described within the ergodicity hypothesis, or not. I.1) Qualitative discussion. Compare the trajectory of the oscillator in the phase space (x,p), as obtained from the equations of motion, with the surface of energy E defined by Hx, p E . I.2) Quant ...
Take silver atoms with an electron that has a moment of µz = −g e(e
... one above the other, where z is the up/down direction and the magnets have length l (not to be mixed up with the quantum number). Although in the area between the magnets in the Stern-Gerlach experiment the magnetic ~ is homogeneous, near the end of the passage thru the magnets, it becomes inhomofie ...
... one above the other, where z is the up/down direction and the magnets have length l (not to be mixed up with the quantum number). Although in the area between the magnets in the Stern-Gerlach experiment the magnetic ~ is homogeneous, near the end of the passage thru the magnets, it becomes inhomofie ...
The Quantum mechanical model of the atom
... atoms. n = principle quantum number = orbital’s energy level and relative size l = describe orbital’s shape (subshell) ml = describe orbital’s orientation in space (magnetic quantum number). ms= describes behaviour of a specific electron in an orbital (spin quantum number). ...
... atoms. n = principle quantum number = orbital’s energy level and relative size l = describe orbital’s shape (subshell) ml = describe orbital’s orientation in space (magnetic quantum number). ms= describes behaviour of a specific electron in an orbital (spin quantum number). ...
Physics 12 Assignmen.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... • Lyman series • Balmer series • Paschen series • quantum number • Bohr radius • ground state • excited states • binding energy (or ionization energy) 2. In Rutherford’s planetary model of the atom, what keeps the electrons from flying off into space? 3. How can the spectrum of hydrogen contain so m ...
... • Lyman series • Balmer series • Paschen series • quantum number • Bohr radius • ground state • excited states • binding energy (or ionization energy) 2. In Rutherford’s planetary model of the atom, what keeps the electrons from flying off into space? 3. How can the spectrum of hydrogen contain so m ...
Quantum Mechanics (this is a sophomore/junior
... me. This is why it is possible to use a mixed lecture-discussion format here. My approach is to present students with experimental findings and then to ask them to try and explain the experiments. Discovering the solution to the atomic structure problem on their own will help students see that this ...
... me. This is why it is possible to use a mixed lecture-discussion format here. My approach is to present students with experimental findings and then to ask them to try and explain the experiments. Discovering the solution to the atomic structure problem on their own will help students see that this ...
Physics 12 Assignment - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Lyman series Balmer series Paschen series quantum number Bohr radius ground state excited states binding energy (or ionization energy) 2. In Rutherford’s planetary model of the atom, what keeps the electrons from flying off into space? 3. How can the spectrum of hydrogen contain so m ...
... Lyman series Balmer series Paschen series quantum number Bohr radius ground state excited states binding energy (or ionization energy) 2. In Rutherford’s planetary model of the atom, what keeps the electrons from flying off into space? 3. How can the spectrum of hydrogen contain so m ...
Quantum and Nuclear Physics
... A similar thing happens to electrons. We can “excite” them and raise their energy level: 0eV -0.85eV -1.5eV -3.4eV ...
... A similar thing happens to electrons. We can “excite” them and raise their energy level: 0eV -0.85eV -1.5eV -3.4eV ...
Chap. 3. Elementary Quantum Physics
... (a) The roller coaster released from A can at most make to C, but not to E. Its PE at A is less than the PE at D. When the car is the bottom its energy is totally KE. CD is the energy barrier which prevents the car making to E. In quantum theory, on the other hand, there is a chance that the car cou ...
... (a) The roller coaster released from A can at most make to C, but not to E. Its PE at A is less than the PE at D. When the car is the bottom its energy is totally KE. CD is the energy barrier which prevents the car making to E. In quantum theory, on the other hand, there is a chance that the car cou ...
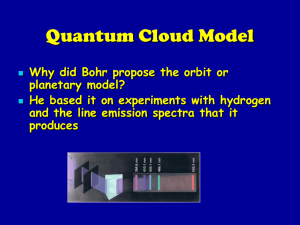
Quantum Cloud Model
... The original location of the electron is referred to as the Ground State The higher level is called the Excited State When the electron returns to the ground state it gives off energy equal to the difference between the two levels (excited and ground state) as electromagnetic radiation with its spec ...
... The original location of the electron is referred to as the Ground State The higher level is called the Excited State When the electron returns to the ground state it gives off energy equal to the difference between the two levels (excited and ground state) as electromagnetic radiation with its spec ...
Chapter 12
... Schrödinger developed a differential equation, which treated the electron as both a wave and a particle. For the H atom it gave the same energies as Bohr. But, it gives quite a different picture of the atom. It was successfully applied to other atoms.When the Schrödinger equation is solved for the H ...
... Schrödinger developed a differential equation, which treated the electron as both a wave and a particle. For the H atom it gave the same energies as Bohr. But, it gives quite a different picture of the atom. It was successfully applied to other atoms.When the Schrödinger equation is solved for the H ...
Chapter 9: Intermolecular Attractions and the Properties
... Ephoton = hn h = Planck’s constant = 6.626 x 10-34 J.s ...
... Ephoton = hn h = Planck’s constant = 6.626 x 10-34 J.s ...
Reakcje jądrowe
... difference applying to daunts, or both, to avoid increases of the particle’s mass. We have a phase-tron, cyclotron, or phase-cyclotron, respectively. These apparatuses are big in diameter. For example, a phase-cyclotron at the CERN, Geneva, consumes many Watt power and has a diameter of about 300 m ...
... difference applying to daunts, or both, to avoid increases of the particle’s mass. We have a phase-tron, cyclotron, or phase-cyclotron, respectively. These apparatuses are big in diameter. For example, a phase-cyclotron at the CERN, Geneva, consumes many Watt power and has a diameter of about 300 m ...
Propagation and Acceleration of High-Energy Cosmic
... travels back out again -- which it does with probability (1 – vshock/c) if the compression factor is 4 – it emerges with energy increased on average by a factor vshock/c (for a relativistic particle). It has bounced from the high-speed advancing gas, and has been knocked back with increased momentum ...
... travels back out again -- which it does with probability (1 – vshock/c) if the compression factor is 4 – it emerges with energy increased on average by a factor vshock/c (for a relativistic particle). It has bounced from the high-speed advancing gas, and has been knocked back with increased momentum ...
Chapter 7 Relativistic Quantum Mechanics
... relation, which explained the gyromagnetic ratio g = 2 of the electron as well as the fine structure of hydrogen. While his equation missed its original task of eliminating negative energy solutions, it was too successful to be wrong so that Dirac went on, inspired by Pauli’s exclusion principle, to ...
... relation, which explained the gyromagnetic ratio g = 2 of the electron as well as the fine structure of hydrogen. While his equation missed its original task of eliminating negative energy solutions, it was too successful to be wrong so that Dirac went on, inspired by Pauli’s exclusion principle, to ...