Hypersensitivity type I
... a)toxic contaminant b)pharmacologic active component or to characteristics of the host a)metabolic disorders b)idiosyncratic responses c)Psychological disorder **** they may not be reproducible *** they are often dose dependent. Food allergy refers to an abnormal immunologic response to a food tha ...
... a)toxic contaminant b)pharmacologic active component or to characteristics of the host a)metabolic disorders b)idiosyncratic responses c)Psychological disorder **** they may not be reproducible *** they are often dose dependent. Food allergy refers to an abnormal immunologic response to a food tha ...
Food intolerance - Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and
... are describing food intolerance, rather than food allergy. During an allergic reaction to food, many irritant chemicals (such as histamine) are released into the tissues. This can result in itchy rashes, stomach upset, cough and wheeze and the more severe allergic symptoms (anaphylaxis). These react ...
... are describing food intolerance, rather than food allergy. During an allergic reaction to food, many irritant chemicals (such as histamine) are released into the tissues. This can result in itchy rashes, stomach upset, cough and wheeze and the more severe allergic symptoms (anaphylaxis). These react ...
4.02 Special Diets
... An intolerance usually is a less serious digestive problem and may include: ...
... An intolerance usually is a less serious digestive problem and may include: ...
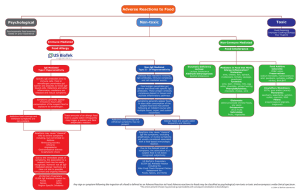
Adverse Reactions to Food Non-toxic Psychological Toxic
... Reactions may cause "classical" IgE-like symptoms, excluding anaphylaxis, or involve symptoms not usually considered associated with a food-based immunologic reaction. Due to the delayed onset of symptoms, the association to a suspect food is not easily recognized subjectively. US BioTek's Proprieta ...
... Reactions may cause "classical" IgE-like symptoms, excluding anaphylaxis, or involve symptoms not usually considered associated with a food-based immunologic reaction. Due to the delayed onset of symptoms, the association to a suspect food is not easily recognized subjectively. US BioTek's Proprieta ...
"Food Allergy Versus Food Intolerance"
... A food allergic reaction involves the immune system. Your immune system controls how your body defends itself. For instance, if you have an allergy to cow’s milk, your immune system identifies cow’s milk as an invader or allergen. Your immune system overreacts by ...
... A food allergic reaction involves the immune system. Your immune system controls how your body defends itself. For instance, if you have an allergy to cow’s milk, your immune system identifies cow’s milk as an invader or allergen. Your immune system overreacts by ...