Psychiatry—Personality Disorders
... people in the world; affectivity, the range, intensity, and the appropriateness of emotional response; interpersonal functioning, and impulse control. 2) Pervasive pattern begins by early adulthood and present in a variety of contexts 3) The enduring pattern must be: inflexible and pervasive across ...
... people in the world; affectivity, the range, intensity, and the appropriateness of emotional response; interpersonal functioning, and impulse control. 2) Pervasive pattern begins by early adulthood and present in a variety of contexts 3) The enduring pattern must be: inflexible and pervasive across ...
Shairah Carpio Tory Lamanivong Grant Foster Christine Zhang
... Causes of PTSD -Posttraumatic stress disorder can be caused by any traumatic event such as being exposed to torture, murder, kidnap, rape, death, abuse (physical or emotional), etc. Other things that can cause PTSD that may not be classified as traumatic events may include things like divorce and ...
... Causes of PTSD -Posttraumatic stress disorder can be caused by any traumatic event such as being exposed to torture, murder, kidnap, rape, death, abuse (physical or emotional), etc. Other things that can cause PTSD that may not be classified as traumatic events may include things like divorce and ...
BN 64_Internet-based Cognitive Behavioral
... All included studies reported a high level of clinically relevant change in experimental group vs. control group: participants had either changed diagnostic category or no longer met any PTSD criteria altogether ...
... All included studies reported a high level of clinically relevant change in experimental group vs. control group: participants had either changed diagnostic category or no longer met any PTSD criteria altogether ...
Chapter 7 Mood Disorders
... •Significant weight loss or gain or change in appetite •Fatigue or loss of energy nearly every day •Psychomotor agitation or retardation –Nearly always accompanied by markedly diminished interest or ability to experience pleasure (anhedonia) from life ...
... •Significant weight loss or gain or change in appetite •Fatigue or loss of energy nearly every day •Psychomotor agitation or retardation –Nearly always accompanied by markedly diminished interest or ability to experience pleasure (anhedonia) from life ...
‘Caring Rather Than Curing,’ the Simulated Syndromes Jonny Gerkin, MD Assistant Professor
... ◦ Most patients show rapid response to treatment ◦ Pseudosz, amnesia, tremor more likely to have poor outcome – sig relationship to childhood (sexual) trauma ...
... ◦ Most patients show rapid response to treatment ◦ Pseudosz, amnesia, tremor more likely to have poor outcome – sig relationship to childhood (sexual) trauma ...
Anxiety Disorders - Terri L. Weaver, Ph.D.
... A person is unwilling to remain in contact with particular private experiences (e.g., bodily sensations, emotions, thoughts, memories, images, behavioral predispositions) and takes steps to alter the form or frequency of these experiences or the contexts that occasion them, even when these forms of ...
... A person is unwilling to remain in contact with particular private experiences (e.g., bodily sensations, emotions, thoughts, memories, images, behavioral predispositions) and takes steps to alter the form or frequency of these experiences or the contexts that occasion them, even when these forms of ...
The Special Challenges of Neurological-Based
... – Insistence on routine and sameness – Difficulty dealing with interruption of routine schedule and change – Monotone voice and difficulty carrying on social conversations – Inflexibility of thought and language ...
... – Insistence on routine and sameness – Difficulty dealing with interruption of routine schedule and change – Monotone voice and difficulty carrying on social conversations – Inflexibility of thought and language ...
Dia 1 - estss
... • The re-experiencing symptoms corresponds to DSM-IV 2,3, and 4 • Avoidance demands one symptom • Hypervigiliance is like DSM-IV (2/5 symptoms • Amnesia can substitute the hypervigiliance symptoms ...
... • The re-experiencing symptoms corresponds to DSM-IV 2,3, and 4 • Avoidance demands one symptom • Hypervigiliance is like DSM-IV (2/5 symptoms • Amnesia can substitute the hypervigiliance symptoms ...
Psychological Disorders
... Personality Disorders • Antisocial or sociopathic personality disorder • a disorder in which individuals tend to display no regard for the moral and ethical rules of society or the rights of others ...
... Personality Disorders • Antisocial or sociopathic personality disorder • a disorder in which individuals tend to display no regard for the moral and ethical rules of society or the rights of others ...
Why transition to adult service system?
... AGES SERVED: approximately age 12 or early teens – aging population; currently our oldest patient is 70 years old. FOCUS and FREQUENCY: patients transitioning to adult services or searching for physicians with expertise that accept insurance. We accept Medicare and Medicaid at our clinic. 50 – 60% o ...
... AGES SERVED: approximately age 12 or early teens – aging population; currently our oldest patient is 70 years old. FOCUS and FREQUENCY: patients transitioning to adult services or searching for physicians with expertise that accept insurance. We accept Medicare and Medicaid at our clinic. 50 – 60% o ...
A Look into the Treatment, 1 Running head: A LOOK INTO THE
... treatment plan for the combination of dual disorders changes as it relates to a specific disorder. Conrad and Steward (2005) states that “there was also some indication that ...
... treatment plan for the combination of dual disorders changes as it relates to a specific disorder. Conrad and Steward (2005) states that “there was also some indication that ...
Stages of Change in the Treatment of Co-occurring Disorders - MI-PTE
... • Does not believe change is possible; sees self as having little influence. ...
... • Does not believe change is possible; sees self as having little influence. ...
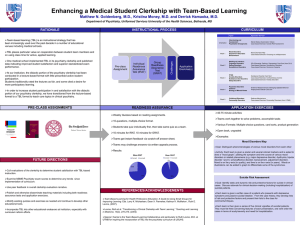
Enhancing a Medical Student Clerkship with Team
... UTMB for inspiring the incorporation of TBL into the psychiatry curriculum at USUHS. ...
... UTMB for inspiring the incorporation of TBL into the psychiatry curriculum at USUHS. ...
Anxiety
... Severe precipitating stressor. Splitting off an idea or emotion from one’s consciousness. Psychological flight from anxiety ...
... Severe precipitating stressor. Splitting off an idea or emotion from one’s consciousness. Psychological flight from anxiety ...
Oppositional Defiant Disorder Or The Taming of the Shrew
... behavior occurs more frequently than is typically observed in individuals of comparable age and developmental level. ...i.e. oppositional behavior normally ...
... behavior occurs more frequently than is typically observed in individuals of comparable age and developmental level. ...i.e. oppositional behavior normally ...
Chapter 14 Psychological Disorders
... mental disorders and is only type of therapist who can prescribe drugs or other biomedical treatment Psychoanalyst: Any of the above types of credential, but with training in psychoanalysis ...
... mental disorders and is only type of therapist who can prescribe drugs or other biomedical treatment Psychoanalyst: Any of the above types of credential, but with training in psychoanalysis ...
Sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of patients with
... or level of education that is inadequate to maintain a sound psychiatric interview; alcohol and substance abuse that may effect symptom distribution within the last 2 weeks; presence of psychiatric disorder associated with a general medical condition at the first axis; factitious disease or malinger ...
... or level of education that is inadequate to maintain a sound psychiatric interview; alcohol and substance abuse that may effect symptom distribution within the last 2 weeks; presence of psychiatric disorder associated with a general medical condition at the first axis; factitious disease or malinger ...
Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
... The symptoms of PTSD fall into the following categories: Intrusive Memories, which can include flashbacks of reliving the moment of trauma, bad dreams and scary thoughts. Avoidance, which can include staying away from certain places or objects that are reminders of the traumatic event. A person ...
... The symptoms of PTSD fall into the following categories: Intrusive Memories, which can include flashbacks of reliving the moment of trauma, bad dreams and scary thoughts. Avoidance, which can include staying away from certain places or objects that are reminders of the traumatic event. A person ...
Unit XII Textbook PowerPoint questions and answers
... 5. Xavier, who has a negative explanatory style, is most likely to get depressed after failing a math test is he believes that he failed because a. He is not good at math and never will be. b. His teacher made it impossible to learn the material. c. He was sick on the day he took the test. d. His pa ...
... 5. Xavier, who has a negative explanatory style, is most likely to get depressed after failing a math test is he believes that he failed because a. He is not good at math and never will be. b. His teacher made it impossible to learn the material. c. He was sick on the day he took the test. d. His pa ...
Dissociative identity disorder

Dissociative identity disorder (DID), previously known as multiple personality disorder (MPD), is a mental disorder on the dissociative spectrum characterized by the appearance of at least two distinct and relatively enduring identities or dissociated personality states that alternately control a person's behavior, accompanied by memory impairment for important information not explained by ordinary forgetfulness. These symptoms are not accounted for by substance abuse, seizures, other medical conditions, nor by imaginative play in children. Diagnosis is often difficult as there is considerable comorbidity with other mental disorders. Malingering should be considered if there is possible financial or forensic gain, as well as factitious disorder if help-seeking behavior is prominent.DID is one of the most controversial psychiatric disorders, with no clear consensus on diagnostic criteria or treatment. Research on treatment efficacy has been concerned primarily with clinical approaches and case studies. Dissociative symptoms range from common lapses in attention, becoming distracted by something else, and daydreaming, to pathological dissociative disorders. No systematic, empirically-supported definition of ""dissociation"" exists. It is not the same as schizophrenia.Although neither epidemiological surveys nor longitudinal studies have been conducted, it is generally believed that DID rarely resolves spontaneously. Symptoms are said to vary over time. In general, the prognosis is poor, especially for those with comorbid disorders. There are few systematic data on the prevalence of DID. The International Society for the Study of Trauma and Dissociation states that the prevalence is between 1 and 3% in the general population, and between 1 and 5% in inpatient groups in Europe and North America. DID is diagnosed more frequently in North America than in the rest of the world, and is diagnosed three to nine times more often in females than in males. The prevalence of DID diagnoses increased greatly in the latter half of the 20th century, along with the number of identities (often referred to as ""alters"") claimed by patients (increasing from an average of two or three to approximately 16). DID is also controversial within the legal system, where it has been used as a rarely successful form of the insanity defense. The 1990s showed a parallel increase in the number of court cases involving the diagnosis.Dissociative disorders including DID have been attributed to disruptions in memory caused by trauma and other forms of stress, but research on this hypothesis has been characterized by poor methodology. So far, scientific studies, usually focusing on memory, have been few and the results have been inconclusive. An alternative hypothesis for the etiology of DID is as a by-product of techniques employed by some therapists, especially those using hypnosis, and disagreement between the two positions is characterized by intense debate. DID became a popular diagnosis in the 1970s, 80s and 90s, but it is unclear if the actual rate of the disorder increased, if it was more recognized by health care providers, or if sociocultural factors caused an increase in therapy-induced (iatrogenic) presentations. The unusual number of diagnoses after 1980, clustered around a small number of clinicians and the suggestibility characteristic of those with DID, support the hypothesis that DID is therapist-induced. The unusual clustering of diagnoses has also been explained as due to a lack of awareness and training among clinicians to recognize cases of DID.