AP Psychology Syllabus - Bremen High School District 228
... • Identify the criteria for judging whether behavior is psychologically disordered. • Describe the medical model of psychological disorders. • Describe the aims of DSMIV, and discuss the potential dangers of diagnostic labels. • Describe the symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder, phobias, obsess ...
... • Identify the criteria for judging whether behavior is psychologically disordered. • Describe the medical model of psychological disorders. • Describe the aims of DSMIV, and discuss the potential dangers of diagnostic labels. • Describe the symptoms of generalized anxiety disorder, phobias, obsess ...
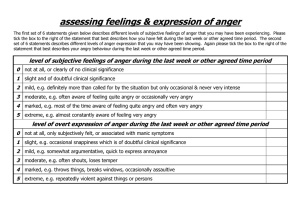
Anger Assessment Questionnaire
... BACKGROUND: This study sought to evaluate the degree of anger and aggression experienced by psychiatric outpatients and to determine whether anger is as prominent an emotional state in these patients as are depression and anxiety. We also sought to determine which Axis I and Axis II disorders were a ...
... BACKGROUND: This study sought to evaluate the degree of anger and aggression experienced by psychiatric outpatients and to determine whether anger is as prominent an emotional state in these patients as are depression and anxiety. We also sought to determine which Axis I and Axis II disorders were a ...
Chapter 016 - Nursing 343
... • Actual number of individuals with EDs is not known because disorders may exist for a long time before the person seeks help. • EDs are culturally influenced with varying prevalence, depending on the culture and social norms. • Female and male athletes demonstrate an increased incidence of EDs. ...
... • Actual number of individuals with EDs is not known because disorders may exist for a long time before the person seeks help. • EDs are culturally influenced with varying prevalence, depending on the culture and social norms. • Female and male athletes demonstrate an increased incidence of EDs. ...
Diagnosis - Healthy Transitions
... I am a psychologist who helps people who have “dual diagnosis.” This term is used when a person with a developmental disability also has a mental illness. It is often hard to diagnose a mental illness in a person who has a developmental disability. However, in order to provide effective treatment, i ...
... I am a psychologist who helps people who have “dual diagnosis.” This term is used when a person with a developmental disability also has a mental illness. It is often hard to diagnose a mental illness in a person who has a developmental disability. However, in order to provide effective treatment, i ...
File - Emily Suzanne Shields, LMHC
... 4. Repeated or extreme indirect exposure to aversive details of the event(s), usually in the course of professional duties (e.g., first responders, collecting body parts; professionals repeatedly exposed to details of child abuse). This does not include indirect non-professional exposure through ele ...
... 4. Repeated or extreme indirect exposure to aversive details of the event(s), usually in the course of professional duties (e.g., first responders, collecting body parts; professionals repeatedly exposed to details of child abuse). This does not include indirect non-professional exposure through ele ...
Report of the Task Force on Mental Disability and the Death Penalty
... extremely disorganized thinking, or very significant disruption of consciousness, memory and perception of the environment.18 Some conditions that are not considered an Axis I condition might also, on rare occasions, become "severe" as that word is used in this Recommendation. For instance, some per ...
... extremely disorganized thinking, or very significant disruption of consciousness, memory and perception of the environment.18 Some conditions that are not considered an Axis I condition might also, on rare occasions, become "severe" as that word is used in this Recommendation. For instance, some per ...
20356-46231-3-SP - Scandinavian Journal of Child and
... development of this disorder. Psychobiological studies when BPD first becomes manifest are of particular interest because there are fewer confounding factors (e.g., duration of illness, drug abuse, comorbid diagnoses, medication, or other therapeutic interventions) at this time. The article focuses ...
... development of this disorder. Psychobiological studies when BPD first becomes manifest are of particular interest because there are fewer confounding factors (e.g., duration of illness, drug abuse, comorbid diagnoses, medication, or other therapeutic interventions) at this time. The article focuses ...
SUICIDE ASSESSMENT PROTOCOL - University of Michigan
... communications of suicidal intent lasting several years In completed suicides, men have higher rates of alcohol abuse, women have higher rates of drug abuse Increased number of substances used, rather than the type of substance appears to be important Most have comorbid psychiatric disorders, ...
... communications of suicidal intent lasting several years In completed suicides, men have higher rates of alcohol abuse, women have higher rates of drug abuse Increased number of substances used, rather than the type of substance appears to be important Most have comorbid psychiatric disorders, ...
Sylvia Plath: A Diagnosis - SPARK: Scholarship at Parkland
... to be taken to the hospital. While Esther is recovering, Joan commits suicide and Buddy comes to terms with their lack of relationship. Esther is permitted to leave the mental hospital in time for the spring semester, but knows she is on the edge of breakdown at any time. After reviewing the DSM-IV ...
... to be taken to the hospital. While Esther is recovering, Joan commits suicide and Buddy comes to terms with their lack of relationship. Esther is permitted to leave the mental hospital in time for the spring semester, but knows she is on the edge of breakdown at any time. After reviewing the DSM-IV ...
Co-Occurring Chronic Depression and Alcohol
... Depression Inventory ≥ 10), not diagnosed depressive disorders [14]. Another study found that adding CBT-D for alcoholics with significant depressive symptoms was more effective on mood and alcohol use measures than standard treatment alone within an individual, but not a group treatment modality [3 ...
... Depression Inventory ≥ 10), not diagnosed depressive disorders [14]. Another study found that adding CBT-D for alcoholics with significant depressive symptoms was more effective on mood and alcohol use measures than standard treatment alone within an individual, but not a group treatment modality [3 ...
What is Bipolar Disorder? - Student Counselling, Career and
... vigilant to your symptoms and physical and emotional responses to the environment. By being aware of you and your body, you will be more effective in your own lifestyle management. Having a positive attitude and mindset - Use therapy and educational materials to improve your selfesteem and change ...
... vigilant to your symptoms and physical and emotional responses to the environment. By being aware of you and your body, you will be more effective in your own lifestyle management. Having a positive attitude and mindset - Use therapy and educational materials to improve your selfesteem and change ...
Sometimes more competent, but always less warm
... Background and aims: Biological conceptualizations of psychopathology are ascendant, including among mental-health clinicians. However, it is unknown how this might affect people’s perceptions of clinicians, which in turn could have considerable public-health implications. The present studies sought ...
... Background and aims: Biological conceptualizations of psychopathology are ascendant, including among mental-health clinicians. However, it is unknown how this might affect people’s perceptions of clinicians, which in turn could have considerable public-health implications. The present studies sought ...
HISTORICAL ARTICLE Schizophrenia – From devilry to
... • A speculation into whether historical references of ‘madness’ could be attributed to cases of psychosis. ...
... • A speculation into whether historical references of ‘madness’ could be attributed to cases of psychosis. ...
What is Psychology?
... Obsessions and Compulsions • Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): – An anxiety disorder in which a person feels trapped in repetitive, persistent thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive, ritualized behaviors (compulsions) designed to reduce anxiety. ...
... Obsessions and Compulsions • Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): – An anxiety disorder in which a person feels trapped in repetitive, persistent thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive, ritualized behaviors (compulsions) designed to reduce anxiety. ...
The Divided Mind - The Divine Conspiracy
... reason, higher intelligence, communication, and morality. There appears to be an ongoing struggle between these two parts of the brain. Sometimes reason prevails, and at other times the more childish, bestial part of human nature is dominant. This duality is one reason for psychosomatic disorders, a ...
... reason, higher intelligence, communication, and morality. There appears to be an ongoing struggle between these two parts of the brain. Sometimes reason prevails, and at other times the more childish, bestial part of human nature is dominant. This duality is one reason for psychosomatic disorders, a ...
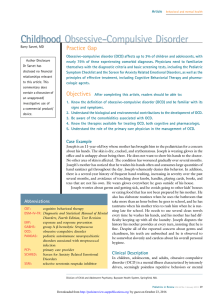
Childhood Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
... with spirituality and exhibit compulsive praying and religious rituals. If the hyperreligiosity is associated primarily with elevated or mixed mood states and does not represent a compensatory behavior in response to intrusive forbidden thoughts, it is likely a sign of a manic state rather than OCD. ...
... with spirituality and exhibit compulsive praying and religious rituals. If the hyperreligiosity is associated primarily with elevated or mixed mood states and does not represent a compensatory behavior in response to intrusive forbidden thoughts, it is likely a sign of a manic state rather than OCD. ...
Short-Term Intensive Family Therapy for Adolescent Eating
... asked to complete an online self-report Eating Disorder Examination Questionnaire (EDE-Q). The EDE-Q (Fairburn & Beglin, 1994) is a 28-item self-report questionnaire with high internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha global scale = 0.93; Mond, Hay, Rodgers, Owen, & Beaumont, 2004) that provides a meas ...
... asked to complete an online self-report Eating Disorder Examination Questionnaire (EDE-Q). The EDE-Q (Fairburn & Beglin, 1994) is a 28-item self-report questionnaire with high internal consistency (Cronbach’s alpha global scale = 0.93; Mond, Hay, Rodgers, Owen, & Beaumont, 2004) that provides a meas ...
Sleep Related Disorders
... Origin(s) of this problem is made clearer by the specifiers used: – Shift work type – Jet lag type – Delayed Sleep Phase type ...
... Origin(s) of this problem is made clearer by the specifiers used: – Shift work type – Jet lag type – Delayed Sleep Phase type ...
Psychological Disorders - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... continuing changes in the DSM have reflected advances in knowledge (First & Pincus, 2002; Widiger, 2000). On the basis of research and clinical experience, categories of disorders have been dropped, added, or revised as new editions of the DSM have been published. DSM-IV-TR (Diagnostic and Statistic ...
... continuing changes in the DSM have reflected advances in knowledge (First & Pincus, 2002; Widiger, 2000). On the basis of research and clinical experience, categories of disorders have been dropped, added, or revised as new editions of the DSM have been published. DSM-IV-TR (Diagnostic and Statistic ...
Dissociative identity disorder

Dissociative identity disorder (DID), previously known as multiple personality disorder (MPD), is a mental disorder on the dissociative spectrum characterized by the appearance of at least two distinct and relatively enduring identities or dissociated personality states that alternately control a person's behavior, accompanied by memory impairment for important information not explained by ordinary forgetfulness. These symptoms are not accounted for by substance abuse, seizures, other medical conditions, nor by imaginative play in children. Diagnosis is often difficult as there is considerable comorbidity with other mental disorders. Malingering should be considered if there is possible financial or forensic gain, as well as factitious disorder if help-seeking behavior is prominent.DID is one of the most controversial psychiatric disorders, with no clear consensus on diagnostic criteria or treatment. Research on treatment efficacy has been concerned primarily with clinical approaches and case studies. Dissociative symptoms range from common lapses in attention, becoming distracted by something else, and daydreaming, to pathological dissociative disorders. No systematic, empirically-supported definition of ""dissociation"" exists. It is not the same as schizophrenia.Although neither epidemiological surveys nor longitudinal studies have been conducted, it is generally believed that DID rarely resolves spontaneously. Symptoms are said to vary over time. In general, the prognosis is poor, especially for those with comorbid disorders. There are few systematic data on the prevalence of DID. The International Society for the Study of Trauma and Dissociation states that the prevalence is between 1 and 3% in the general population, and between 1 and 5% in inpatient groups in Europe and North America. DID is diagnosed more frequently in North America than in the rest of the world, and is diagnosed three to nine times more often in females than in males. The prevalence of DID diagnoses increased greatly in the latter half of the 20th century, along with the number of identities (often referred to as ""alters"") claimed by patients (increasing from an average of two or three to approximately 16). DID is also controversial within the legal system, where it has been used as a rarely successful form of the insanity defense. The 1990s showed a parallel increase in the number of court cases involving the diagnosis.Dissociative disorders including DID have been attributed to disruptions in memory caused by trauma and other forms of stress, but research on this hypothesis has been characterized by poor methodology. So far, scientific studies, usually focusing on memory, have been few and the results have been inconclusive. An alternative hypothesis for the etiology of DID is as a by-product of techniques employed by some therapists, especially those using hypnosis, and disagreement between the two positions is characterized by intense debate. DID became a popular diagnosis in the 1970s, 80s and 90s, but it is unclear if the actual rate of the disorder increased, if it was more recognized by health care providers, or if sociocultural factors caused an increase in therapy-induced (iatrogenic) presentations. The unusual number of diagnoses after 1980, clustered around a small number of clinicians and the suggestibility characteristic of those with DID, support the hypothesis that DID is therapist-induced. The unusual clustering of diagnoses has also been explained as due to a lack of awareness and training among clinicians to recognize cases of DID.