Quantum Field Theory
... Negative energy electrons can be excited into a positive energy state (by a photon) leaving behind a hole in the sea of negative energy electrons. The hole has a positive ...
... Negative energy electrons can be excited into a positive energy state (by a photon) leaving behind a hole in the sea of negative energy electrons. The hole has a positive ...
Lecture 25: Wave mechanics
... location of this electron wave we must develop an equation like Newton’s force =ma equation. How can we use Bohr’s picture to define the electron as a wave in it’s own orbit? ...
... location of this electron wave we must develop an equation like Newton’s force =ma equation. How can we use Bohr’s picture to define the electron as a wave in it’s own orbit? ...
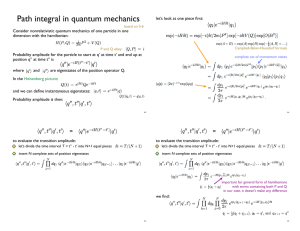
Path integral in quantum mechanics
... Finally, if perturbing hamiltonian depends only on q, and we want to ...
... Finally, if perturbing hamiltonian depends only on q, and we want to ...
Electrons in Atoms
... where exactly an electron is at any given moment, it is actually in all possible states simultaneously, as long as we don't look to check. It is the measurement itself that causes the object to be limited to a single possibility. ...
... where exactly an electron is at any given moment, it is actually in all possible states simultaneously, as long as we don't look to check. It is the measurement itself that causes the object to be limited to a single possibility. ...
Basics of wave functions - Department of Physics | Oregon State
... Quantum Mechanics – kets and operators The state of electron is represented by a quantity called a state vector or a ket, y , which in general is a function of many variables, including time. In PH425, you learned about kets that contained information about a particle’s spin state. We’ll be interest ...
... Quantum Mechanics – kets and operators The state of electron is represented by a quantity called a state vector or a ket, y , which in general is a function of many variables, including time. In PH425, you learned about kets that contained information about a particle’s spin state. We’ll be interest ...
Photon localizability - Current research interest: photon position
... space in nonzero. Due to interference there exists a single instant when QM says that the photon can be detected at only one place. But this is just familiar spooky quantum mechanics, and I think the effect is physically real. ...
... space in nonzero. Due to interference there exists a single instant when QM says that the photon can be detected at only one place. But this is just familiar spooky quantum mechanics, and I think the effect is physically real. ...
Axioms of Quantum Mechanics
... system, while the second to observables. The state gives a complete description of the set of probabilities for all observables, while these last ones are all dynamical variables that in principle can be measured. All the information is contained in the state, irrespectively on how I got the state, ...
... system, while the second to observables. The state gives a complete description of the set of probabilities for all observables, while these last ones are all dynamical variables that in principle can be measured. All the information is contained in the state, irrespectively on how I got the state, ...
poster
... P. Grangier, et al., Experimental Evidence for a Photon Anticorrelation Effect on a Beam Splitter: A New Light on Single-Photon ...
... P. Grangier, et al., Experimental Evidence for a Photon Anticorrelation Effect on a Beam Splitter: A New Light on Single-Photon ...
Probability amplitude

In quantum mechanics, a probability amplitude is a complex number used in describing the behaviour of systems. The modulus squared of this quantity represents a probability or probability density.Probability amplitudes provide a relationship between the wave function (or, more generally, of a quantum state vector) of a system and the results of observations of that system, a link first proposed by Max Born. Interpretation of values of a wave function as the probability amplitude is a pillar of the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum mechanics. In fact, the properties of the space of wave functions were being used to make physical predictions (such as emissions from atoms being at certain discrete energies) before any physical interpretation of a particular function was offered. Born was awarded half of the 1954 Nobel Prize in Physics for this understanding (see #References), and the probability thus calculated is sometimes called the ""Born probability"". These probabilistic concepts, namely the probability density and quantum measurements, were vigorously contested at the time by the original physicists working on the theory, such as Schrödinger and Einstein. It is the source of the mysterious consequences and philosophical difficulties in the interpretations of quantum mechanics—topics that continue to be debated even today.