Social-Anxiety-Disorder-Herring-2013-Final
... F. The fear, anxiety, or avoidance is persistent, typically lasting for 6 months or more. G. The fear, anxiety, or avoidance causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. H. The fear, anxiety, or avoidance is not attributable t ...
... F. The fear, anxiety, or avoidance is persistent, typically lasting for 6 months or more. G. The fear, anxiety, or avoidance causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. H. The fear, anxiety, or avoidance is not attributable t ...
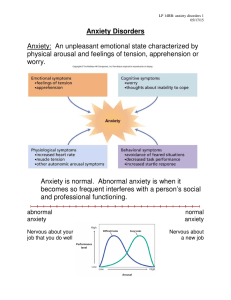
Anxiety: An unpleasant emotional state characterized
... Anxiety Disorders Anxiety disorders: Disorders characterized by excessive anxiety in the absence of true danger. It is normal to be anxious in stressful or threatening situations. It is abnormal to feel strong chronic anxiety without cause. People often experience more than one type of anxiety disor ...
... Anxiety Disorders Anxiety disorders: Disorders characterized by excessive anxiety in the absence of true danger. It is normal to be anxious in stressful or threatening situations. It is abnormal to feel strong chronic anxiety without cause. People often experience more than one type of anxiety disor ...
Psychological Disorders notes 16-1 objectives 1-4
... Philippe Pinel (1745-1826) from France, insisted that madness was not due to demonic possession, but an ailment of the mind. ...
... Philippe Pinel (1745-1826) from France, insisted that madness was not due to demonic possession, but an ailment of the mind. ...
Guided and unguided CBT for social anxiety
... The study sample will consist of adults (>18 years old) living in Sweden with sufficient Swedish and daily access to the Internet by both computer and smartphone. Participants must satisfy DSM-IV-TR [33] diagnostic criteria for either social anxiety disorder (SAD) or panic disorder (PD), or both. Pr ...
... The study sample will consist of adults (>18 years old) living in Sweden with sufficient Swedish and daily access to the Internet by both computer and smartphone. Participants must satisfy DSM-IV-TR [33] diagnostic criteria for either social anxiety disorder (SAD) or panic disorder (PD), or both. Pr ...
Personality Disorder
... I felt the need to clean my room … would spend four to five hours at it … At the time I loved doing it. Then I didn't want to do it any more, but I couldn’t stop … The clothes hung … two fingers apart …I touched my bedroom wall before leaving the house … I had constant anxiety … I thought I might be ...
... I felt the need to clean my room … would spend four to five hours at it … At the time I loved doing it. Then I didn't want to do it any more, but I couldn’t stop … The clothes hung … two fingers apart …I touched my bedroom wall before leaving the house … I had constant anxiety … I thought I might be ...
2- obsessive compulsive disorders DSM 5
... response to an obsession or according to rules that must be followed rigidly. • The behaviors or mental acts are aimed at preventing or reducing anxiety or distress or preventing some dreaded event or situation; however, these behaviors or mental acts are not connected in a realistic way with what t ...
... response to an obsession or according to rules that must be followed rigidly. • The behaviors or mental acts are aimed at preventing or reducing anxiety or distress or preventing some dreaded event or situation; however, these behaviors or mental acts are not connected in a realistic way with what t ...
Illness Summaries from DSM 5
... degree of memory loss goes beyond normal forgetfulness and includes gaps in memory for long periods of time or of memories involving the traumatic event. ...
... degree of memory loss goes beyond normal forgetfulness and includes gaps in memory for long periods of time or of memories involving the traumatic event. ...
Personality Disorder
... I felt the need to clean my room … would spend four to five hours at it … At the time I loved doing it. Then I didn't want to do it any more, but I couldn’t stop … The clothes hung … two fingers apart …I touched my bedroom wall before leaving the house … I had constant anxiety … I thought I might be ...
... I felt the need to clean my room … would spend four to five hours at it … At the time I loved doing it. Then I didn't want to do it any more, but I couldn’t stop … The clothes hung … two fingers apart …I touched my bedroom wall before leaving the house … I had constant anxiety … I thought I might be ...
Clinical Psychology
... disorders/developmental disorder - may not require immediate care - may be predisposing the person to the Axis I problem - can complicate treatment Axis 3: general medical conditions/neurological problems that may be relevant to the individual's current or past psychiatric problems - sometimes psych ...
... disorders/developmental disorder - may not require immediate care - may be predisposing the person to the Axis I problem - can complicate treatment Axis 3: general medical conditions/neurological problems that may be relevant to the individual's current or past psychiatric problems - sometimes psych ...
Navigating the Kraepelinian Vortex2
... consequences added as criteria. Minimum of 6 years old Differential diagnoses clarified between this and other disorders such as ADHD DMDD. ...
... consequences added as criteria. Minimum of 6 years old Differential diagnoses clarified between this and other disorders such as ADHD DMDD. ...
Research-Based Direction for the Use of Amino
... actually affect and shape brain structures, and create enduring neuronal pathways. In turn, these pathways create automatic responses which can be changed, but only with focused attention, practice, and new interpersonal experiences, such as those created in long-term therapy. In the DSM IV (Diagnos ...
... actually affect and shape brain structures, and create enduring neuronal pathways. In turn, these pathways create automatic responses which can be changed, but only with focused attention, practice, and new interpersonal experiences, such as those created in long-term therapy. In the DSM IV (Diagnos ...
UNDERSTANDING AND HELPING YOUR CHILD MANAGE ANXIETY
... one or in anticipation of taking a test. o In fact, anxiety is necessary for optimal functioning - without anxiety we would probably never do things we did not want to do. Anxiety becomes a problem when it interferes with the ability to function. Anxiety disorders are the most common type of psy ...
... one or in anticipation of taking a test. o In fact, anxiety is necessary for optimal functioning - without anxiety we would probably never do things we did not want to do. Anxiety becomes a problem when it interferes with the ability to function. Anxiety disorders are the most common type of psy ...
It Could Just Be Stress: The Teens of LeRoy and Conversion Disorder
... distributed to the community this past week, according to CNN. "There is no evidence of an environmental or infectious cause. Environmental causes would not discriminate (regarding who becomes infected)." There is at least one other theory, though. On Friday, a pediatric neurologist working out of B ...
... distributed to the community this past week, according to CNN. "There is no evidence of an environmental or infectious cause. Environmental causes would not discriminate (regarding who becomes infected)." There is at least one other theory, though. On Friday, a pediatric neurologist working out of B ...
Social Anxiety Disorder (Social Phobia)
... the responders relative to nonresponders in the affective division of the anterior cingulate cortex corresponding to areas 24/33 (B) Furmark, T. et al. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2002;59:425-433. ...
... the responders relative to nonresponders in the affective division of the anterior cingulate cortex corresponding to areas 24/33 (B) Furmark, T. et al. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2002;59:425-433. ...
Psychological Disorders - Purdue - Psychological Sciences
... – “Social Risk Hypothesis” • Depressive state evolved as alerting mechanism when at risk of social exclusion, necessary since Pleistocene period, because social exclusion would equal death. • Mechanism works to minimize social exclusion by changing social perception and social behavior in response t ...
... – “Social Risk Hypothesis” • Depressive state evolved as alerting mechanism when at risk of social exclusion, necessary since Pleistocene period, because social exclusion would equal death. • Mechanism works to minimize social exclusion by changing social perception and social behavior in response t ...
Psychological Disorders - Psychological Sciences
... Etiology: Cause and development of the disorder. Diagnosis: Identifying (symptoms) and distinguishing one disease from another. Treatment: Treating a disorder in a psychiatric ...
... Etiology: Cause and development of the disorder. Diagnosis: Identifying (symptoms) and distinguishing one disease from another. Treatment: Treating a disorder in a psychiatric ...
depressive disorders
... Schizophrenia is the most debilitating and complex of all the psychological disorders. Diverse symptoms; one common denominator: psychoticism ...
... Schizophrenia is the most debilitating and complex of all the psychological disorders. Diverse symptoms; one common denominator: psychoticism ...
ABNORMAL BEHAVIOR Theories and Diagnoses of Psychopathology
... reduced through exposure without negative consequences •Behavioral contracts and token economies prohibit undersirable behaviors and reward desirable ones •Rational emotive behavior therapy challenges irrational thoughts, helping to create realistic cause and effect connections between behaviors and ...
... reduced through exposure without negative consequences •Behavioral contracts and token economies prohibit undersirable behaviors and reward desirable ones •Rational emotive behavior therapy challenges irrational thoughts, helping to create realistic cause and effect connections between behaviors and ...
Schizoaffective Disorder
... have somewhat different side effect profiles. Changing from one antipsychotic to another one may help if a person with schizoaffective disorder does not respond well or develops distressing side effects with the first medication. The same principle applies to the use of antidepressants or mood stabl ...
... have somewhat different side effect profiles. Changing from one antipsychotic to another one may help if a person with schizoaffective disorder does not respond well or develops distressing side effects with the first medication. The same principle applies to the use of antidepressants or mood stabl ...
Anxiety Disorders
... exposed to unfamiliar people or to possible scrutiny by others. The individual fears that he or she will act in a way (or show anxiety symptoms) that will be humiliating or embarrassing. Note: In children, there must be evidence of the capacity for age-appropriate social relationships with familiar ...
... exposed to unfamiliar people or to possible scrutiny by others. The individual fears that he or she will act in a way (or show anxiety symptoms) that will be humiliating or embarrassing. Note: In children, there must be evidence of the capacity for age-appropriate social relationships with familiar ...
Cross-cultural adjustment & mental illness
... Anxiety Disorders • Anxiety is a normal reaction to stress • Most of time anxiety will pass, and normal functioning is resumed • Defined as a disorder when a certain group of symptoms are present • Each disorder has dominant symptoms but they all are a form of ...
... Anxiety Disorders • Anxiety is a normal reaction to stress • Most of time anxiety will pass, and normal functioning is resumed • Defined as a disorder when a certain group of symptoms are present • Each disorder has dominant symptoms but they all are a form of ...
Impulse Control Disorders Not Elsewhere Classified
... A. Several discrete episodes of failure to resist aggressive impulses that result in serious assaultive acts or destruction of property B. The degree of aggressiveness expressed during the episodes is grossly out of proportion to any precipitating psychological stressors C. The aggressive episodes a ...
... A. Several discrete episodes of failure to resist aggressive impulses that result in serious assaultive acts or destruction of property B. The degree of aggressiveness expressed during the episodes is grossly out of proportion to any precipitating psychological stressors C. The aggressive episodes a ...
Abnormal Psychology
... Understanding Mood Disorders Many behavioral and cognitive changes accompany ...
... Understanding Mood Disorders Many behavioral and cognitive changes accompany ...
Positive affect regulation in anxiety disorders
... do not appear to be explained by depression (Kashdan & Steger, 2006), suggesting that minimizing of PA may be an element in anxiety disorders even without comorbid depression. These findings pertaining to anxiety suggest maladaptive responses to PA in social phobia and generalized anxiety disorder. A ...
... do not appear to be explained by depression (Kashdan & Steger, 2006), suggesting that minimizing of PA may be an element in anxiety disorders even without comorbid depression. These findings pertaining to anxiety suggest maladaptive responses to PA in social phobia and generalized anxiety disorder. A ...