Comorbid Bipolar Disorder Among Patients with Conversion Disorder
... study. SCID-I and sociodemographical form were administered to the patients. Results: Bipolar disorder was found in 28% of the patients. The rate of dissociative disorder not otherwise specified (NOS), panic disorder, eating disorder comorbidity were higher in conversion disorder patients with bipol ...
... study. SCID-I and sociodemographical form were administered to the patients. Results: Bipolar disorder was found in 28% of the patients. The rate of dissociative disorder not otherwise specified (NOS), panic disorder, eating disorder comorbidity were higher in conversion disorder patients with bipol ...
- Psychiatry Lectures
... disorders with psychotic features. • Patients with paranoid personality disorder show more social engagement, aggressive v ...
... disorders with psychotic features. • Patients with paranoid personality disorder show more social engagement, aggressive v ...
Handout 13: The Psychological Stress Disorders
... Handout 22: Why Do People Develop a Psychological Stress Disorder? Biological and genetic factors • Traumatic events trigger physical changes in the brain and body that may lead to severe stress reactions • Some research suggests abnormal NT and hormone activity (especially norepinephrine and cort ...
... Handout 22: Why Do People Develop a Psychological Stress Disorder? Biological and genetic factors • Traumatic events trigger physical changes in the brain and body that may lead to severe stress reactions • Some research suggests abnormal NT and hormone activity (especially norepinephrine and cort ...
Cross,Cultural Perspectives on Posttraumatic
... an important role in the development and treatment of posttraumatic reactions. Despite such concerns, Western biomedical models of trauma and associated interventions are increasingly exported throughout the world. According to the United Nations, there ...
... an important role in the development and treatment of posttraumatic reactions. Despite such concerns, Western biomedical models of trauma and associated interventions are increasingly exported throughout the world. According to the United Nations, there ...
Chapter 22: Mental Illness
... • Schizophrenia and the ventricle to-brain-size ratio • Other structural observation of the brains of ...
... • Schizophrenia and the ventricle to-brain-size ratio • Other structural observation of the brains of ...
ASD and pscyhosis the overlap - Royal College of Psychiatrists
... Emotional commitment to it does not separate out. ...
... Emotional commitment to it does not separate out. ...
Coping with Anxiety Disorder
... Anxiety disorders and how to cope Like many other illnesses, anxiety disorders often have an underlying biological cause and frequently run in families. These disorders can be treated by several methods, yet only about one-third of those suffering receive treatment. Without treatment, many people wi ...
... Anxiety disorders and how to cope Like many other illnesses, anxiety disorders often have an underlying biological cause and frequently run in families. These disorders can be treated by several methods, yet only about one-third of those suffering receive treatment. Without treatment, many people wi ...
-full page part 1
... With/without agoraphobia • Understand the difference between anxiety disorder and panic disorder • Can present as anger aVacks ...
... With/without agoraphobia • Understand the difference between anxiety disorder and panic disorder • Can present as anger aVacks ...
The Psychological Emotional Dimensions of Gifted
... The moods and behaviors occur only at certain times of the day, several hours after a meal or after eating certain foods The extreme emotions occur primarily when the child hild is i overly l tired ti d The extreme emotions are related to a longstanding passionate interest area for the child The emo ...
... The moods and behaviors occur only at certain times of the day, several hours after a meal or after eating certain foods The extreme emotions occur primarily when the child hild is i overly l tired ti d The extreme emotions are related to a longstanding passionate interest area for the child The emo ...
What is an Eating Disorder?
... Binge Eating Disorder (BED) This was once referred to as compulsive overeating, and is typically characterized by: 1) A larger amount of food is eaten than would normally be eaten under the circumstances (usually over 2500 calories) within about a two hour period of time. 2) Accompanying feelings of ...
... Binge Eating Disorder (BED) This was once referred to as compulsive overeating, and is typically characterized by: 1) A larger amount of food is eaten than would normally be eaten under the circumstances (usually over 2500 calories) within about a two hour period of time. 2) Accompanying feelings of ...
Co-occurring Disorders The Mix of Meds and Therapy
... Serial Treatment—treat disorder one at a time • May help empirically evaluate whether the untreated condition is resolved by treating other • Allows use of established treatment resources • Initially untreated comorbid disorder could undermine resolution of the treated disorder. • Not always clear w ...
... Serial Treatment—treat disorder one at a time • May help empirically evaluate whether the untreated condition is resolved by treating other • Allows use of established treatment resources • Initially untreated comorbid disorder could undermine resolution of the treated disorder. • Not always clear w ...
Depressive Disorders in Women
... Psychomotor agitation or retardation Recurrent thoughts of death or suicide ...
... Psychomotor agitation or retardation Recurrent thoughts of death or suicide ...
inattention and neurobehavioral disorders of
... chronological age. Their parents were retrospectively questioned on pre-, peri-, and postnatal complications and on atypical or delayed development of the children between birth and 4 years of age. This exploratory study revealed almost no differences between both groups with respect to pregnancy or ...
... chronological age. Their parents were retrospectively questioned on pre-, peri-, and postnatal complications and on atypical or delayed development of the children between birth and 4 years of age. This exploratory study revealed almost no differences between both groups with respect to pregnancy or ...
Discussion Questions
... The Center for Eating Disorders This site provides definitions, resources and the opportunity to ask questions related to eating disorders. ANRED: Anorexia Nervosa and Related Eating Disorders This is a nonprofit organization that provides information about anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, binge e ...
... The Center for Eating Disorders This site provides definitions, resources and the opportunity to ask questions related to eating disorders. ANRED: Anorexia Nervosa and Related Eating Disorders This is a nonprofit organization that provides information about anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, binge e ...
Advances in Environmental Biology
... Cardarelli [9] wrote about the psychological variables as critical and risky factors in some of the diseases that threaten mental health of human – which directly influence physical health- should the patient be deprived from social support. In the case of MS, avoiding stressful situation and effect ...
... Cardarelli [9] wrote about the psychological variables as critical and risky factors in some of the diseases that threaten mental health of human – which directly influence physical health- should the patient be deprived from social support. In the case of MS, avoiding stressful situation and effect ...
MENTAL HEALTH RESOURCES IN RICE COUNTY
... employee assistance. Depression, anxiety, Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD), job performance, panic attacks, behavior problems, stress, marital/family/other relationship difficulties, ADHD testing and treatment, learning problems, eating disorders in youth and adults, alcohol and drug use, disturb ...
... employee assistance. Depression, anxiety, Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD), job performance, panic attacks, behavior problems, stress, marital/family/other relationship difficulties, ADHD testing and treatment, learning problems, eating disorders in youth and adults, alcohol and drug use, disturb ...
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is an approach developed by
... alone and a need to have other people with them. Frantic efforts to avoid abandonment may include impulsive actions such as self-injurious or suicidal behaviors. It was originally postulated that fear of abandonment developed as a result of failures in a child’s development during the rapprochement ...
... alone and a need to have other people with them. Frantic efforts to avoid abandonment may include impulsive actions such as self-injurious or suicidal behaviors. It was originally postulated that fear of abandonment developed as a result of failures in a child’s development during the rapprochement ...
The Process and Implications of Diagnosing Oppositional Defiant
... According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5; American Psychiatric Association [APA], 2013), ODD is characterized by a pattern of behavior that includes angry and irritable mood, argumentative and defiant behavior, and/or vindictiveness. Symptoms must ...
... According to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5; American Psychiatric Association [APA], 2013), ODD is characterized by a pattern of behavior that includes angry and irritable mood, argumentative and defiant behavior, and/or vindictiveness. Symptoms must ...
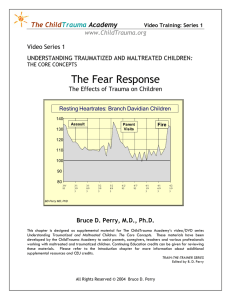
The Fear Response: The Effects of Trauma on Children
... along the arousal continuum. During the traumatic event, all aspects of individual functioning change--feeling, thinking, and behaving. Someone being assaulted doesn’t spend a lot of time thinking about the future or making an abstract plan for survival. At that moment, their feeling, thinking, and ...
... along the arousal continuum. During the traumatic event, all aspects of individual functioning change--feeling, thinking, and behaving. Someone being assaulted doesn’t spend a lot of time thinking about the future or making an abstract plan for survival. At that moment, their feeling, thinking, and ...
Major Depressive Disorder in Adults
... disorders (e.g., disruptive mood dysregulation disorder, persistent depressive disorder (dysthmymia), premenstrual dysphoric disorder, treatment resistant/induced depression), psychosis, bipolar disorder, anxiety disorders, or substance abuse disorders. ...
... disorders (e.g., disruptive mood dysregulation disorder, persistent depressive disorder (dysthmymia), premenstrual dysphoric disorder, treatment resistant/induced depression), psychosis, bipolar disorder, anxiety disorders, or substance abuse disorders. ...
How are medications used to treat mental disorders?
... Below is a summary of information about the medications most commonly used to treat major mental illness. This information is excerpted from the website of the National Institute of Mental Health. You can find more detailed information at http://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/publications/mental-health-med ...
... Below is a summary of information about the medications most commonly used to treat major mental illness. This information is excerpted from the website of the National Institute of Mental Health. You can find more detailed information at http://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/publications/mental-health-med ...
as Adobe PDF - Edinburgh Research Explorer
... risks of hospital admission for each diagnostic category per standard deviation (SD) decrease in the nine-point total IQ score and by IQ categories. Survival time in days was calculated from date of conscription to date of first hospital admission for the diagnosis being considered, date of death, d ...
... risks of hospital admission for each diagnostic category per standard deviation (SD) decrease in the nine-point total IQ score and by IQ categories. Survival time in days was calculated from date of conscription to date of first hospital admission for the diagnosis being considered, date of death, d ...
Document
... coping skills and function, probably uses this less than once a month • 2 mg “bars” have high street value • Once people have tried this, it’s really hard to get them to use something else (nothing else gets you high the same way!) • Interferes with therapy! ...
... coping skills and function, probably uses this less than once a month • 2 mg “bars” have high street value • Once people have tried this, it’s really hard to get them to use something else (nothing else gets you high the same way!) • Interferes with therapy! ...
Antisocial Personality, Sociopathy and
... Most will believe they are justified in this because they feel they were cheated in some way themselves by society, and a few will be more than happy to rant and rave about it to anyone who listens. They are chronic complainers, and underneath it all, they would like to see nothing better than all o ...
... Most will believe they are justified in this because they feel they were cheated in some way themselves by society, and a few will be more than happy to rant and rave about it to anyone who listens. They are chronic complainers, and underneath it all, they would like to see nothing better than all o ...
Dissociative identity disorder

Dissociative identity disorder (DID), previously known as multiple personality disorder (MPD), is a mental disorder on the dissociative spectrum characterized by the appearance of at least two distinct and relatively enduring identities or dissociated personality states that alternately control a person's behavior, accompanied by memory impairment for important information not explained by ordinary forgetfulness. These symptoms are not accounted for by substance abuse, seizures, other medical conditions, nor by imaginative play in children. Diagnosis is often difficult as there is considerable comorbidity with other mental disorders. Malingering should be considered if there is possible financial or forensic gain, as well as factitious disorder if help-seeking behavior is prominent.DID is one of the most controversial psychiatric disorders, with no clear consensus on diagnostic criteria or treatment. Research on treatment efficacy has been concerned primarily with clinical approaches and case studies. Dissociative symptoms range from common lapses in attention, becoming distracted by something else, and daydreaming, to pathological dissociative disorders. No systematic, empirically-supported definition of ""dissociation"" exists. It is not the same as schizophrenia.Although neither epidemiological surveys nor longitudinal studies have been conducted, it is generally believed that DID rarely resolves spontaneously. Symptoms are said to vary over time. In general, the prognosis is poor, especially for those with comorbid disorders. There are few systematic data on the prevalence of DID. The International Society for the Study of Trauma and Dissociation states that the prevalence is between 1 and 3% in the general population, and between 1 and 5% in inpatient groups in Europe and North America. DID is diagnosed more frequently in North America than in the rest of the world, and is diagnosed three to nine times more often in females than in males. The prevalence of DID diagnoses increased greatly in the latter half of the 20th century, along with the number of identities (often referred to as ""alters"") claimed by patients (increasing from an average of two or three to approximately 16). DID is also controversial within the legal system, where it has been used as a rarely successful form of the insanity defense. The 1990s showed a parallel increase in the number of court cases involving the diagnosis.Dissociative disorders including DID have been attributed to disruptions in memory caused by trauma and other forms of stress, but research on this hypothesis has been characterized by poor methodology. So far, scientific studies, usually focusing on memory, have been few and the results have been inconclusive. An alternative hypothesis for the etiology of DID is as a by-product of techniques employed by some therapists, especially those using hypnosis, and disagreement between the two positions is characterized by intense debate. DID became a popular diagnosis in the 1970s, 80s and 90s, but it is unclear if the actual rate of the disorder increased, if it was more recognized by health care providers, or if sociocultural factors caused an increase in therapy-induced (iatrogenic) presentations. The unusual number of diagnoses after 1980, clustered around a small number of clinicians and the suggestibility characteristic of those with DID, support the hypothesis that DID is therapist-induced. The unusual clustering of diagnoses has also been explained as due to a lack of awareness and training among clinicians to recognize cases of DID.