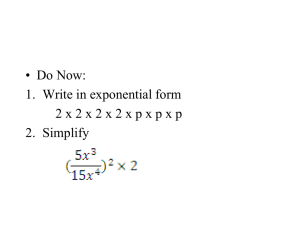Foundations - Algebra - University of Strathclyde
... Example 5.1 In the expression x3 + 2x2 − x, x is common to each term, so it can be taken out as common factor: x3 + 2x2 − x = x(x2 + 2x − 1). Example 5.2 In the expression 3(x − 1) + (x − 1)2 the common factor is (x − 1): 3(x − 1) + (x − 1)2 = (3 + (x − 1))(x − 1) = (2 + x)(x − 1). WARNING! It can b ...
... Example 5.1 In the expression x3 + 2x2 − x, x is common to each term, so it can be taken out as common factor: x3 + 2x2 − x = x(x2 + 2x − 1). Example 5.2 In the expression 3(x − 1) + (x − 1)2 the common factor is (x − 1): 3(x − 1) + (x − 1)2 = (3 + (x − 1))(x − 1) = (2 + x)(x − 1). WARNING! It can b ...
Everything I Know About Exponents
... that they are the same thing. But when you put it in repeated multiplication form, it's often easier to tell. For example: 45= 4x4x4x4x4= 1,024 54= 5x5x5x5= 625 They result in different answers because the exponents are different and the bases are not the same. 5) Evaluate powers with integral base ...
... that they are the same thing. But when you put it in repeated multiplication form, it's often easier to tell. For example: 45= 4x4x4x4x4= 1,024 54= 5x5x5x5= 625 They result in different answers because the exponents are different and the bases are not the same. 5) Evaluate powers with integral base ...
Hero's Journey Project
... steaming oatmeal on the table…. She stepped inside and sat down in the first chair she came to” (Southey 8). Context: Goldilocks has been walking for hours in the forest, and she is tired and hungry. Being a child, she is naturally curious. Since the bears have left their door open, she decides to s ...
... steaming oatmeal on the table…. She stepped inside and sat down in the first chair she came to” (Southey 8). Context: Goldilocks has been walking for hours in the forest, and she is tired and hungry. Being a child, she is naturally curious. Since the bears have left their door open, she decides to s ...
PDF
... A quadratic expression may be factorised by the method of “completing the square” even when the factors are not rational. A perfect square is of the form (x + b)2 = x2 + 2bx + b2 The first two terms of the right-hand side of the above equation are ( x 2 2bx ). To make a perfect square or to comple ...
... A quadratic expression may be factorised by the method of “completing the square” even when the factors are not rational. A perfect square is of the form (x + b)2 = x2 + 2bx + b2 The first two terms of the right-hand side of the above equation are ( x 2 2bx ). To make a perfect square or to comple ...
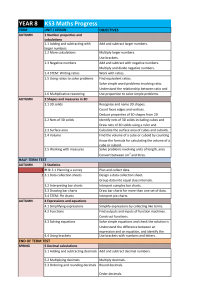
Year 8 Scheme of Work
... Use a probability scale with words and numbers. Write probabilities as fractions, decimals and percentages. Find all the possible outcomes of an event. Use equally likely outcomes to calculate probabilities. Learn and use probability notation. Calculate the probability of an event not happening. Fin ...
... Use a probability scale with words and numbers. Write probabilities as fractions, decimals and percentages. Find all the possible outcomes of an event. Use equally likely outcomes to calculate probabilities. Learn and use probability notation. Calculate the probability of an event not happening. Fin ...
Chapter 2.7 Inequalitities
... Essentially, all of the properties that you learned to solve linear equations apply to solving linear inequalities with the exception that if you multiply or divide by a negative you must reverse the inequality sign. So to solve an inequality just do the same steps as with an equality to get the var ...
... Essentially, all of the properties that you learned to solve linear equations apply to solving linear inequalities with the exception that if you multiply or divide by a negative you must reverse the inequality sign. So to solve an inequality just do the same steps as with an equality to get the var ...
Order of Operations
... Objective The student will be able to: use the order of operations to evaluate expressions. ...
... Objective The student will be able to: use the order of operations to evaluate expressions. ...
Order of Operations
... Objective The student will be able to: use the order of operations to evaluate expressions. ...
... Objective The student will be able to: use the order of operations to evaluate expressions. ...
Cold-formed steel members provide substantial savings due to their
... • The International system of units (SI) should be used; Equivalents in other units may be given in parentheses • The International system of units (SI) should be used; Equivalents in other units may be given in parentheses • The International system of units (SI) should be used; Equivalents in othe ...
... • The International system of units (SI) should be used; Equivalents in other units may be given in parentheses • The International system of units (SI) should be used; Equivalents in other units may be given in parentheses • The International system of units (SI) should be used; Equivalents in othe ...
Chapter 13: Polynomials - Wayne State University
... A polynomial is the sum of two or more monomials. Each monomial is called a term of the polynomial and are separated by either a “+” or “-“ sign. A polynomial is written in standard form when its terms are arranged in order from the greatest or least powers of one of the variables. Like terms are te ...
... A polynomial is the sum of two or more monomials. Each monomial is called a term of the polynomial and are separated by either a “+” or “-“ sign. A polynomial is written in standard form when its terms are arranged in order from the greatest or least powers of one of the variables. Like terms are te ...
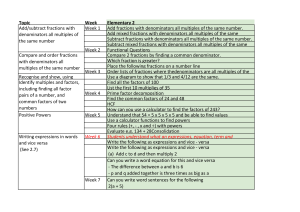
Lesson 1 and 2
... Multiplying terms together In algebra we usually leave out the multiplication sign ×. Any numbers must be written at the front and all letters should be written in alphabetical order. ...
... Multiplying terms together In algebra we usually leave out the multiplication sign ×. Any numbers must be written at the front and all letters should be written in alphabetical order. ...