PS1000: Introduction to Abnormal Psychology Mood disorders and
... Distinctly elevated or irritable mood. At least 3 of the following (4 if mood irritable); •Increase in goal-directed activity or physical restlessness •Unusual talkativeness; rapid speech •Flights of ideas or subjective impression that thoughts are racing •Decreased need for sleep •Inflated self est ...
... Distinctly elevated or irritable mood. At least 3 of the following (4 if mood irritable); •Increase in goal-directed activity or physical restlessness •Unusual talkativeness; rapid speech •Flights of ideas or subjective impression that thoughts are racing •Decreased need for sleep •Inflated self est ...
Understanding Students with Emotional or Behavioral Disorders
... Diagnostic Information in Children’s Mental Health O DSM-IV is the accepted guide to psychiatric ...
... Diagnostic Information in Children’s Mental Health O DSM-IV is the accepted guide to psychiatric ...
Letter of Medical Necessity Customizable Template
... under the patient’s IN-NETWORK benefits because Moleculera Labs, Inc. is the sole provider of this test in the US. This test is medically necessary for the following reasons: [list one or more reasons] I believe my patient’s neuropsychiatric symptoms (insert symptoms) could be the result of an autoi ...
... under the patient’s IN-NETWORK benefits because Moleculera Labs, Inc. is the sole provider of this test in the US. This test is medically necessary for the following reasons: [list one or more reasons] I believe my patient’s neuropsychiatric symptoms (insert symptoms) could be the result of an autoi ...
Mental Health/Wellness
... Conduct disorder- Person regularly violates the rights of others and breaks social rules Eating disorder- When a person has the urge to binge, purge or starve oneself Personality disorder- A disorder in which a person’s pattern of thoughts, feelings and actions interfere with daily life (schizophre ...
... Conduct disorder- Person regularly violates the rights of others and breaks social rules Eating disorder- When a person has the urge to binge, purge or starve oneself Personality disorder- A disorder in which a person’s pattern of thoughts, feelings and actions interfere with daily life (schizophre ...
Differential Diagnosis: Factitious Disorders vs. Somatoform Disorders
... • Anxiety about physical symptoms increases the intensity of the sensation (i.e. hyperfocused) and associated catastrophic – (i.e. anxiety) thinking further magnifies the ...
... • Anxiety about physical symptoms increases the intensity of the sensation (i.e. hyperfocused) and associated catastrophic – (i.e. anxiety) thinking further magnifies the ...
Treating Panic Disorder With Exposure Response Prevention (ER/P
... Exposure Response Prevention “Reprograms” The Brain ER/P therapy is based on the premise that a primary problem with panic disorder is the patient's fear of attacks and avoidance of situations that might trigger them. It is comprised of two components: exposure to the anxiety-producing thoughts or ...
... Exposure Response Prevention “Reprograms” The Brain ER/P therapy is based on the premise that a primary problem with panic disorder is the patient's fear of attacks and avoidance of situations that might trigger them. It is comprised of two components: exposure to the anxiety-producing thoughts or ...
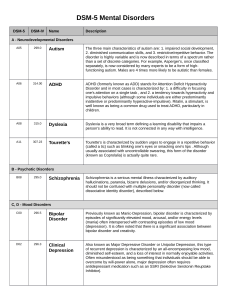
DSM V Mental Disorders
... A person who suffers from Illness Anxiety Disorder is commonly known as a hypochondriac. Such as person constantly worries about their health even when they have no reason to do so and often any minor symptom is perceived as being a sign of a serious illness. ...
... A person who suffers from Illness Anxiety Disorder is commonly known as a hypochondriac. Such as person constantly worries about their health even when they have no reason to do so and often any minor symptom is perceived as being a sign of a serious illness. ...
November 8, 2012
... Not normally seen in a child For males, late teens to mid 20s. For females, early 20s to early 30s. More likely to have degree since they get degree before they are diagnosed o Course varies, but generally 3 phrases Prodromal Phase Before the person becomes fully psychotic. This is for e ...
... Not normally seen in a child For males, late teens to mid 20s. For females, early 20s to early 30s. More likely to have degree since they get degree before they are diagnosed o Course varies, but generally 3 phrases Prodromal Phase Before the person becomes fully psychotic. This is for e ...
Assessing Abnormal Behaviors Chris Heimerl, MA
... •What have we tried? •What have we learned? •What are we pleased with? •What are we concerned with? The fifth question and its questions: •Now what? • -what will we continue to do? • -what will we do less of or stop doing? • -what will we begin or return to doing? ...
... •What have we tried? •What have we learned? •What are we pleased with? •What are we concerned with? The fifth question and its questions: •Now what? • -what will we continue to do? • -what will we do less of or stop doing? • -what will we begin or return to doing? ...
5.1 Abnormal psychology_concepts of normality
... Today psychiatrist use classification system, designed to be more objective. More holistic approach which is biopsychosocial. Tomasz Szasz (1962)– US psychiatrist was most critical of the concept “mental illness,” he argued that although some disorders were associated with disease of the brain, ...
... Today psychiatrist use classification system, designed to be more objective. More holistic approach which is biopsychosocial. Tomasz Szasz (1962)– US psychiatrist was most critical of the concept “mental illness,” he argued that although some disorders were associated with disease of the brain, ...
General Psychology - Pearson Education
... depression) results from the interaction of an inherited predisposition and the experience of stress or trauma ...
... depression) results from the interaction of an inherited predisposition and the experience of stress or trauma ...
Bipolar disorder I and II
... Ethiology Bipolar Disorder is hereditary. If a family member does not have Bipolar Disorder it does not mean that you will not be able to get it. It is just rare that you will. ...
... Ethiology Bipolar Disorder is hereditary. If a family member does not have Bipolar Disorder it does not mean that you will not be able to get it. It is just rare that you will. ...
2.2 What are Mood Disorders? - Counselling and Psychotherapy in
... diagnosis, depends on the presence or absence of certain episodes: Major Depressive Episode; Manic Episode; Mixed Episode and Hypomanic Episode. The DSM-IV provides clear definitions and criteria for each of these episodes and subsequent definitions and criteria for the related Mood Disorder diagnos ...
... diagnosis, depends on the presence or absence of certain episodes: Major Depressive Episode; Manic Episode; Mixed Episode and Hypomanic Episode. The DSM-IV provides clear definitions and criteria for each of these episodes and subsequent definitions and criteria for the related Mood Disorder diagnos ...
a severe mood disorder characterized by major
... Having adoptive relatives who were depressed also increases your chances, but not as much. The probability is especially high if your biological relatives were diagnosed with depression before age 30. B. Why women more than men? ...
... Having adoptive relatives who were depressed also increases your chances, but not as much. The probability is especially high if your biological relatives were diagnosed with depression before age 30. B. Why women more than men? ...
Adjustment disorders
... Anyone and everyone! Each one of us has had plenty of stressful events in our lives (remember, good stress is still stress) and each one of us reacts differently to each stressor. For instance, the loss of a pet is devastating for some people, whereas other people may not be affected at all. ...
... Anyone and everyone! Each one of us has had plenty of stressful events in our lives (remember, good stress is still stress) and each one of us reacts differently to each stressor. For instance, the loss of a pet is devastating for some people, whereas other people may not be affected at all. ...
Functional illness in elderly
... Symptoms usually of long duration Slow progression of symptoms throughout course ...
... Symptoms usually of long duration Slow progression of symptoms throughout course ...
Schizophrenia and assotiated disorders
... • False perceptions in the absence of a real external stimulus • May involve any of the sensory modalities • The most common are auditory hallucinations in the form of voices (60-70%) • Visual hallucinations occur 10% (but:organic disorder!!!) • Olfactory are more common in temporal lobe epilepsy • ...
... • False perceptions in the absence of a real external stimulus • May involve any of the sensory modalities • The most common are auditory hallucinations in the form of voices (60-70%) • Visual hallucinations occur 10% (but:organic disorder!!!) • Olfactory are more common in temporal lobe epilepsy • ...
Personality Disorders
... Cognitive disturbances – depressive triad Low self-esteem and unstable self-esteem ...
... Cognitive disturbances – depressive triad Low self-esteem and unstable self-esteem ...
FRQ Post-Guidance for Abnormal Behavior and Treatments FRQ
... A behavioral etiology of a somatoform disorder may be that somatoform disorders, like hypochondriasis for example, have physical symptoms but no physical origins. The symptoms come from the patient’s fears of becoming sick and reinforcement from his environment in the form of attention. Therefore, a ...
... A behavioral etiology of a somatoform disorder may be that somatoform disorders, like hypochondriasis for example, have physical symptoms but no physical origins. The symptoms come from the patient’s fears of becoming sick and reinforcement from his environment in the form of attention. Therefore, a ...
DISSOCIATIVE AMNESIA
... departments and then to neurologists, but is only seen secondarily in psychiatric departments ...
... departments and then to neurologists, but is only seen secondarily in psychiatric departments ...
A complex case of bipolar disorder responding to combined drug
... per cent develop rapid cycling disorder, in which four or more episodes occur within a year.2 Several organic factors have been linked with bipolar disorder, particularly in patients whose illness begins in older age (over 65 years). For example, non-dominant hemisphere cerebrovascular accidents can ...
... per cent develop rapid cycling disorder, in which four or more episodes occur within a year.2 Several organic factors have been linked with bipolar disorder, particularly in patients whose illness begins in older age (over 65 years). For example, non-dominant hemisphere cerebrovascular accidents can ...
Mixed Features Specifier - American Psychiatric Association
... The upcoming fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) will replace the diagnosis of “mixed episode” with a mixed-features specifier that can be applied to episodes of major depression, hypomania or mania. The change reflects ways these behaviors intersect an ...
... The upcoming fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) will replace the diagnosis of “mixed episode” with a mixed-features specifier that can be applied to episodes of major depression, hypomania or mania. The change reflects ways these behaviors intersect an ...
History of Hysteria – The Pharos
... to 60 percent of patients initially diagnosed with conversion disorder ultimately are found to have an underlying organic illness that may have accounted for their original symptoms.(6,9) Furthermore, while Freud’s placement of hysteria under the domain of psychology continues to be accepted by many ...
... to 60 percent of patients initially diagnosed with conversion disorder ultimately are found to have an underlying organic illness that may have accounted for their original symptoms.(6,9) Furthermore, while Freud’s placement of hysteria under the domain of psychology continues to be accepted by many ...
Chapter 10 Lesson 1 - Brimley Area Schools
... • Caused by a physical illness or an injury that affects the brain • Brain tumors, alcoholism, infections such as syphilis and meningitis, lupus and stroke • Some are inherited chemical imbalances ...
... • Caused by a physical illness or an injury that affects the brain • Brain tumors, alcoholism, infections such as syphilis and meningitis, lupus and stroke • Some are inherited chemical imbalances ...