View Attached Document - Dr. Judith Aronson
... Additional Criteria • Some symptoms that cause impairment were present before age 7 years. • Some impairment from the symptoms is present in two or more settings (e.g. at school and home). • There must be clear evidence of clinically significant impairment in social, school, or work functioning. • ...
... Additional Criteria • Some symptoms that cause impairment were present before age 7 years. • Some impairment from the symptoms is present in two or more settings (e.g. at school and home). • There must be clear evidence of clinically significant impairment in social, school, or work functioning. • ...
Psychological Disorders - Eric Sweetwood's PTHS Psychology
... individual is exposed to possible scrutiny by others and fears he or she may act in a way that will be humiliating or embarrassing". Social phobias often develop in adolescence and include a fear of criticism, fear of making mistakes and fear of public speaking. AGORAPHOBIA is an extreme fear of bei ...
... individual is exposed to possible scrutiny by others and fears he or she may act in a way that will be humiliating or embarrassing". Social phobias often develop in adolescence and include a fear of criticism, fear of making mistakes and fear of public speaking. AGORAPHOBIA is an extreme fear of bei ...
Anxiety - Lifeline
... Anxiety is the excessive, uncontrollable and often irrational anticipation of future threats. It differs from fear, which is the emotional response to a real or perceived threat. While, these two states do overlap, there is a difference. Where fear is associated with the activation of the autonomic ...
... Anxiety is the excessive, uncontrollable and often irrational anticipation of future threats. It differs from fear, which is the emotional response to a real or perceived threat. While, these two states do overlap, there is a difference. Where fear is associated with the activation of the autonomic ...
Hypochondriasis and Health Anxiety
... fronted with possible danger (i.e., the fight or flight response). Some degree Pattern of Within-sess ...
... fronted with possible danger (i.e., the fight or flight response). Some degree Pattern of Within-sess ...
Pediatric Mood Disorders: From Neurobiology to Clinical Practice
... They are more likely to have oppositional bossiness and irritability. • The co-morbidity of other disorders can make medical treatment very difficult in children. Children are more likely to be activated by certain medications, namely antidepressants and psychostimulants, than adults. • Bipolar diso ...
... They are more likely to have oppositional bossiness and irritability. • The co-morbidity of other disorders can make medical treatment very difficult in children. Children are more likely to be activated by certain medications, namely antidepressants and psychostimulants, than adults. • Bipolar diso ...
MCQ PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS
... 12.With regards to schizophrenia which is false? a) it affects 1% of the population b) it usually has a gradual onset over months c) there is up to a 25% incidence of secondary depression d) the diagnosis of schizophrenia can only be made after the illness has been going for 6 weeks e) the earlier ...
... 12.With regards to schizophrenia which is false? a) it affects 1% of the population b) it usually has a gradual onset over months c) there is up to a 25% incidence of secondary depression d) the diagnosis of schizophrenia can only be made after the illness has been going for 6 weeks e) the earlier ...
citalopram-induced major depression in a patient with panic disorder
... range of 20 to 60 mg/day citalopram has proven to be an effective agent in depression (Keller 2000). Citalopram is also effective in the treatment of panic disorder, especially in a dose of 20 to 30 mg/day (Lepola et al. 1998). The anti-panic effect of citalopram is explained by a deficient serotone ...
... range of 20 to 60 mg/day citalopram has proven to be an effective agent in depression (Keller 2000). Citalopram is also effective in the treatment of panic disorder, especially in a dose of 20 to 30 mg/day (Lepola et al. 1998). The anti-panic effect of citalopram is explained by a deficient serotone ...
melatonin Mood disorders
... -Studies show that families of individuals who later develop Schizophrenia are often on the verge of falling apart. Diathesis-stress hypothesis: a person may inherit a predisposition toward Schizophrenia and from there environmental factors play a role. ...
... -Studies show that families of individuals who later develop Schizophrenia are often on the verge of falling apart. Diathesis-stress hypothesis: a person may inherit a predisposition toward Schizophrenia and from there environmental factors play a role. ...
Describe dissociative disorders in general several
... analysis used to create Hans Eysenck's trait theory of personality? (two to five sentences) Briefly, in terms of human behavior, how would you define or explain latent learning? (Two to five sentences) Dissociative disorders are psychological phenomena in which there is a breakdown in an individual’ ...
... analysis used to create Hans Eysenck's trait theory of personality? (two to five sentences) Briefly, in terms of human behavior, how would you define or explain latent learning? (Two to five sentences) Dissociative disorders are psychological phenomena in which there is a breakdown in an individual’ ...
201lecture32010Somat..
... flaws of face or head • Symptoms of depression and characteristics associated with OCD common in people with body dysmorphic disorder ...
... flaws of face or head • Symptoms of depression and characteristics associated with OCD common in people with body dysmorphic disorder ...
Psychotherapy for Depression in an Aging Population
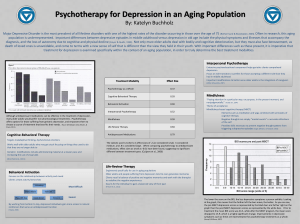
... Major Depressive Disorder is the most prevalent of all lifetime disorders with one of the highest rates of the disorder occurring in those over the age of 75 (Rothermund & Brandstater, 2003). Often in research, this aging population is underrepresented. Important differences between depressive episo ...
... Major Depressive Disorder is the most prevalent of all lifetime disorders with one of the highest rates of the disorder occurring in those over the age of 75 (Rothermund & Brandstater, 2003). Often in research, this aging population is underrepresented. Important differences between depressive episo ...
Supplementary Information (doc 127K)
... adverse impact at both the individual and societal level, it is of critical importance to treat child anxiety disorders successfully and prevent development of other subsequent severe disorders. Cognitive-behavior therapy (CBT) is the most established treatment for child anxiety, with remission in a ...
... adverse impact at both the individual and societal level, it is of critical importance to treat child anxiety disorders successfully and prevent development of other subsequent severe disorders. Cognitive-behavior therapy (CBT) is the most established treatment for child anxiety, with remission in a ...
Psychiatry Turkey Book
... MDD w/ seasonal pattern: recurrent episodes of depression w/ pattern of onset at the same time each year; full remissions occur at characteristic times of year; over 2-yr period, at least 2 seasonal episodes w/ no nonseasonal episodes ...
... MDD w/ seasonal pattern: recurrent episodes of depression w/ pattern of onset at the same time each year; full remissions occur at characteristic times of year; over 2-yr period, at least 2 seasonal episodes w/ no nonseasonal episodes ...
Psychological Disorders
... Positive symptoms: characteristics of schizophrenia that are added to a person’s personality, such as hallucinations, delusions, inappropriate emotions, and word salad. Negative symptoms: characteristics of schizophrenia that are taken away from a person’s personality, such as flattening of the emot ...
... Positive symptoms: characteristics of schizophrenia that are added to a person’s personality, such as hallucinations, delusions, inappropriate emotions, and word salad. Negative symptoms: characteristics of schizophrenia that are taken away from a person’s personality, such as flattening of the emot ...
Personality disorders
... trauma, feelings of detachment from others, restricted range of affect, and sense of foreshortened future. 5. Persistent symptoms of increased arousal (i.e., sleep disturbance, irritability/anger outburst, difficulty concentrating, hypervigilance, and exaggerated startle response. 6. At least one-mo ...
... trauma, feelings of detachment from others, restricted range of affect, and sense of foreshortened future. 5. Persistent symptoms of increased arousal (i.e., sleep disturbance, irritability/anger outburst, difficulty concentrating, hypervigilance, and exaggerated startle response. 6. At least one-mo ...
Ch. 18: Psychological Disorders Sec. 1: Understanding
... Psychological disorders are illnesses that an individual experiences as episodes. In contrast, personality disorders are enduring traits that are major components of the individual’s personality. ...
... Psychological disorders are illnesses that an individual experiences as episodes. In contrast, personality disorders are enduring traits that are major components of the individual’s personality. ...
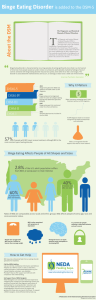
Binge Eating Disorder is added to the DSM-5
... the criteria established by the APA to diagnose them. For a particular mental disorder to be diagnosed in an individual, the individual must exhibit the symptoms listed in the criteria for that disorder. ...
... the criteria established by the APA to diagnose them. For a particular mental disorder to be diagnosed in an individual, the individual must exhibit the symptoms listed in the criteria for that disorder. ...
(2) loss of interest or pleasure. Major depressive disorder
... MOOD DISORDERS Diagnostic issues – Types of symptoms • Mood and Emotion ...
... MOOD DISORDERS Diagnostic issues – Types of symptoms • Mood and Emotion ...
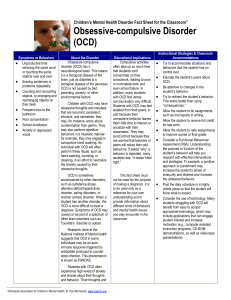
Children`s Mental Health Disorder Fact Sheet for the Classroom
... another anxiety disorder. When a student has another disorder, the OCD is more difficult to treat or diagnose. Symptoms of OCD may coexist or be part of a spectrum of other brain disorders such as Tourette’s disorder or autism. Research done at the National Institute of Mental health suggests that O ...
... another anxiety disorder. When a student has another disorder, the OCD is more difficult to treat or diagnose. Symptoms of OCD may coexist or be part of a spectrum of other brain disorders such as Tourette’s disorder or autism. Research done at the National Institute of Mental health suggests that O ...