13 chapter
... In the economy as a whole, producers learn how much consumers are willing to pay for a bit more of one good versus a bit more of another when market prices operate as economic signals. This process ensures that a competitive market economy in general equilibrium produces the right mix of goods. To s ...
... In the economy as a whole, producers learn how much consumers are willing to pay for a bit more of one good versus a bit more of another when market prices operate as economic signals. This process ensures that a competitive market economy in general equilibrium produces the right mix of goods. To s ...
Growth & DSGE
... • A market is available to exchange capital (using double auction rules, because a competitive model is being tested). • There is money, an experimental currency, in the economy, which agents use for purchases and sales of capital. The money is not fiat money, but is convertible into dollar earnings ...
... • A market is available to exchange capital (using double auction rules, because a competitive model is being tested). • There is money, an experimental currency, in the economy, which agents use for purchases and sales of capital. The money is not fiat money, but is convertible into dollar earnings ...
Document
... Buchanan’s Public Choice Theory adds political content to concept of individual decision-making ...
... Buchanan’s Public Choice Theory adds political content to concept of individual decision-making ...
Chapter 7
... to exchange coupons for money, and after their death their coupons must be returned to the society to be equally distributed among all citizens. "Coupon socialist" enterprises are believed to be able to run efficiently for they run exactly like capitalist corporations, based on wage labor and pursui ...
... to exchange coupons for money, and after their death their coupons must be returned to the society to be equally distributed among all citizens. "Coupon socialist" enterprises are believed to be able to run efficiently for they run exactly like capitalist corporations, based on wage labor and pursui ...
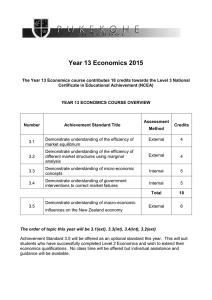
year 13 economics course overview
... Government interventions refer to interventions in a market by central or local government. For example, these may include, for each market failure, a selection from: subsidies, taxes, regulations, property rights and government provision (consumption externalities) subsidies, taxes, regulations ...
... Government interventions refer to interventions in a market by central or local government. For example, these may include, for each market failure, a selection from: subsidies, taxes, regulations, property rights and government provision (consumption externalities) subsidies, taxes, regulations ...
19 The Participatory Economy: The Case of Yugoslavia
... From this list of characteristics it is clear that the objective of the labor-managed firm in a participatory economy will be quite different from that of either the capitalist firm or a typical enterprise in a centrally planned economy. Under capitalism profit maximization is assumed to be the object ...
... From this list of characteristics it is clear that the objective of the labor-managed firm in a participatory economy will be quite different from that of either the capitalist firm or a typical enterprise in a centrally planned economy. Under capitalism profit maximization is assumed to be the object ...
Indonesia – a country of contrasts
... The food consumption growth in 2014 amounted 7,5% and is forecasted to grow 6,9% for 2017. For alcoholic drinks, the growth amounted 11,7% in 2014 and is forecasted to grow 8,4% in 2017. Soft drinks value sales’ growth in 2014 increased by 9,5% and by are expected to increase by 8,8% in 2017. The m ...
... The food consumption growth in 2014 amounted 7,5% and is forecasted to grow 6,9% for 2017. For alcoholic drinks, the growth amounted 11,7% in 2014 and is forecasted to grow 8,4% in 2017. Soft drinks value sales’ growth in 2014 increased by 9,5% and by are expected to increase by 8,8% in 2017. The m ...
Capitalism and Socialism: A Review of Kornai`s Dynamism
... Kornai characterized capitalism as surplus economy, which is in contrast to socialism as a shortage economy, more than four decades ago in the book Anti-Equilibrium, published in 1971. That book was cited by Kenneth Arrow as an alternative approach to general equilibrium theory in his Nobel lecture ...
... Kornai characterized capitalism as surplus economy, which is in contrast to socialism as a shortage economy, more than four decades ago in the book Anti-Equilibrium, published in 1971. That book was cited by Kenneth Arrow as an alternative approach to general equilibrium theory in his Nobel lecture ...
Whirlpool Enters the Indian Market
... were all just like Aunt Mary at home in Benton Harbor, MI with her washer dryer combo in the basement, seemed like the proverbial pot of gold at the end of the global rainbow. Whirlpool waited for the World Washer to fly out of the showrooms. It went down the drain instead. The Indian partner, Mr. S ...
... were all just like Aunt Mary at home in Benton Harbor, MI with her washer dryer combo in the basement, seemed like the proverbial pot of gold at the end of the global rainbow. Whirlpool waited for the World Washer to fly out of the showrooms. It went down the drain instead. The Indian partner, Mr. S ...
Liberalism, Capitalism, and “Socialist” Principles Richard J. Arneson
... fairly and efficiently, so that the necessary burdens impinge on each member of the party in about the same way and impose similar levels of sacrifice on each. Claims to justified inequality in benefits, on the basis that some have contributed more to the group enterprise even though they have not p ...
... fairly and efficiently, so that the necessary burdens impinge on each member of the party in about the same way and impose similar levels of sacrifice on each. Claims to justified inequality in benefits, on the basis that some have contributed more to the group enterprise even though they have not p ...
Chapter 27, 28, & 29
... Based on its revenue/worker(mrp) vs. its costs(mrc) firms determine how many workers to hire (mrp=mrc). Based on their Marginal Benefit vs. Marginal Cost workers determine whether or not they will work for this wage (msc=msb). ...
... Based on its revenue/worker(mrp) vs. its costs(mrc) firms determine how many workers to hire (mrp=mrc). Based on their Marginal Benefit vs. Marginal Cost workers determine whether or not they will work for this wage (msc=msb). ...
Values, The Dominant Social Par
... the only way to avoid explanations of the present rise of neoliberal globalisation which consider it as an exogenous or policy change rather than as an endogenous or systemic change, which can only be transcended from without rather than from within this system ―as the ID approach suggests. ...
... the only way to avoid explanations of the present rise of neoliberal globalisation which consider it as an exogenous or policy change rather than as an endogenous or systemic change, which can only be transcended from without rather than from within this system ―as the ID approach suggests. ...
alternative explanations of the operation of a capitalist economy
... economists are based. The Arrow-Debreu presumption is that markets exist today to permit participants to buy and sell all the products and services that will be delivered today and at every date in the future. Thus at the initial instant of time, it is presumed that all market participants enter in ...
... economists are based. The Arrow-Debreu presumption is that markets exist today to permit participants to buy and sell all the products and services that will be delivered today and at every date in the future. Thus at the initial instant of time, it is presumed that all market participants enter in ...
From Free to Civilized Markets
... corporations in the global North and farmers in the global South, western consumer and Bangladeshi seamstress, etc. In all of these contexts, we find that the powerful define moral standards. The latter are in turn often further deteriorated by the effects of intense competition, which ...
... corporations in the global North and farmers in the global South, western consumer and Bangladeshi seamstress, etc. In all of these contexts, we find that the powerful define moral standards. The latter are in turn often further deteriorated by the effects of intense competition, which ...
Word file#3 - Islamic Development Bank
... which is essentially secularist. It was shaped by the Enlightenment philosophy, which placed great confidence in the power of reason to establish ultimate metaphysical truths, and tried to undermine the hold of religion as a collective force in society. Value judgments based on moral values became a ...
... which is essentially secularist. It was shaped by the Enlightenment philosophy, which placed great confidence in the power of reason to establish ultimate metaphysical truths, and tried to undermine the hold of religion as a collective force in society. Value judgments based on moral values became a ...
Government versus Market: A Contemporary and
... At that time economists identified an increasing number of market failures, that justified a growing economic role for the state and especially for more public spending. As James Buchanan, a conservative economist, put it: “The 1950s were dark days for classical liberals. Big government [became] ...
... At that time economists identified an increasing number of market failures, that justified a growing economic role for the state and especially for more public spending. As James Buchanan, a conservative economist, put it: “The 1950s were dark days for classical liberals. Big government [became] ...
ECONOMICS
... Section 3: Centrally Planned Economies Organization of Centrally Planned Economies In a centrally planned economy, the government owns both land and capital. The government decides what to produce, how much to produce, and how much to charge. Government controls where individuals work and what wage ...
... Section 3: Centrally Planned Economies Organization of Centrally Planned Economies In a centrally planned economy, the government owns both land and capital. The government decides what to produce, how much to produce, and how much to charge. Government controls where individuals work and what wage ...
here - Kornai János
... Thus, social welfare states in the West (e.g., Sweden ruled by Social democrats for 40 years) are not socialist countries but democratic capitalist market economies with sensitivity and responsibility toward social problems. Kornai’s operational definition of socialism is consistent with those of Ka ...
... Thus, social welfare states in the West (e.g., Sweden ruled by Social democrats for 40 years) are not socialist countries but democratic capitalist market economies with sensitivity and responsibility toward social problems. Kornai’s operational definition of socialism is consistent with those of Ka ...
On the Enlightenment from Danish Flexibility Labor Market
... The Danish labor market flexibility lies in the number of external flexibility, primarily in two areas: (a) Deregulate labor market regulation, reduce the stringency of the employment protection legislation. Unlike most other industrialized countries and the Nordic countries, Denmark has low stringe ...
... The Danish labor market flexibility lies in the number of external flexibility, primarily in two areas: (a) Deregulate labor market regulation, reduce the stringency of the employment protection legislation. Unlike most other industrialized countries and the Nordic countries, Denmark has low stringe ...
Some Observations on the Great Depression
... France. The French experience is more in line with the prediction of growth theory. The difference between the French and U.S. experiences indicates that some factor or factors not present in the French economy must have disrupted the U.S. economy in the early 1930s. This difference is of the busine ...
... France. The French experience is more in line with the prediction of growth theory. The difference between the French and U.S. experiences indicates that some factor or factors not present in the French economy must have disrupted the U.S. economy in the early 1930s. This difference is of the busine ...
The Market System and the Circular Flow
... 68. "For whom is a given mix of goods and services to be produced? How, in other words, are the society's outputs to be distributed among its members?" In a market economy, this problem is resolved primarily in the: A. Public sector through the mechanism of central planning B. Business sector throug ...
... 68. "For whom is a given mix of goods and services to be produced? How, in other words, are the society's outputs to be distributed among its members?" In a market economy, this problem is resolved primarily in the: A. Public sector through the mechanism of central planning B. Business sector throug ...
ECONOMICS
... • outcome by market allocations may not be socially acceptable • the market, if left unregulated and free to follow its own rules, does not function well Market supporter • most efficient mechanism • autghomatic capacity to increase well-being • moral qualities (i.e.: meritocracy) ...
... • outcome by market allocations may not be socially acceptable • the market, if left unregulated and free to follow its own rules, does not function well Market supporter • most efficient mechanism • autghomatic capacity to increase well-being • moral qualities (i.e.: meritocracy) ...
Why Austrian Economics Matters
... possible to have both high inflation and high unemployment at the same time. The Nobel Prize that Hayek received in 1974 for his business-cycle research with Mises caused an explosion of academic interest in the Austrian School and free-market economics in general. A generation of graduate students ...
... possible to have both high inflation and high unemployment at the same time. The Nobel Prize that Hayek received in 1974 for his business-cycle research with Mises caused an explosion of academic interest in the Austrian School and free-market economics in general. A generation of graduate students ...