prereq reading
... The Schrödinger equation (1926) plays the role of Newton's laws and conservation of energy in classical mechanics - i.e., it predicts the future behavior of a dynamic system. It is a wave equation in terms of the wavefunction which predicts analytically and precisely the probability of events or ...
... The Schrödinger equation (1926) plays the role of Newton's laws and conservation of energy in classical mechanics - i.e., it predicts the future behavior of a dynamic system. It is a wave equation in terms of the wavefunction which predicts analytically and precisely the probability of events or ...
Basic Principles of Microwave Energy
... and falling away from the point where the pebble hits the water are called waves. Because these waves move up and down at right angles (or perpendicular) to the direction they are traveling, they are called transverse waves (Fig. 2-2). Electromagnetic waves are examples of transverse waves. Observin ...
... and falling away from the point where the pebble hits the water are called waves. Because these waves move up and down at right angles (or perpendicular) to the direction they are traveling, they are called transverse waves (Fig. 2-2). Electromagnetic waves are examples of transverse waves. Observin ...
History of "s,p,d,f"
... The concept of spectral “terms” and the use of series names such as principal, sharp, etc., has now passed from common use, replaced by the quantitative understanding of atomic structure provided by quantum mechanics. However, the notational shorthand used by the early spectroscopists was adapted an ...
... The concept of spectral “terms” and the use of series names such as principal, sharp, etc., has now passed from common use, replaced by the quantitative understanding of atomic structure provided by quantum mechanics. However, the notational shorthand used by the early spectroscopists was adapted an ...
Spectra and energy levels - Teaching Advanced Physics
... It is all a question of scale. We do not 'see' quantum effects generally in everyday life because of the very small value of Planck's constant. Think about a person and an ant walking across a gravelled path. The size of the individual pieces of gravel may seem small to us but they are giant boulder ...
... It is all a question of scale. We do not 'see' quantum effects generally in everyday life because of the very small value of Planck's constant. Think about a person and an ant walking across a gravelled path. The size of the individual pieces of gravel may seem small to us but they are giant boulder ...
TAP501-0: Spectra and energy levels
... levels are discrete. An electron can only move directly between such levels, emitting or absorbing individual photons as it does so. The ground state is the condition of lowest energy – most electrons are in this state. Think about a bookcase with adjustable shelves. The bookshelves are quantised – ...
... levels are discrete. An electron can only move directly between such levels, emitting or absorbing individual photons as it does so. The ground state is the condition of lowest energy – most electrons are in this state. Think about a bookcase with adjustable shelves. The bookshelves are quantised – ...
Electron Corral
... Ultraviolet light is needed for zinc. Radiation of a frequency below f0 does not eject any electrons from the metal, no matter how intense the light is. However, even if the incident light is very dim, radiation at or above the threshold frequency causes electrons to leave the metal immediately; the ...
... Ultraviolet light is needed for zinc. Radiation of a frequency below f0 does not eject any electrons from the metal, no matter how intense the light is. However, even if the incident light is very dim, radiation at or above the threshold frequency causes electrons to leave the metal immediately; the ...
On the Planck Scale Potential Associated with Particles
... scale potential is presented. By defining the self-energy of a particle in terms of its scalarpotential, equivalences between charge-energy and mass-energy are obtained. The electromagnetic energy-momentum equation and de-Broglie’s electromagnetic wave-length and frequency associated with a charge p ...
... scale potential is presented. By defining the self-energy of a particle in terms of its scalarpotential, equivalences between charge-energy and mass-energy are obtained. The electromagnetic energy-momentum equation and de-Broglie’s electromagnetic wave-length and frequency associated with a charge p ...
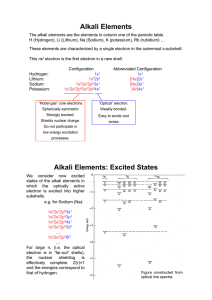
Alkali Elements Alkali Elements: Excited States
... Most of the energetics of these atoms is well described by the Hartree model; however, in detail (e.g. in high-resolution spectroscopy), spin-orbit coupling and the residual coulomb interaction are important. Residual Coulomb Interaction: The Coulomb interaction that is not captured by the effective ...
... Most of the energetics of these atoms is well described by the Hartree model; however, in detail (e.g. in high-resolution spectroscopy), spin-orbit coupling and the residual coulomb interaction are important. Residual Coulomb Interaction: The Coulomb interaction that is not captured by the effective ...
From Last Time… Wavelength of 1 eV electron Question Can this be
... The energy carried away by the photon must be given up by the electron. The electron can give up energy by dropping to a lower energy state. So possible photon energies correspond to differences between electron orbital energies. The 10.2 eV photon is emitted when the electron jumps from the -3.4 eV ...
... The energy carried away by the photon must be given up by the electron. The electron can give up energy by dropping to a lower energy state. So possible photon energies correspond to differences between electron orbital energies. The 10.2 eV photon is emitted when the electron jumps from the -3.4 eV ...
Online Course Evaluation Chapters 15-20
... Question: The bright-line spectrum produced by the excited atoms of an element contains wavelength that (a) are the same for all elements (b) are characteristic of the particular element (c) are evenly distributed throughout the entire visible spectrum (d) are different from the wavelength in its d ...
... Question: The bright-line spectrum produced by the excited atoms of an element contains wavelength that (a) are the same for all elements (b) are characteristic of the particular element (c) are evenly distributed throughout the entire visible spectrum (d) are different from the wavelength in its d ...
Derivation of Einstein`s Energy Equation from Maxwell`s Electric
... The special relativity theory (SRT) [1] has removed the barrier between matter and energy, but it has created a new barrier that cannot be transcended. This barrier separates what is known as non-relativistic from relativistic physics. Einstein was the first to derive mass-energy equivalence from th ...
... The special relativity theory (SRT) [1] has removed the barrier between matter and energy, but it has created a new barrier that cannot be transcended. This barrier separates what is known as non-relativistic from relativistic physics. Einstein was the first to derive mass-energy equivalence from th ...
The Inner Magnetosphere
... Ionosphere injection Substorm and storm particle injections Diffusion (adiabatic invariants do not strictly hold). ...
... Ionosphere injection Substorm and storm particle injections Diffusion (adiabatic invariants do not strictly hold). ...