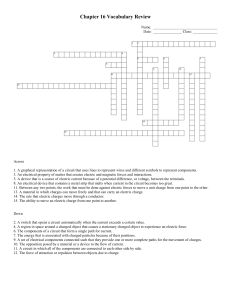
Chapter 16 Vocabulary Review Name: Date: Class: ______ Across
... 1. A graphical representation of a circuit that uses lines to represent wires and different symbols to represent components. 3. An electrical property of matter that creates electric and magnetic forces and interactions. 5. A device that is a source of electric current because of a potential differe ...
... 1. A graphical representation of a circuit that uses lines to represent wires and different symbols to represent components. 3. An electrical property of matter that creates electric and magnetic forces and interactions. 5. A device that is a source of electric current because of a potential differe ...
Article #1: How Does An Electrical Generator Work?
... A generator is basically created by a mechanical force that turns a conductive wire or bar within a magnetic field. The force used to spin the conductive object can be provided by many sources, such as moving water, steam, wind, gas engine or even hand-cranked levers. The electricity then flows into ...
... A generator is basically created by a mechanical force that turns a conductive wire or bar within a magnetic field. The force used to spin the conductive object can be provided by many sources, such as moving water, steam, wind, gas engine or even hand-cranked levers. The electricity then flows into ...
Equivalent Circuit Model
... The three-phase winding are displaced from each other by 120 electrical degrees in space Current flows in a phase coil produce a sinusoidally distributed mmf wave centered on the axis of the coil. Alternating current in each coil produces a pulsating mmf wave. Mmf waves are displaced by 120 degrees ...
... The three-phase winding are displaced from each other by 120 electrical degrees in space Current flows in a phase coil produce a sinusoidally distributed mmf wave centered on the axis of the coil. Alternating current in each coil produces a pulsating mmf wave. Mmf waves are displaced by 120 degrees ...
Ch 4 - MyWeb at WIT
... Reversal of rotation, Construction, Synchronous speed, Slip, Equivalent circuit, locus of current, Air-gap power, Mechanical power, Torque, and Efficiency ...
... Reversal of rotation, Construction, Synchronous speed, Slip, Equivalent circuit, locus of current, Air-gap power, Mechanical power, Torque, and Efficiency ...
modello di descrizione delle singole attivita`formative
... conductors; electric potential and potential energy; capacitors; energy density of the electric field; D field. Electric current: electromotive force; Ohm, Joule, Kirchhoff’s laws. Magnetism: magnets and magnetic dipoles; Lorenz force; Ampère’s equivalence principle; 1st and 2nd Laplace formula; Amp ...
... conductors; electric potential and potential energy; capacitors; energy density of the electric field; D field. Electric current: electromotive force; Ohm, Joule, Kirchhoff’s laws. Magnetism: magnets and magnetic dipoles; Lorenz force; Ampère’s equivalence principle; 1st and 2nd Laplace formula; Amp ...
Chapter 17-3 Electric Currents
... magnetic field requires work • Greater the magnetic field – stronger the force required to push loop through field ...
... magnetic field requires work • Greater the magnetic field – stronger the force required to push loop through field ...
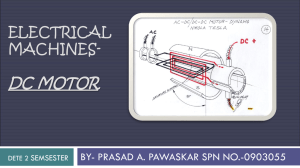
AC/DC and Stepper Motors
... – AC cables could transmit much further than DC – AC cables were smaller as well ...
... – AC cables could transmit much further than DC – AC cables were smaller as well ...