Atomic arrangment
... Diamond cubic structure Elements such as silicon, germanium and carbon in its diamond form are bonded by four covalent bonds and produce a tetrahedron This lattice can be describes as an FCC lattice with two atoms associated with each lattice point or two FCC structures that are shifted by ¼ main ...
... Diamond cubic structure Elements such as silicon, germanium and carbon in its diamond form are bonded by four covalent bonds and produce a tetrahedron This lattice can be describes as an FCC lattice with two atoms associated with each lattice point or two FCC structures that are shifted by ¼ main ...
Module 4: Light Emitting Diodes
... semiconductor devices. It has been coined as the isoelectronic impurity since it comes from column V in the periodic table of elements and therefore has five valence electrons, as do arsenic and phosphorous that it replaces in the crystal. As a consequence, nitrogen, unlike a donor or acceptor, intr ...
... semiconductor devices. It has been coined as the isoelectronic impurity since it comes from column V in the periodic table of elements and therefore has five valence electrons, as do arsenic and phosphorous that it replaces in the crystal. As a consequence, nitrogen, unlike a donor or acceptor, intr ...
Similarities in the electrical properties of transition metal–hydrogen
... concentration depth profiles with Eq. (1) can be formed for the various complexes and provide an estimate of the number of H atoms. This means for platinum (Fig. 3) that E(250) has the largest penetration depth and is therefore assigned to a complex with only one hydrogen atom. E(90) and H(210) exhi ...
... concentration depth profiles with Eq. (1) can be formed for the various complexes and provide an estimate of the number of H atoms. This means for platinum (Fig. 3) that E(250) has the largest penetration depth and is therefore assigned to a complex with only one hydrogen atom. E(90) and H(210) exhi ...
What is a Mineral?
... Here, the Li atom loses an electron to become a + positively charged cation. The F atom gains an electron to become a negatively charged anion. Positive and negative charges attract each other to form an IONIC BOND N. Lindsley-Griffin, 1999 ...
... Here, the Li atom loses an electron to become a + positively charged cation. The F atom gains an electron to become a negatively charged anion. Positive and negative charges attract each other to form an IONIC BOND N. Lindsley-Griffin, 1999 ...
The effect of EWG and EDG on the HOMO and LUMO of Alq3.
... Figure 2 shows the absorption spectra for the three Alq3 samples dissolved in DCM. The spectrum of Alq3 is dominated by an intense absorption band at ~380 nm. In addition to this intense band, there are 2 weak absorption bands at ~320 and ~330 nm. The broad band at 380 nm is reported to be a ligand ...
... Figure 2 shows the absorption spectra for the three Alq3 samples dissolved in DCM. The spectrum of Alq3 is dominated by an intense absorption band at ~380 nm. In addition to this intense band, there are 2 weak absorption bands at ~320 and ~330 nm. The broad band at 380 nm is reported to be a ligand ...
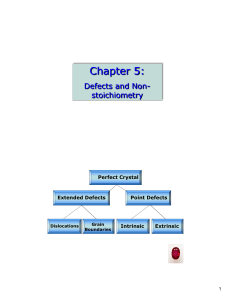
Crystallographic defects in diamond
Imperfections in the crystal lattice of diamond are common. Such crystallographic defects in diamond may be the result of lattice irregularities or extrinsic substitutional or interstitial impurities, introduced during or after the diamond growth. They affect the material properties of diamond and determine to which type a diamond is assigned; the most dramatic effects are on the diamond color and electrical conductivity, as explained by the band theory.The defects can be detected by different types of spectroscopy, including electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR), luminescence induced by light (photoluminescence, PL) or electron beam (cathodoluminescence, CL), and absorption of light in the infrared (IR), visible and UV parts of the spectrum. Absorption spectrum is used not only to identify the defects, but also to estimate their concentration; it can also distinguish natural from synthetic or enhanced diamonds.