Introduction to JSON (JavaScript Object Notation)
... • Lighter and faster than XML as on-the-wire data format • JSON objects are typed while XML data is typeless > JSON types: string, number, array, boolean, > XML data are all string ...
... • Lighter and faster than XML as on-the-wire data format • JSON objects are typed while XML data is typeless > JSON types: string, number, array, boolean, > XML data are all string ...
Constructor Methods
... Encapsulation increases reliability tremendously. In this chapter no attempt will be made to explain polymorphism and inheritance. Both polymorphism and inheritance are important programming tools in the goal to design reliable programs. How this is done will be explained in future chapters and cour ...
... Encapsulation increases reliability tremendously. In this chapter no attempt will be made to explain polymorphism and inheritance. Both polymorphism and inheritance are important programming tools in the goal to design reliable programs. How this is done will be explained in future chapters and cour ...
Object Oriented Programming
... Summary • Object-oriented Programming (OOP) is a methodology of programming where new types of objects are defined • An object is a single software unit that combines attributes and methods • An attribute is a “characteristic” of an object; it’s a variable associated with an object (“instance varia ...
... Summary • Object-oriented Programming (OOP) is a methodology of programming where new types of objects are defined • An object is a single software unit that combines attributes and methods • An attribute is a “characteristic” of an object; it’s a variable associated with an object (“instance varia ...
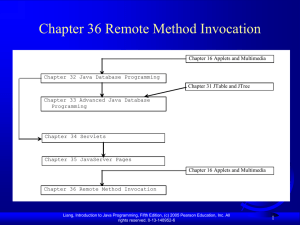
Chapter 18 Networking
... RMI enables you to program at a higher level of abstraction. It hides the details of socket server, socket, connection, and sending or receiving data. It even implements a multithreading server under the hood, whereas with socket-level programming you have to explicitly implement threads for handlin ...
... RMI enables you to program at a higher level of abstraction. It hides the details of socket server, socket, connection, and sending or receiving data. It even implements a multithreading server under the hood, whereas with socket-level programming you have to explicitly implement threads for handlin ...
Objectives
... Local object type. A parameter of local object type such as java.lang.String is also passed by value. This is completely different from passing object parameter in a local call. In a local call, an object parameter is passed by reference, which corresponds to the memory address of the object. In a r ...
... Local object type. A parameter of local object type such as java.lang.String is also passed by value. This is completely different from passing object parameter in a local call. In a local call, an object parameter is passed by reference, which corresponds to the memory address of the object. In a r ...
Chapter 18 Networking
... RMI enables you to program at a higher level of abstraction. It hides the details of socket server, socket, connection, and sending or receiving data. It even implements a multithreading server under the hood, whereas with socket-level programming you have to explicitly implement threads for handlin ...
... RMI enables you to program at a higher level of abstraction. It hides the details of socket server, socket, connection, and sending or receiving data. It even implements a multithreading server under the hood, whereas with socket-level programming you have to explicitly implement threads for handlin ...
43slide - SIUE Computer Science
... RMI enables you to program at a higher level of abstraction. It hides the details of socket server, socket, connection, and sending or receiving data. It even implements a multithreading server under the hood, whereas with socket-level programming you have to explicitly implement threads for handlin ...
... RMI enables you to program at a higher level of abstraction. It hides the details of socket server, socket, connection, and sending or receiving data. It even implements a multithreading server under the hood, whereas with socket-level programming you have to explicitly implement threads for handlin ...
Chapter 19 Java Data Structures
... Two unequal objects may have the same hash code. but you must implement the hashCode method to avoid too many such cases. Additionally, it is required that invoking the hasCode method multiple times returns the same integer during one execution of the program Y.Daniel Liang Introduction to Java Prog ...
... Two unequal objects may have the same hash code. but you must implement the hashCode method to avoid too many such cases. Additionally, it is required that invoking the hasCode method multiple times returns the same integer during one execution of the program Y.Daniel Liang Introduction to Java Prog ...
1 Introduction
... explicitly changeable state. Objects posses value semantics, they are immutable values like the notions in mathematics. This property opens ways to discuss formally the properties of programs and even sometimes makes the properties of programs provable. From the engineer's point of view the lack of ...
... explicitly changeable state. Objects posses value semantics, they are immutable values like the notions in mathematics. This property opens ways to discuss formally the properties of programs and even sometimes makes the properties of programs provable. From the engineer's point of view the lack of ...
What`s in store in CS1101?
... Objects of the same class have the same fields/attributes. But each object may have it own set of values for its attributes. State of circle1 object. ...
... Objects of the same class have the same fields/attributes. But each object may have it own set of values for its attributes. State of circle1 object. ...
Bibliography on OOAD
... These two books are a great introduction to Java for C and C++ programmers. They give excellent examples of good Java usage. This book is much less negative about other languages than most of the books written by people from Sun. David Flanagan, Java in a Nutshell, second edition, O’Reilly & Associa ...
... These two books are a great introduction to Java for C and C++ programmers. They give excellent examples of good Java usage. This book is much less negative about other languages than most of the books written by people from Sun. David Flanagan, Java in a Nutshell, second edition, O’Reilly & Associa ...
Programming - NC FRC Teams wiki
... Object Oriented – Class and Instance An object bundles data (attributes) and code to perform actions (methods) into one, cohesive unit Class ...
... Object Oriented – Class and Instance An object bundles data (attributes) and code to perform actions (methods) into one, cohesive unit Class ...
Slide 20 - Ursinus College Student, Faculty and Staff Web Pages
... 2 O-O Identity, Object Structure and Type Constructors 3 Encapsulation of Operations, Methods and ...
... 2 O-O Identity, Object Structure and Type Constructors 3 Encapsulation of Operations, Methods and ...
cse142-15-Abstract - University of Washington
... that is common to a group of subclasses • The subclasses differ in some way from the superclass and from each other, and yet they share some characteristics • So we have the notion of common or shared characteristics and unique or non-shared characteristics 31-July-2002 ...
... that is common to a group of subclasses • The subclasses differ in some way from the superclass and from each other, and yet they share some characteristics • So we have the notion of common or shared characteristics and unique or non-shared characteristics 31-July-2002 ...
View
... The expression blank.x means, "Go to the object blank refers to and get the value of x." In this case, we assign that value to a variable named x. There is no conflict between the variable x and the attribute x. The purpose of dot notation is to identify which variable you are referring to unambiguo ...
... The expression blank.x means, "Go to the object blank refers to and get the value of x." In this case, we assign that value to a variable named x. There is no conflict between the variable x and the attribute x. The purpose of dot notation is to identify which variable you are referring to unambiguo ...
Object Oriented Programming
... represents an instance of the counter type; a counter object. We can now communicate with this object by calling it's methods, for example we can set the counter to the value '50' by calling i.InitialiseCounter(50);. We can increment the counter - i.IncrementCounter(); and we can get the counter val ...
... represents an instance of the counter type; a counter object. We can now communicate with this object by calling it's methods, for example we can set the counter to the value '50' by calling i.InitialiseCounter(50);. We can increment the counter - i.IncrementCounter(); and we can get the counter val ...
Lecture 06 Java Coll..
... object-oriented languages like Java, these interfaces generally form a hierarchy. Implementations: concrete implementations of the collection interfaces. In essence, these are reusable data structures. Algorithms: methods that perform useful computations, like searching and sorting, on objects that ...
... object-oriented languages like Java, these interfaces generally form a hierarchy. Implementations: concrete implementations of the collection interfaces. In essence, these are reusable data structures. Algorithms: methods that perform useful computations, like searching and sorting, on objects that ...
Chapter 6 Objects and Classes
... special kind of methods that are Circle() { radius = 1.0; invoked to construct objects. ...
... special kind of methods that are Circle() { radius = 1.0; invoked to construct objects. ...
Arrays
... Location if find the key (positive number) (-(insertion point) - 1) if not find key (negative) ...
... Location if find the key (positive number) (-(insertion point) - 1) if not find key (negative) ...