Marx`s Democratic Critique of Capitalism and Its Implications for a
... As we all know, Marx's powerful and compelling critique of capitalism provided no explicit model for a viable alternative to capitalism, no "recipes for cookshops of the future," in his disdainful phrase.1 Marx shouldn’t be faulted for this omission. He was a "scientific" socialist. Although there w ...
... As we all know, Marx's powerful and compelling critique of capitalism provided no explicit model for a viable alternative to capitalism, no "recipes for cookshops of the future," in his disdainful phrase.1 Marx shouldn’t be faulted for this omission. He was a "scientific" socialist. Although there w ...
capitalism - worldhistorynulty
... lead to economic equality but instead led to the exploitation of workers and the concentration of wealth in the industrial capitalists. Those factors led to the utopian socialist movements in France and Great Britain during the early 19th century. For example, Henri de Saint-Simon believed that the ...
... lead to economic equality but instead led to the exploitation of workers and the concentration of wealth in the industrial capitalists. Those factors led to the utopian socialist movements in France and Great Britain during the early 19th century. For example, Henri de Saint-Simon believed that the ...
The Prosperity of Economies and the Poverty of Economics: Why
... Resources tend to be automatically allocated to their highest value-creating uses because it is in the selfinterest of their owners to find those uses. This system of natural liberty thus provides the fertile environment for the automatic development of an extended division of labor that results in ...
... Resources tend to be automatically allocated to their highest value-creating uses because it is in the selfinterest of their owners to find those uses. This system of natural liberty thus provides the fertile environment for the automatic development of an extended division of labor that results in ...
Development and Regionalism Karl Polanyi’s Ideas and the Contemporary World System
... countries showed an extraordinary growth in the contribution of financial services to GDP. In some developing countries this financialisation equalled or surpassed the contribution of manufacturing, reflecting the rewards to holders of government debt and other financial assets. This financialisati ...
... countries showed an extraordinary growth in the contribution of financial services to GDP. In some developing countries this financialisation equalled or surpassed the contribution of manufacturing, reflecting the rewards to holders of government debt and other financial assets. This financialisati ...
By Jeffrey Hatcher
... The political scene was also booming: The Second Boer War was coming to an end in 1902. It started in 1899, when waves of Boers migrated away from the Cape Colony, which was ruled by Britain. The United Kingdom and France signed the Entente Cordiale, intended to end the almost millennium-year-old co ...
... The political scene was also booming: The Second Boer War was coming to an end in 1902. It started in 1899, when waves of Boers migrated away from the Cape Colony, which was ruled by Britain. The United Kingdom and France signed the Entente Cordiale, intended to end the almost millennium-year-old co ...
CCFF Bargainng Update
... chemists, including [Justus von] Liebig, and applied it to socio-ecological relations. All life is based on metabolic processes between organisms and their environment. Organisms carry out an exchange of energy and matter with their environment, which are integrated with their own internal life proc ...
... chemists, including [Justus von] Liebig, and applied it to socio-ecological relations. All life is based on metabolic processes between organisms and their environment. Organisms carry out an exchange of energy and matter with their environment, which are integrated with their own internal life proc ...
How to End Poverty
... school” of economics of Adam Smith and David Ricardo, he was well aware that increasing capital accumulation is necessary for increasing industrial growth. And he readily agreed with the classical economists that as capital (machinery) increases, the result will be more and more production of more a ...
... school” of economics of Adam Smith and David Ricardo, he was well aware that increasing capital accumulation is necessary for increasing industrial growth. And he readily agreed with the classical economists that as capital (machinery) increases, the result will be more and more production of more a ...
Requests for Information PUB 22.3 NP Q.
... The net present value analysis associated with improvements to the MRO inventory processes is provided in Attachment A. The estimated labour cost savings, due to a reduction in employees purchasing materials on an ad hoc basis, is $37,950 per year, based on 2004 labour costs. The labour savings are ...
... The net present value analysis associated with improvements to the MRO inventory processes is provided in Attachment A. The estimated labour cost savings, due to a reduction in employees purchasing materials on an ad hoc basis, is $37,950 per year, based on 2004 labour costs. The labour savings are ...
The Simple Macro Model Firm Guide
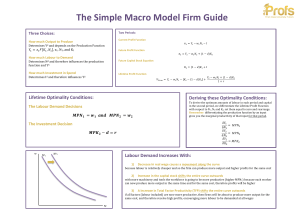
... with more machinery and tools the workforce is going to be more productive (higher MPN1) because each worker can now produce more output in the same time and for the same cost, therefore profits wi ...
... with more machinery and tools the workforce is going to be more productive (higher MPN1) because each worker can now produce more output in the same time and for the same cost, therefore profits wi ...
Chinese enterprise`labor-capital relationship
... competitions among capital, the worker’s struggle, the globalization of capital and so on, from all above, Marx concluded that the labor-capital relationship of the capitalism must be replaced by the new tape of relationship. Thus it can be seen, Marx explained the nature and evolution of labor rela ...
... competitions among capital, the worker’s struggle, the globalization of capital and so on, from all above, Marx concluded that the labor-capital relationship of the capitalism must be replaced by the new tape of relationship. Thus it can be seen, Marx explained the nature and evolution of labor rela ...
Interfield Microeconomics Ph.D. Qualification Examination Examiners: Borcherding, Denzau and Filson
... You may answer any two of these in place of one of the elective questions in Section A1. ...
... You may answer any two of these in place of one of the elective questions in Section A1. ...
Chapter 1 - Foothill College
... carefully articulated assumptions regarding the conditions under which such selforganizing processes would indeed lead to socially optimal outcomes. For example: Buyers and sellers must be too small to influence the market price. Complete information must be available to all participants and there a ...
... carefully articulated assumptions regarding the conditions under which such selforganizing processes would indeed lead to socially optimal outcomes. For example: Buyers and sellers must be too small to influence the market price. Complete information must be available to all participants and there a ...
ARCHIVE: MARX, CLASSICAL POLITICAL ECONOMY AND THE
... material form of the real relations between people becomes obscured . Marx therefore speaks of the deceptive appearance of all forms of value . In contrast to the transparent, pre-capitalist forms, the relations between exploiter and exploited in the modern capitalist form of value are made opaque b ...
... material form of the real relations between people becomes obscured . Marx therefore speaks of the deceptive appearance of all forms of value . In contrast to the transparent, pre-capitalist forms, the relations between exploiter and exploited in the modern capitalist form of value are made opaque b ...
MARXISM
... materialist interpretation of historical development, a dialectical view of social change, and an analysis of class-relations within society and their application in the analysis and critique of the development of capitalism. Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. Marxist analyses and methodologies hav ...
... materialist interpretation of historical development, a dialectical view of social change, and an analysis of class-relations within society and their application in the analysis and critique of the development of capitalism. Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. Marxist analyses and methodologies hav ...
Ch - OnCourse
... Unlimited WantsSelf-sufficiencyEntrepreneurshipAllocateCreditWantEfficiencyGoodBarterCapital resourcesHuman resourcesUtilityProductivityDivision of laborTrade-offExchangeServices- ...
... Unlimited WantsSelf-sufficiencyEntrepreneurshipAllocateCreditWantEfficiencyGoodBarterCapital resourcesHuman resourcesUtilityProductivityDivision of laborTrade-offExchangeServices- ...
WHAT IS ECONOMICS WHERE DID IT COME FROM HOW DID IT
... everybody pursuing their own self-interest… • …would be that the general good of all would be served “as if by an invisible hand” • By the invisible hand all-knowing providence harmonizes the work of individuals, to that the good of all results from each pursuing his own good. ...
... everybody pursuing their own self-interest… • …would be that the general good of all would be served “as if by an invisible hand” • By the invisible hand all-knowing providence harmonizes the work of individuals, to that the good of all results from each pursuing his own good. ...
slides 6 - MyCourses
... As can easily be demonstrated, Portugal is more efficient in both sectors, but Portugal can achieve more production by specializing in wine and importing cloth from England. Conversely, England will produce cloth and exchange part of its output for wine imported from Portugal. Both countries gain by ...
... As can easily be demonstrated, Portugal is more efficient in both sectors, but Portugal can achieve more production by specializing in wine and importing cloth from England. Conversely, England will produce cloth and exchange part of its output for wine imported from Portugal. Both countries gain by ...
Positive economics revalued (the fact/value distinction in economics)
... e. Fact/theory/value interaction. Mere ‘border disputes’ between facts and values (Sen) or more general intermingling? (Compare parallel issue of fact/theory interaction: von Mises on the primacy of the a priory but Stone on the a priori and the empirical as a matter of ‘chicken and egg’) (Whiskey a ...
... e. Fact/theory/value interaction. Mere ‘border disputes’ between facts and values (Sen) or more general intermingling? (Compare parallel issue of fact/theory interaction: von Mises on the primacy of the a priory but Stone on the a priori and the empirical as a matter of ‘chicken and egg’) (Whiskey a ...
socialism.
... • It is a philosophy of history that outlines why capitalism isdoomed and why socialism is destined to replace it. • Marx: ‘The philosophers have only interpreted the world, in various ways; the point is to change it.’ • Unity of theory and practice in Marx. • Rejecting Hegel’s idealism, materialist ...
... • It is a philosophy of history that outlines why capitalism isdoomed and why socialism is destined to replace it. • Marx: ‘The philosophers have only interpreted the world, in various ways; the point is to change it.’ • Unity of theory and practice in Marx. • Rejecting Hegel’s idealism, materialist ...
the development of socialist economic thought
... He explains the system of material balances used by the Soviet planners and how these differed from the full input output table formalism later developed by Leontief. This is interesting because although the system of material balances is often refered to, it is rare to see an explanation of just ho ...
... He explains the system of material balances used by the Soviet planners and how these differed from the full input output table formalism later developed by Leontief. This is interesting because although the system of material balances is often refered to, it is rare to see an explanation of just ho ...
Theories - TPP-PED
... 2. What is general to more people and agencies, their actions, and their products within the time frame of contemporary capitalism 3. What is specific to people, agencies, their activities, and products due to their emergence and functioning within capitalist society, anywhere and at any time. Remai ...
... 2. What is general to more people and agencies, their actions, and their products within the time frame of contemporary capitalism 3. What is specific to people, agencies, their activities, and products due to their emergence and functioning within capitalist society, anywhere and at any time. Remai ...
Karl Marx
... political economy. We have accepted its terminology and its laws… • From political economy itself, in its own words, we have shown that the worker sinks to the level of a commodity, and to a most miserable commodity; • that the misery of the worker increases with the power and volume of his producti ...
... political economy. We have accepted its terminology and its laws… • From political economy itself, in its own words, we have shown that the worker sinks to the level of a commodity, and to a most miserable commodity; • that the misery of the worker increases with the power and volume of his producti ...
HISTORY OF ECONOMIC THOUGHTS
... predictions that population growth would always tend to outstrip advances in the means of subsistence earned for economics the title “the dismal science.” he contended that poverty and distress are unavoidable, since population increases by geometrical ratio and the means of subsistence by arithmeti ...
... predictions that population growth would always tend to outstrip advances in the means of subsistence earned for economics the title “the dismal science.” he contended that poverty and distress are unavoidable, since population increases by geometrical ratio and the means of subsistence by arithmeti ...