Magnetism guide 2
... a) a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy by rotating a coil of wire in a magnetic field. _____2) magnetic pole ...
... a) a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy by rotating a coil of wire in a magnetic field. _____2) magnetic pole ...
Document
... electricity and current electricity? Static electricity is stationary or collects on the surface of an object, whereas current electricity is flowing very rapidly through a conductor. The flow of electricity in current electricity has electrical pressure or voltage. Electric charges flow from an are ...
... electricity and current electricity? Static electricity is stationary or collects on the surface of an object, whereas current electricity is flowing very rapidly through a conductor. The flow of electricity in current electricity has electrical pressure or voltage. Electric charges flow from an are ...
what is alternating current (ac)?
... current (DC) can only produce steady magnetic fields, transformers simply will not work with direct current. Of course, direct current may be interrupted (pulsed) through the primary winding of a transformer to create a changing magnetic field (as is done in automotive ignition systems to produce hi ...
... current (DC) can only produce steady magnetic fields, transformers simply will not work with direct current. Of course, direct current may be interrupted (pulsed) through the primary winding of a transformer to create a changing magnetic field (as is done in automotive ignition systems to produce hi ...
Zahn, M., and J.K. Skinner, Novel Self-excited Alternating Operation of Coupled Commutator Machines, Journal of the Franklin Institute 296, 1-13, 1973
... For this reason, most texts on machines only present a qualitative explanation of self-excited operation (2, 3). However, we will show here that the linear representation where L,, L, and G are assumed constant, yields useful and easily solvable information. The nonlinearities are not essential in d ...
... For this reason, most texts on machines only present a qualitative explanation of self-excited operation (2, 3). However, we will show here that the linear representation where L,, L, and G are assumed constant, yields useful and easily solvable information. The nonlinearities are not essential in d ...
Answer on Question #66811, Physics / Electromagnetism An
... Answer on Question #66811, Physics / Electromagnetism An electron moving parallel to the x-axis has an initial speed of 3.70×(10)^6 m/s at the origin. It's speed is reduced to 1.40×(10)^5 m/s at the point x=2c.m -calculate the electric potenial difference between the origin and that point? Find: vE ...
... Answer on Question #66811, Physics / Electromagnetism An electron moving parallel to the x-axis has an initial speed of 3.70×(10)^6 m/s at the origin. It's speed is reduced to 1.40×(10)^5 m/s at the point x=2c.m -calculate the electric potenial difference between the origin and that point? Find: vE ...
ichLarge quantities of electrical energy are produced in power
... of induction. Where does all this energy come from? Simply put, the root source of a power station’s energy depends on what type of power station/ plant it is. That is being said, large generators that have coils moving between magnets produce nearly all electricity from a power station. An electric ...
... of induction. Where does all this energy come from? Simply put, the root source of a power station’s energy depends on what type of power station/ plant it is. That is being said, large generators that have coils moving between magnets produce nearly all electricity from a power station. An electric ...
Theories In Electronics Vocabulary Teacher`s Guide
... Voltage – The basic unit of electrical pressure and sometimes known as EMF. Current - A flow of electrons in an electrical circuit. Resistance – The ability to oppose an electrical current. Conductor – A material that has a loose grip on its electrons so the electrical current can pass through it. I ...
... Voltage – The basic unit of electrical pressure and sometimes known as EMF. Current - A flow of electrons in an electrical circuit. Resistance – The ability to oppose an electrical current. Conductor – A material that has a loose grip on its electrons so the electrical current can pass through it. I ...
t6_transformers
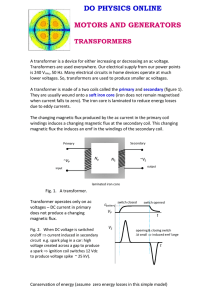
... TRANSFORMERS A transformer is a device for either increasing or decreasing an ac voltage. Transformers are used everywhere. Our electrical supply from our power points is 240 Vrms, 50 Hz. Many electrical circuits in home devices operate at much lower voltages. So, transformers are used to produce sm ...
... TRANSFORMERS A transformer is a device for either increasing or decreasing an ac voltage. Transformers are used everywhere. Our electrical supply from our power points is 240 Vrms, 50 Hz. Many electrical circuits in home devices operate at much lower voltages. So, transformers are used to produce sm ...
Electricity Terms
... AC & DC Alternating Current and Direct Current. DC is electricity moving in one direction (batteries produce this). AC is current moving back and forth (this is how it comes out of electrical receptacles). Ampere see electric current Coulomb The standard international unit of electric charge. It's t ...
... AC & DC Alternating Current and Direct Current. DC is electricity moving in one direction (batteries produce this). AC is current moving back and forth (this is how it comes out of electrical receptacles). Ampere see electric current Coulomb The standard international unit of electric charge. It's t ...
HR3513381342
... Index Terms—AC generators, induction motors, power system dynamic stability, reactive power control, torque control, variable speed drives, wind energy. ...
... Index Terms—AC generators, induction motors, power system dynamic stability, reactive power control, torque control, variable speed drives, wind energy. ...
Guass`s Law for magnetism
... An electric field is produced by: • Charged particle (moving or stationary) • Changing magnetic field A magnetic field is produced by: • A curent (moving charge) • Changing electric field ...
... An electric field is produced by: • Charged particle (moving or stationary) • Changing magnetic field A magnetic field is produced by: • A curent (moving charge) • Changing electric field ...