Red Giants - Faculty Web Pages
... Most blue stars are Main Sequence stars. But whereas some red stars in the list are simply tiny, cool Main Sequence stars, other red stars of the exact same color are huge Red Giants! Telling the difference between the Main Sequence red stars and the Red Giant stars involves some complex measurement ...
... Most blue stars are Main Sequence stars. But whereas some red stars in the list are simply tiny, cool Main Sequence stars, other red stars of the exact same color are huge Red Giants! Telling the difference between the Main Sequence red stars and the Red Giant stars involves some complex measurement ...
Slide 1
... The naked eye, upon optimum conditions, can see down to around the sixth magnitude, that is +6. Under Pogson's system, a few of the brighter stars now have negative magnitudes. For example, Sirius is –1.5. The lower the magnitude number, the brighter the object. The full moon has a magnitude of abou ...
... The naked eye, upon optimum conditions, can see down to around the sixth magnitude, that is +6. Under Pogson's system, a few of the brighter stars now have negative magnitudes. For example, Sirius is –1.5. The lower the magnitude number, the brighter the object. The full moon has a magnitude of abou ...
Slides from Dr. Frank`s Lecture17
... 1) The binary separation decreases because of gravitational radiation and other angular momentum losses. 2) The component stars will evolve and change size (for example becoming a red giant) Conclusion: Long period (wide) binaries may never become interacting while short period (close) binaries are ...
... 1) The binary separation decreases because of gravitational radiation and other angular momentum losses. 2) The component stars will evolve and change size (for example becoming a red giant) Conclusion: Long period (wide) binaries may never become interacting while short period (close) binaries are ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... The diameter of Alpha Centauri A is 1.71 x 109 meters. The Sun’s diameter is 1.39 x 109 meters as determined from the table in the text’s appendix. Thus, Alpha Centauri A is slightly larger than the Sun with a diameter of 1.23 solar diameters. Alpha Centauri B is (60/85) = 0.706 times smaller than A ...
... The diameter of Alpha Centauri A is 1.71 x 109 meters. The Sun’s diameter is 1.39 x 109 meters as determined from the table in the text’s appendix. Thus, Alpha Centauri A is slightly larger than the Sun with a diameter of 1.23 solar diameters. Alpha Centauri B is (60/85) = 0.706 times smaller than A ...
Chapter 17 Measuring the Stars
... diagram, a pattern begins to form: These are the 80 closest stars to us; note the dashed lines of constant radius. The darkened curve is called the main sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but not very luminous, as they are quite s ...
... diagram, a pattern begins to form: These are the 80 closest stars to us; note the dashed lines of constant radius. The darkened curve is called the main sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but not very luminous, as they are quite s ...
Slide 1
... Stellar spectra are much more informative than the blackbody curves. There are seven general categories of stellar spectra, corresponding to different ...
... Stellar spectra are much more informative than the blackbody curves. There are seven general categories of stellar spectra, corresponding to different ...
17_LectureOutline
... Stellar spectra are much more informative than the blackbody curves. There are seven general categories of stellar spectra, corresponding to different ...
... Stellar spectra are much more informative than the blackbody curves. There are seven general categories of stellar spectra, corresponding to different ...
Stars
... planets. Doppler shift measurements are usually done on spectral lines. • Essentially all of the mass measurements that we have for stars are for stars in binary systems – two stars orbiting each other. • The mass of the stars can be measured from their velocities and the distance between the stars. ...
... planets. Doppler shift measurements are usually done on spectral lines. • Essentially all of the mass measurements that we have for stars are for stars in binary systems – two stars orbiting each other. • The mass of the stars can be measured from their velocities and the distance between the stars. ...
epsilon Aur
... especially when it is low in the sky. At maximum, Epsilon Aurigae is close in brightness to nearby Eta Aurigae, but does sometimes show small semi-regular fluctuations of 0.1-0.2 magnitudes - it is not clear as to whether it is the supergiant star or the secondary object that is responsible for thes ...
... especially when it is low in the sky. At maximum, Epsilon Aurigae is close in brightness to nearby Eta Aurigae, but does sometimes show small semi-regular fluctuations of 0.1-0.2 magnitudes - it is not clear as to whether it is the supergiant star or the secondary object that is responsible for thes ...
Ch. 17 (RGs & WDs)
... independently discover the proper way to relate stellar properties in order to plot stars on one graph. The two properties they chose to use are stellar temperature and magnitude Remember they are trying to understand stars while not yet really knowing how they work! It’s 1926 when Eddington propose ...
... independently discover the proper way to relate stellar properties in order to plot stars on one graph. The two properties they chose to use are stellar temperature and magnitude Remember they are trying to understand stars while not yet really knowing how they work! It’s 1926 when Eddington propose ...
The Stars: Distance, Luminosity, Size
... 1) the stars were further away. 2) Earth's orbit were larger. 3) Earth moved backwards along its orbit. 4) none of these. ...
... 1) the stars were further away. 2) Earth's orbit were larger. 3) Earth moved backwards along its orbit. 4) none of these. ...
Shining Light on the Stars: The Hertzsprung-Russell
... At the turn of the last century, two astronomers, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell, realized independently that if you plotted the luminosity of stars versus their temperatures on a graph, the stars didn’t fall in random places, but instead grouped together, forming curious patterns. These ...
... At the turn of the last century, two astronomers, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell, realized independently that if you plotted the luminosity of stars versus their temperatures on a graph, the stars didn’t fall in random places, but instead grouped together, forming curious patterns. These ...
BAS Visit to the Norman Lockyer Observatory, October 2015
... Mira variables. There are between 6,000 to 7,000 known stars belonging to this group. They are all red giants whose surfaces oscillate in such a way as to cause variations in brightness over periods ranging from 80 to 1,000 days. Mira was the first non-supernova variable star discovered, and is beli ...
... Mira variables. There are between 6,000 to 7,000 known stars belonging to this group. They are all red giants whose surfaces oscillate in such a way as to cause variations in brightness over periods ranging from 80 to 1,000 days. Mira was the first non-supernova variable star discovered, and is beli ...
Name: pd: ______ Date: Constellation Scavenger Hunt! Google Sky
... - Find the constellation Orion & name the stars in Orion’s Belt a) ____________________________________________ b) ____________________________________________ c) ____________________________________________ 3. If you click on the stars and read the information windows for each, you will find two of ...
... - Find the constellation Orion & name the stars in Orion’s Belt a) ____________________________________________ b) ____________________________________________ c) ____________________________________________ 3. If you click on the stars and read the information windows for each, you will find two of ...
ASTR100 Class 01 - University of Maryland Department of
... Two stars have the same surface temperature but different luminosities. How can that be? Answer: one is bigger than the other! Why? Thermal radiation law: objects at a given temperature emit a certain luminosity per unit surface area. Hence the more luminous star has a larger surface area, ...
... Two stars have the same surface temperature but different luminosities. How can that be? Answer: one is bigger than the other! Why? Thermal radiation law: objects at a given temperature emit a certain luminosity per unit surface area. Hence the more luminous star has a larger surface area, ...
Where to begin the adventure with variable stars?
... stars. In a dark sky they are visible with the naked eye but it is a good idea to use a finderscope. These two stars form a triangle with the star HIP 52469. ...
... stars. In a dark sky they are visible with the naked eye but it is a good idea to use a finderscope. These two stars form a triangle with the star HIP 52469. ...
Star luminosity info and HR diagram
... from us, from several light-years to over 1,000 lightyears. Telescopes show the light of stars millions or billions of light-years away. Today, when we talk about a star’s brightness, we might mean one of two things: its intrinsic brightness or its apparent brightness. When astronomers speak of the ...
... from us, from several light-years to over 1,000 lightyears. Telescopes show the light of stars millions or billions of light-years away. Today, when we talk about a star’s brightness, we might mean one of two things: its intrinsic brightness or its apparent brightness. When astronomers speak of the ...
Star Maps and Constellations (pdf 3.7 Megs)
... Stars are not all the same brightness. The Greek astronomer Hipparchus (160-127 B.C.) invented the scheme of classifying stars by their brightness where the brightest were first magnitude, the next brightest second magnitude, and the faintest visible stars were sixth magnitude. ...
... Stars are not all the same brightness. The Greek astronomer Hipparchus (160-127 B.C.) invented the scheme of classifying stars by their brightness where the brightest were first magnitude, the next brightest second magnitude, and the faintest visible stars were sixth magnitude. ...
Orion - Starry Starry Night!
... Taurus Taurus is a large and prominent constellation in the northern hemisphere's winter sky. It is one of the oldest constellations, dating back to at least the Early Bronze Age when it marked the location of the Sun during the spring equinox. Taurus hosts two of the nearest open clusters to Earth ...
... Taurus Taurus is a large and prominent constellation in the northern hemisphere's winter sky. It is one of the oldest constellations, dating back to at least the Early Bronze Age when it marked the location of the Sun during the spring equinox. Taurus hosts two of the nearest open clusters to Earth ...
Crux The Southern Cross
... outer atmosphere. This abundance of free carbon is responsible for their deep red colour. Binoculars do not give enough magnification to resolve it from a very bright neighbour in Mimosa. You can see this star in a small Mimosa with Ruby Crucis selected telescope. However you need a 200 - 300mm refl ...
... outer atmosphere. This abundance of free carbon is responsible for their deep red colour. Binoculars do not give enough magnification to resolve it from a very bright neighbour in Mimosa. You can see this star in a small Mimosa with Ruby Crucis selected telescope. However you need a 200 - 300mm refl ...
Rogava_Course_-_First_lecture
... • Mizar A was the very first spectroscopic binary: in 1889 Edward PIckering found that it is a binary star.This binary is 35 times brigter than the Sun. • Orbital period ~20 days. • There exist double-lined (SB2) and single-lined (SB1) spectroscopic binaries. • Famous SB1 - Cygnus X-1 System. ...
... • Mizar A was the very first spectroscopic binary: in 1889 Edward PIckering found that it is a binary star.This binary is 35 times brigter than the Sun. • Orbital period ~20 days. • There exist double-lined (SB2) and single-lined (SB1) spectroscopic binaries. • Famous SB1 - Cygnus X-1 System. ...
Why Study Binary Stars?
... 1 & 2 are Mizar A & B a “Visual Binary” at 78ly=24pc 3 Alcor distance 81±1 ly =25pc Same proper motion so “Visual Binary” with Mizar 4 Sidus Ludoviciana is at a distance of 600ly =180pc so a chance superposition “Optical Double” ...
... 1 & 2 are Mizar A & B a “Visual Binary” at 78ly=24pc 3 Alcor distance 81±1 ly =25pc Same proper motion so “Visual Binary” with Mizar 4 Sidus Ludoviciana is at a distance of 600ly =180pc so a chance superposition “Optical Double” ...
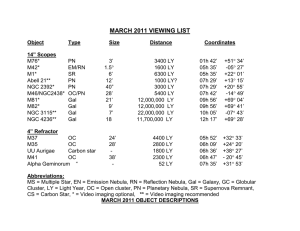
March
... sky. The expanding gas cloud is the result of an exploding star observed in 1054 A.D. At it’s brightest it was four times brighter than Venus and was a visible daylight object for 23 days. The gaseous shell is about 10 light years in diameter and is still expanding outward at the high rate of 1800 k ...
... sky. The expanding gas cloud is the result of an exploding star observed in 1054 A.D. At it’s brightest it was four times brighter than Venus and was a visible daylight object for 23 days. The gaseous shell is about 10 light years in diameter and is still expanding outward at the high rate of 1800 k ...
Capella

Capella is the brightest star in the constellation Auriga, the sixth brightest in the night sky and the third brightest in the northern celestial hemisphere, after Arcturus and Vega. Its name is derived from the diminutive of the Latin capra ""goat"", hence ""little goat"". Capella also bears the Bayer designation Alpha Aurigae (often abbreviated to α Aurigae, α Aur or Alpha Aur). Although it appears to be a single star to the naked eye, it is actually a star system of four stars in two binary pairs. The first pair consists of two bright, large type-G giant stars, both with a radius around 10 times that of the Sun and two and a half times its mass, in close orbit around each other. Designated Capella Aa and Capella Ab, these two stars have both exhausted their core hydrogen fuel and become giant stars, though it is unclear exactly what stage they are on the stellar evolutionary pathway. The second pair, around 10,000 astronomical units from the first, consists of two faint, small and relatively cool red dwarfs. They are designated Capella H and Capella L. The stars labelled Capella C through to G and I through to K are actually unrelated stars in the same visual field. The Capella system is relatively close, at only 42.8 light-years (13.1 pc) from Earth.