DIAGNOSIS
... (1) recurrent and intrusive distressing recollections of the event, including images, thoughts, or perceptions. (2) recurrent distressing dreams of the event (3) acting or feeling as if the traumatic event were recurring (illusions, hallucinations, dissociative flashbacks, sense of reliving) (4) int ...
... (1) recurrent and intrusive distressing recollections of the event, including images, thoughts, or perceptions. (2) recurrent distressing dreams of the event (3) acting or feeling as if the traumatic event were recurring (illusions, hallucinations, dissociative flashbacks, sense of reliving) (4) int ...
Attention Deficit Disorder - ADD with hyperactivity
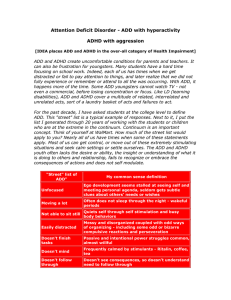
... ADHD often negatively affects a person’s educational achievements. Lack of school success can contribute to a myriad of economic, social and life adjustment problems throughout a person’s life. Educational functioning should be reviewed carefully. In children, adolescents, or adult students, a revie ...
... ADHD often negatively affects a person’s educational achievements. Lack of school success can contribute to a myriad of economic, social and life adjustment problems throughout a person’s life. Educational functioning should be reviewed carefully. In children, adolescents, or adult students, a revie ...
Guidelines for the assessment and treatment of children and
... The following components are necessary: • Comprehensive information needs to be obtained regarding the history of the child with specific reference to early bonding, attachment relationships, traumatic experiences, emotional, social, physical and cognitive development, behavior and previous treatmen ...
... The following components are necessary: • Comprehensive information needs to be obtained regarding the history of the child with specific reference to early bonding, attachment relationships, traumatic experiences, emotional, social, physical and cognitive development, behavior and previous treatmen ...
USING DYNAMIC FACTOR ANALYSIS TO MODEL
... for Personality, Psychopathology, and Psychotherapy Research for their ongoing work and their dedication to this research. Many thanks also go to graduate students involved in the project, especially Wes Scala, Emily Dowgwillo, Mike Roche, Ross MacLean, and Lauren Szkodny. I would also like to expre ...
... for Personality, Psychopathology, and Psychotherapy Research for their ongoing work and their dedication to this research. Many thanks also go to graduate students involved in the project, especially Wes Scala, Emily Dowgwillo, Mike Roche, Ross MacLean, and Lauren Szkodny. I would also like to expre ...
Tell Us Your Story: Investigating the Linguistic Features of Trauma... Jeremy A. Luno ()
... symptoms include re-experiencing the traumatic event, avoiding thoughts of the event, mental/emotional numbing, as well as hyper-arousal. These symptoms are further delineated to include flashbacks, nightmares, sleep difficulties, and irritability. These symptoms are clustered into three overarching ...
... symptoms include re-experiencing the traumatic event, avoiding thoughts of the event, mental/emotional numbing, as well as hyper-arousal. These symptoms are further delineated to include flashbacks, nightmares, sleep difficulties, and irritability. These symptoms are clustered into three overarching ...
Risk Factors for PTSD 1 Obstacles to the Study of Risk
... neuroticism, those with higher neuroticism are more likely to develop PTSD (e.g., Breslau et al., 1991; McFarlane, 1989). Research on these individual difference variables provides clues to vulnerability. Yet constructs emerging from psychometric studies do not directly illuminate the mechanisms ope ...
... neuroticism, those with higher neuroticism are more likely to develop PTSD (e.g., Breslau et al., 1991; McFarlane, 1989). Research on these individual difference variables provides clues to vulnerability. Yet constructs emerging from psychometric studies do not directly illuminate the mechanisms ope ...
Thought Process Disorders
... Care of the Patient with a Psychiatric Disorder • The nurse should have basic understanding of the classifications of human responses and treatments for mental illness. • It is important for nurses to be able to interact therapeutically with both the physical and emotional aspects of patient care. ...
... Care of the Patient with a Psychiatric Disorder • The nurse should have basic understanding of the classifications of human responses and treatments for mental illness. • It is important for nurses to be able to interact therapeutically with both the physical and emotional aspects of patient care. ...
Treating anxiety disorders - Children`s Health Policy Centre
... As an interdisciplinary research group in the Faculty of Health Sciences at Simon Fraser University, we aim to connect research and policy to improve children’s social and emotional well-being, or children’s mental health. We advocate the following public health strategy for children’s mental health ...
... As an interdisciplinary research group in the Faculty of Health Sciences at Simon Fraser University, we aim to connect research and policy to improve children’s social and emotional well-being, or children’s mental health. We advocate the following public health strategy for children’s mental health ...
PN Mental Health Chapter 18
... Copyright © 2011 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ...
... Copyright © 2011 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ...
... depending on diagnostic concordance: Individuals who met the diagnostic criteria according to the DSM-IV but not the DSM-5 (Yes/ No group) were compared with individuals who met the diagnostic criteria according to both classifications (Yes/Yes group); individuals who did not meet the DSM-IV criteri ...
Too much sex, a mental disorder? - Open Access Journal Hosting
... the negative emotions that stem from their underlying mood and anxiety disorders (Winters, 2010). Therefore, if the underlying disorder(s) are treated, the maladaptive sexual fantasies and behaviours should also be ameliorated (Winters, 2010). In short, opponents argue that there is insufficient dat ...
... the negative emotions that stem from their underlying mood and anxiety disorders (Winters, 2010). Therefore, if the underlying disorder(s) are treated, the maladaptive sexual fantasies and behaviours should also be ameliorated (Winters, 2010). In short, opponents argue that there is insufficient dat ...
Mash Chapter 8
... In the past, it was mistakenly believed that depression did not exist in children in a form comparable to that in adults We now know that children do experience depression, and that depression in children is not masked, but rather may be overlooked because it frequently co-occurs with other more ...
... In the past, it was mistakenly believed that depression did not exist in children in a form comparable to that in adults We now know that children do experience depression, and that depression in children is not masked, but rather may be overlooked because it frequently co-occurs with other more ...
Melatonin
... introduced in 1984 and has since been included in the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. SAD is characterized by recurring, cyclic bouts of depression, increased appetite, and an increased need for sleep (Ford 1992; Magnusson 2003). It contrasts ...
... introduced in 1984 and has since been included in the American Psychiatric Association’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. SAD is characterized by recurring, cyclic bouts of depression, increased appetite, and an increased need for sleep (Ford 1992; Magnusson 2003). It contrasts ...
Article Title Goes Here
... widespread, with a wide range of cognitive and behavioral responses/outcomes among trauma survivors [1]. The association of traumatic exposures with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and other mental health conditions is well known [2]. Although traumatic events are associated with PTSD in the li ...
... widespread, with a wide range of cognitive and behavioral responses/outcomes among trauma survivors [1]. The association of traumatic exposures with posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and other mental health conditions is well known [2]. Although traumatic events are associated with PTSD in the li ...
Eating disorders, anxiety and depression
... about and handling issues such as self-esteem, control, perfectionism and family problems. This can include individual and family therapy and psycho-education (information on psychological issues). Psychological therapies are also used to treat anxiety and depression. ...
... about and handling issues such as self-esteem, control, perfectionism and family problems. This can include individual and family therapy and psycho-education (information on psychological issues). Psychological therapies are also used to treat anxiety and depression. ...
The construct validity of passive
... than sociotropy/communion personality dimensions (Morey, 1985; Morse, Robins, & Gittes-Fox, 2002) and has been linked to authority conflicts among adolescents (Vereycken, Vertommen & Corvelyn, 2002). However, research has been limited; the relations of PAPD to other common models of personality have ...
... than sociotropy/communion personality dimensions (Morey, 1985; Morse, Robins, & Gittes-Fox, 2002) and has been linked to authority conflicts among adolescents (Vereycken, Vertommen & Corvelyn, 2002). However, research has been limited; the relations of PAPD to other common models of personality have ...
Trichotillomania and emotion regulation: Is symptom severity related
... pulling behavior (Diefenbach et al., 2008; Shusterman et al., 2009). The hair pulling behavior is frequently preceded by an increase of tension followed by relief when pulling out the hair. In addition, situations associated with unpleasant emotions are common triggers for hair pulling. Thus, it has ...
... pulling behavior (Diefenbach et al., 2008; Shusterman et al., 2009). The hair pulling behavior is frequently preceded by an increase of tension followed by relief when pulling out the hair. In addition, situations associated with unpleasant emotions are common triggers for hair pulling. Thus, it has ...
13 - Cengage Learning
... • First, the language of children with autism is generally delayed or disrupted in its normal development. The language of children with schizophrenia does not consistently show impaired development • Second, the language of children with autism confused and the content impoverished; Children with s ...
... • First, the language of children with autism is generally delayed or disrupted in its normal development. The language of children with schizophrenia does not consistently show impaired development • Second, the language of children with autism confused and the content impoverished; Children with s ...
USABILITY EVALUATION OF MOBILE APPLICATION Usability
... post-trauma mental health symptoms and those of related conditions. This flexibility is important given that post-trauma symptoms develop at different rates after a trauma [21], [22]. In order for mobile application post-trauma care to have the proposed impact on health care, it is necessary to desi ...
... post-trauma mental health symptoms and those of related conditions. This flexibility is important given that post-trauma symptoms develop at different rates after a trauma [21], [22]. In order for mobile application post-trauma care to have the proposed impact on health care, it is necessary to desi ...
Dissociative identity disorder

Dissociative identity disorder (DID), previously known as multiple personality disorder (MPD), is a mental disorder on the dissociative spectrum characterized by the appearance of at least two distinct and relatively enduring identities or dissociated personality states that alternately control a person's behavior, accompanied by memory impairment for important information not explained by ordinary forgetfulness. These symptoms are not accounted for by substance abuse, seizures, other medical conditions, nor by imaginative play in children. Diagnosis is often difficult as there is considerable comorbidity with other mental disorders. Malingering should be considered if there is possible financial or forensic gain, as well as factitious disorder if help-seeking behavior is prominent.DID is one of the most controversial psychiatric disorders, with no clear consensus on diagnostic criteria or treatment. Research on treatment efficacy has been concerned primarily with clinical approaches and case studies. Dissociative symptoms range from common lapses in attention, becoming distracted by something else, and daydreaming, to pathological dissociative disorders. No systematic, empirically-supported definition of ""dissociation"" exists. It is not the same as schizophrenia.Although neither epidemiological surveys nor longitudinal studies have been conducted, it is generally believed that DID rarely resolves spontaneously. Symptoms are said to vary over time. In general, the prognosis is poor, especially for those with comorbid disorders. There are few systematic data on the prevalence of DID. The International Society for the Study of Trauma and Dissociation states that the prevalence is between 1 and 3% in the general population, and between 1 and 5% in inpatient groups in Europe and North America. DID is diagnosed more frequently in North America than in the rest of the world, and is diagnosed three to nine times more often in females than in males. The prevalence of DID diagnoses increased greatly in the latter half of the 20th century, along with the number of identities (often referred to as ""alters"") claimed by patients (increasing from an average of two or three to approximately 16). DID is also controversial within the legal system, where it has been used as a rarely successful form of the insanity defense. The 1990s showed a parallel increase in the number of court cases involving the diagnosis.Dissociative disorders including DID have been attributed to disruptions in memory caused by trauma and other forms of stress, but research on this hypothesis has been characterized by poor methodology. So far, scientific studies, usually focusing on memory, have been few and the results have been inconclusive. An alternative hypothesis for the etiology of DID is as a by-product of techniques employed by some therapists, especially those using hypnosis, and disagreement between the two positions is characterized by intense debate. DID became a popular diagnosis in the 1970s, 80s and 90s, but it is unclear if the actual rate of the disorder increased, if it was more recognized by health care providers, or if sociocultural factors caused an increase in therapy-induced (iatrogenic) presentations. The unusual number of diagnoses after 1980, clustered around a small number of clinicians and the suggestibility characteristic of those with DID, support the hypothesis that DID is therapist-induced. The unusual clustering of diagnoses has also been explained as due to a lack of awareness and training among clinicians to recognize cases of DID.