BINOMIAL distribution and applications
... to order of the objects in the subset, the result is called a combination • The number of combinations of n objects taken x at a time is given by – nCk = n! / (k! ( n-k)!) – Where k! (factorial) is the product of all numbers from k to 0 ...
... to order of the objects in the subset, the result is called a combination • The number of combinations of n objects taken x at a time is given by – nCk = n! / (k! ( n-k)!) – Where k! (factorial) is the product of all numbers from k to 0 ...
5-2 to 5-4 - El Camino College
... candies in such groups of 100. G: In a study of 420,095 cell phone users in Denmark, it was found that 135 developed cancer of the brain or nervous system. If we assume that the use of cell phones has no effect on developing such cancer, then the probability of a person having such a cancer is 0.000 ...
... candies in such groups of 100. G: In a study of 420,095 cell phone users in Denmark, it was found that 135 developed cancer of the brain or nervous system. If we assume that the use of cell phones has no effect on developing such cancer, then the probability of a person having such a cancer is 0.000 ...
solutions activity 5 - Penn State Department of Statistics
... a. Is X = music rating a discrete variable or a continuous variable? Explain. Discrete. There are a small number of distinct possible outcomes (the ratings 1-6). b. What must be the value of the probability for X = 4 (the probability that rating equals 4)? Explain how you determined this. P(x=4) is ...
... a. Is X = music rating a discrete variable or a continuous variable? Explain. Discrete. There are a small number of distinct possible outcomes (the ratings 1-6). b. What must be the value of the probability for X = 4 (the probability that rating equals 4)? Explain how you determined this. P(x=4) is ...
Winter 2009 - Queen`s Economics Department
... which is even worse! 5. (10 Marks) A manufacturer of a liquid detergent claims that the mean weight of liquid in containers sold is at least 30 ounces. It is known that the population distribution of weights is normal with standard deviation 1.3 ounces. In order to check the manufacturer’s claim, a ...
... which is even worse! 5. (10 Marks) A manufacturer of a liquid detergent claims that the mean weight of liquid in containers sold is at least 30 ounces. It is known that the population distribution of weights is normal with standard deviation 1.3 ounces. In order to check the manufacturer’s claim, a ...
Statistics
... Typical Problem • Repeated counts are made in 1min intervals with a long-lived source. The observed mean is 813 counts with s = 28.5 counts. What is the probability of observing 800 or fewer counts? Answer • This is about -0.45s. • Look up P((x-m)/s < -0.45) – P = 0.324 ...
... Typical Problem • Repeated counts are made in 1min intervals with a long-lived source. The observed mean is 813 counts with s = 28.5 counts. What is the probability of observing 800 or fewer counts? Answer • This is about -0.45s. • Look up P((x-m)/s < -0.45) – P = 0.324 ...
X - Physics
... N: value of quantity measured (or determined) by experiment. XX: statistical error, usually assumed to be from a Gaussian distribution. With the assumption of Gaussian statistics we can say (calculate) something about how well our experiment agrees with other experiments and/or theories. Expect ~ 68 ...
... N: value of quantity measured (or determined) by experiment. XX: statistical error, usually assumed to be from a Gaussian distribution. With the assumption of Gaussian statistics we can say (calculate) something about how well our experiment agrees with other experiments and/or theories. Expect ~ 68 ...
Wave
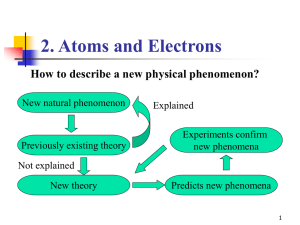
... Fortunately, the strange rules of quantum physics affect only very small objects, such as individual atoms and electrons. As soon as we have a macroscopic object consisting of many atoms, an experiment becomes more predictable. Typically, a macroscopic object consists of 1024 atoms (Avogadro’s numb ...
... Fortunately, the strange rules of quantum physics affect only very small objects, such as individual atoms and electrons. As soon as we have a macroscopic object consisting of many atoms, an experiment becomes more predictable. Typically, a macroscopic object consists of 1024 atoms (Avogadro’s numb ...
Lesson 18 Nov IV
... One other pearl of wisdom – You could always compute mu (μ) and sigma (σ) using the 1-var stat L1, L2 computation on the calculator {providing you have the distribution in L1 and L2} ...
... One other pearl of wisdom – You could always compute mu (μ) and sigma (σ) using the 1-var stat L1, L2 computation on the calculator {providing you have the distribution in L1 and L2} ...
Homework No. 01 (Fall 2013) PHYS 530B: Quantum Mechanics II
... δθ when a beam of such atoms passes through a slit of width 10−2 cm. (See Fig. 3.3 in Milton’s notes and discussion of Eq. (3.26) there.) Compare this diffraction angle with the deflection angle produced in a Stern-Gerlach experiment. 4. (Ref: Milton’s notes.) Using the notation for the probability ...
... δθ when a beam of such atoms passes through a slit of width 10−2 cm. (See Fig. 3.3 in Milton’s notes and discussion of Eq. (3.26) there.) Compare this diffraction angle with the deflection angle produced in a Stern-Gerlach experiment. 4. (Ref: Milton’s notes.) Using the notation for the probability ...
headingE2170: Polarization of two-spheres system inside a tube The problem:
... (a) Write the hamiltonian of the system H (p1 , p2 , x1 , x2 ) = Ek + V (x) when Ek is the kinetic energy. Define properly V (x) when x = x2 − x1 an–d write a diagram of V (x). (b) Calculate the partition function Z (β, ε). (c) Find the probability function of x, ρ (x) and the average distance hxi b ...
... (a) Write the hamiltonian of the system H (p1 , p2 , x1 , x2 ) = Ek + V (x) when Ek is the kinetic energy. Define properly V (x) when x = x2 − x1 an–d write a diagram of V (x). (b) Calculate the partition function Z (β, ε). (c) Find the probability function of x, ρ (x) and the average distance hxi b ...
Probability amplitude

In quantum mechanics, a probability amplitude is a complex number used in describing the behaviour of systems. The modulus squared of this quantity represents a probability or probability density.Probability amplitudes provide a relationship between the wave function (or, more generally, of a quantum state vector) of a system and the results of observations of that system, a link first proposed by Max Born. Interpretation of values of a wave function as the probability amplitude is a pillar of the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics. In fact, the properties of the space of wave functions were being used to make physical predictions (such as emissions from atoms being at certain discrete energies) before any physical interpretation of a particular function was offered. Born was awarded half of the 1954 Nobel Prize in Physics for this understanding (see #References), and the probability thus calculated is sometimes called the ""Born probability"". These probabilistic concepts, namely the probability density and quantum measurements, were vigorously contested at the time by the original physicists working on the theory, such as Schrödinger and Einstein. It is the source of the mysterious consequences and philosophical difficulties in the interpretations of quantum mechanics—topics that continue to be debated even today.