Unit 1
... were farther away (dimmer) had even more pronounced redshifts! This redshift was interpreted as a measure of radial velocity, and it became clear that the more distant a galaxy is, the faster it is receding! ...
... were farther away (dimmer) had even more pronounced redshifts! This redshift was interpreted as a measure of radial velocity, and it became clear that the more distant a galaxy is, the faster it is receding! ...
Galaxies and the Universe bb
... • _________ Law – the recessional speed of galaxies is proportional to their distance • Accounts for red shifts ...
... • _________ Law – the recessional speed of galaxies is proportional to their distance • Accounts for red shifts ...
Written in the stars THE NOBEL PRIZE IN PHYSICS 2011
... receding from us. The light’s wavelength gets stretched, and the longer the wave, the redder its colour. The conclusion was that the galaxies are rushing away from us and each other, and the farther away they are, the faster they move – this is known as Hubble’s law. The Universe is growing. ...
... receding from us. The light’s wavelength gets stretched, and the longer the wave, the redder its colour. The conclusion was that the galaxies are rushing away from us and each other, and the farther away they are, the faster they move – this is known as Hubble’s law. The Universe is growing. ...
Facilitator`s Guide PDF
... 1. Describe and explain how astronomers use luminosity and redshift to measure the distance and speed of celestial objects. 2. Describe, using pictures, graphs and/or words, what astronomers mean by an expanding universe. Describe several different ways that the expansion could change over time (e.g ...
... 1. Describe and explain how astronomers use luminosity and redshift to measure the distance and speed of celestial objects. 2. Describe, using pictures, graphs and/or words, what astronomers mean by an expanding universe. Describe several different ways that the expansion could change over time (e.g ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • measure distances to other galaxies using the periodluminosity relationship for Cepheid variables • Type I supernovae also used to measure distances – Predictable luminosity – a standard candle ...
... • measure distances to other galaxies using the periodluminosity relationship for Cepheid variables • Type I supernovae also used to measure distances – Predictable luminosity – a standard candle ...
Goal: To understand how we know distances to
... Variable stars • The other secondary is variable stars. • The most common is Cepheid variables (because they are the brightest). • As has been mentioned before, the period of the variable depends on the size. • So, if you know the period, you know the size. • If you know the size and temperature th ...
... Variable stars • The other secondary is variable stars. • The most common is Cepheid variables (because they are the brightest). • As has been mentioned before, the period of the variable depends on the size. • So, if you know the period, you know the size. • If you know the size and temperature th ...
Goal: To understand how we know distances to various
... Variable stars • The other secondary is variable stars. • The most common is Cepheid variables (because they are the brightest). • As has been mentioned before, the period of the variable depends on the size. • So, if you know the period, you know the size. • If you know the size and temperature th ...
... Variable stars • The other secondary is variable stars. • The most common is Cepheid variables (because they are the brightest). • As has been mentioned before, the period of the variable depends on the size. • So, if you know the period, you know the size. • If you know the size and temperature th ...
Cosmology Handouts
... emission spectrum. A similar spectrum is produced when light shines through a gas; however, in this case certain colours, or wavelengths, are absorbed by the gas. An absorption spectrum is the pattern of colours and dark lines that is produced when light shines through a gas and the gas absorbs cert ...
... emission spectrum. A similar spectrum is produced when light shines through a gas; however, in this case certain colours, or wavelengths, are absorbed by the gas. An absorption spectrum is the pattern of colours and dark lines that is produced when light shines through a gas and the gas absorbs cert ...
Determining Distances to Other Galaxies
... The range and frequency of different morphological types is sensitive to the sample of galaxies studied. Some key results: •The Local Group is the only sample that includes a significant number of very faint galaxies. Of the ~35 galaxies in the Local Group, only the 3 brightest (M31, MW and M33) are ...
... The range and frequency of different morphological types is sensitive to the sample of galaxies studied. Some key results: •The Local Group is the only sample that includes a significant number of very faint galaxies. Of the ~35 galaxies in the Local Group, only the 3 brightest (M31, MW and M33) are ...
Document
... This diagram shows a single closed dimension of cosmological space (a huge cosmic great circle) and many local ‘directions’ or dimensions of time. We may think of time in spacetime in much the same way that we think of the gravitational gradient on Earth; time is not a single dimension of spacetime, ...
... This diagram shows a single closed dimension of cosmological space (a huge cosmic great circle) and many local ‘directions’ or dimensions of time. We may think of time in spacetime in much the same way that we think of the gravitational gradient on Earth; time is not a single dimension of spacetime, ...
Effects of Gravitation
... and radiation. In fact, what we see in the interval between the galaxies is the light from the universe when it was about 300,000 years old. At this time, the universe was a hot sea of matter and mostly photons. The light that comes into the detectors is the light of last scatter off the surface of ...
... and radiation. In fact, what we see in the interval between the galaxies is the light from the universe when it was about 300,000 years old. At this time, the universe was a hot sea of matter and mostly photons. The light that comes into the detectors is the light of last scatter off the surface of ...
Birth, Age and the Future of the Universe
... Figure 3. A yeast cake as a model for the expanding Universe. As the cake increases in size the distances between the raisins become larger. Close raisins get separated by small (absolute) amounts, distant raisins by large amounts.The aspect is the same for all raisins. (Neglect the rim).The model h ...
... Figure 3. A yeast cake as a model for the expanding Universe. As the cake increases in size the distances between the raisins become larger. Close raisins get separated by small (absolute) amounts, distant raisins by large amounts.The aspect is the same for all raisins. (Neglect the rim).The model h ...
24.1 Hubble`s Galaxy Classification
... resolved, but you could get this from the width of a spectral line if you couldn’t resolve the galaxy. This galaxy is NGC 4603, about 30 Mpc away. ...
... resolved, but you could get this from the width of a spectral line if you couldn’t resolve the galaxy. This galaxy is NGC 4603, about 30 Mpc away. ...
Teaching Text Structure with Understanding the Scale of the Universe
... By 1920, many scientists began to think that some of the objects they were seeing must be other galaxies like the Milky Way but separate from the Milky Way. They spoke of these separate clusters of stars as island universes. ...
... By 1920, many scientists began to think that some of the objects they were seeing must be other galaxies like the Milky Way but separate from the Milky Way. They spoke of these separate clusters of stars as island universes. ...
High-Speed Ballistic Stellar Interlopers
... approach between two binary star systems—or a binary system and a third star. In such cases, one or more of the stars can pick up enough energy through gravitational interaction with the others to be thrown from the system. Determining how many stars have been ejected from their neighbors is importa ...
... approach between two binary star systems—or a binary system and a third star. In such cases, one or more of the stars can pick up enough energy through gravitational interaction with the others to be thrown from the system. Determining how many stars have been ejected from their neighbors is importa ...
Slide 1
... • Measuring distances to remote galaxies is difficult, but measuring Doppler shifts (velocities) is easier from spectra • Use Hubble’s Law to estimate biggest distances (really LOOKBACK TIME)! ...
... • Measuring distances to remote galaxies is difficult, but measuring Doppler shifts (velocities) is easier from spectra • Use Hubble’s Law to estimate biggest distances (really LOOKBACK TIME)! ...
Structure of the solar system
... This produces what is called “radiation pressure” which tries to expand the star (essentially blow it up). The star is massive enough that it has a large “gravitional pressure” which tries to compress and crush the star. In a stable star there is an equilibrium between the gravitational and radiatio ...
... This produces what is called “radiation pressure” which tries to expand the star (essentially blow it up). The star is massive enough that it has a large “gravitional pressure” which tries to compress and crush the star. In a stable star there is an equilibrium between the gravitational and radiatio ...
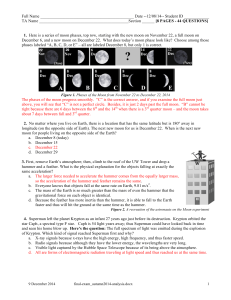
12/08/14-- Student ID ______ TA Name
... Because all of this type of supernovae come from white dwarfs that have roughly the same mass and the same process produces the supernovae. 31. What observations provide evidence that our theories about Type Ia supernovae are correct? a. observations of supernovae occurring in galaxies having indepe ...
... Because all of this type of supernovae come from white dwarfs that have roughly the same mass and the same process produces the supernovae. 31. What observations provide evidence that our theories about Type Ia supernovae are correct? a. observations of supernovae occurring in galaxies having indepe ...
Build your own FREE website at Tripod.com
... Fireball, the theory gained momentum until it received a worthy adversarial cosmology known as the Steady State Theory. Fred Hoyle (who despairingly coined the term Big Bang) and his colleagues constructed a model of the universe that was widely accepted for religious reasons if not so much for its ...
... Fireball, the theory gained momentum until it received a worthy adversarial cosmology known as the Steady State Theory. Fred Hoyle (who despairingly coined the term Big Bang) and his colleagues constructed a model of the universe that was widely accepted for religious reasons if not so much for its ...
Galaxies and the Universe
... distances to galaxies using a type of variable star called a Cephied, and plotted those distances against the redshifts of those galaxies (as measured by Vesto Slipher). ...
... distances to galaxies using a type of variable star called a Cephied, and plotted those distances against the redshifts of those galaxies (as measured by Vesto Slipher). ...
ASTR 1120-001 Final Examination Phil Armitage, Bruce Ferguson
... 67. Suppose that we lived in a Big Crunch Universe at a time when it was contracting, rather than expanding. If you measured the velocities of many galaxies, you would find that typically: (a) Galaxies (except very nearby ones) were moving away from you, with the most distant ones moving away the sl ...
... 67. Suppose that we lived in a Big Crunch Universe at a time when it was contracting, rather than expanding. If you measured the velocities of many galaxies, you would find that typically: (a) Galaxies (except very nearby ones) were moving away from you, with the most distant ones moving away the sl ...
Lecture 22 - Cosmic distance scale
... As the Earth moves from one side of the Sun to the other, a nearby star will seem to change its position relative to the distant background stars. ...
... As the Earth moves from one side of the Sun to the other, a nearby star will seem to change its position relative to the distant background stars. ...
Measuring Astronomical Distances
... Important to have data at many different wavelengths Different instruments are capable of observing at different wavelengths This requires us to use more than one instrument ...
... Important to have data at many different wavelengths Different instruments are capable of observing at different wavelengths This requires us to use more than one instrument ...
Hubble Space Telescope Image
... The Universe is filled with these star systems which themselves cluster together into larger systems. Earth & Space Science March 2015 ...
... The Universe is filled with these star systems which themselves cluster together into larger systems. Earth & Space Science March 2015 ...
Interacting Galaxies
... Tides between galaxies, however, are much more disruptive than oceanic tides for two main reasons. First, stars in galaxies, unlike the matter that comprises Earth, are bound together only by gravity, so they have no other forces holding them together. Second, galaxies can pass much closer to each o ...
... Tides between galaxies, however, are much more disruptive than oceanic tides for two main reasons. First, stars in galaxies, unlike the matter that comprises Earth, are bound together only by gravity, so they have no other forces holding them together. Second, galaxies can pass much closer to each o ...