View Full PDF - Biochemical Society Transactions
... treatment [47], suggesting that TORC1 also plays a role in the mobilization of TAGs (triacylglycerols). Interestingly, Tgl5 has both a TAG lipase domain as well as a lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase domain. Thus this enzyme can function in both anabolic and catabolic pathways [75]; perhaps TORC ...
... treatment [47], suggesting that TORC1 also plays a role in the mobilization of TAGs (triacylglycerols). Interestingly, Tgl5 has both a TAG lipase domain as well as a lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase domain. Thus this enzyme can function in both anabolic and catabolic pathways [75]; perhaps TORC ...
Metabolic transformation in cancer
... intracellular pH unless HIF1 activity also up-regulated proteins necessary to remove this waste product. The monocarboxylic acid transporter-4 is a HIF1 target, and is used for the export of lactate, symported with hydrogen ions (49). Intracellular Hþ is also excreted using an antiporter—the Naþ/Hþ ...
... intracellular pH unless HIF1 activity also up-regulated proteins necessary to remove this waste product. The monocarboxylic acid transporter-4 is a HIF1 target, and is used for the export of lactate, symported with hydrogen ions (49). Intracellular Hþ is also excreted using an antiporter—the Naþ/Hþ ...
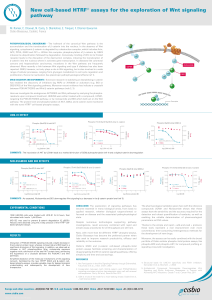
New cell-based HTRF® assays for the exploration of Wnt signaling
... induces its ubiquitination followed by degradation. Conversely, binding of Wnt to its frizzled receptor leads to the disruption of the destruction complex, inducing the translocation of β-catenin into the nucleus where it activates gene transcription. In diseases like colorectal cancers and hepatoce ...
... induces its ubiquitination followed by degradation. Conversely, binding of Wnt to its frizzled receptor leads to the disruption of the destruction complex, inducing the translocation of β-catenin into the nucleus where it activates gene transcription. In diseases like colorectal cancers and hepatoce ...
The Emerging Role of Branched-Chain Amino Acids in Insulin
... Together with insulin, BCAAs also function as anabolic signals to alter the growth of energy-consuming tissues such as skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Amino acids are required for protein synthesis. Amino acids, BCAAs in particular, also stimulate mTORC1 signaling pathways to regulate mRNA trans ...
... Together with insulin, BCAAs also function as anabolic signals to alter the growth of energy-consuming tissues such as skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. Amino acids are required for protein synthesis. Amino acids, BCAAs in particular, also stimulate mTORC1 signaling pathways to regulate mRNA trans ...
Nutrient-Sensing Mechanisms across Evolution - Sabatini Lab
... adenylylation state and activity of glutamine synthetase (GS). When nitrogen is absent, the precursor of nitrogen assimilation reactions, 2-OG, accumulates, binds to, and inhibits the unmodified PII protein GlnB, which is unable to stimulate the adenylylation reaction of ATase. The unmodified and ac ...
... adenylylation state and activity of glutamine synthetase (GS). When nitrogen is absent, the precursor of nitrogen assimilation reactions, 2-OG, accumulates, binds to, and inhibits the unmodified PII protein GlnB, which is unable to stimulate the adenylylation reaction of ATase. The unmodified and ac ...
The Hippo-YAP Pathway: New Connection between
... directly targets the Hippo signaling pathway. However, many possible targets for therapy are being investigated that would also affect the Hippo signaling pathway5. One of these is targeting the homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 2 (HIPK2) which has been demonstrated to activate YAP 5.In additio ...
... directly targets the Hippo signaling pathway. However, many possible targets for therapy are being investigated that would also affect the Hippo signaling pathway5. One of these is targeting the homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 2 (HIPK2) which has been demonstrated to activate YAP 5.In additio ...
The Complex Role of Branched Chain Amino Acids
... Several other studies have shown that a branched chain amino acid signature is associated with insulin resistance. In a cross sectional study, a group of sedentary metabolic syndrome subjects underwent frequent oral glucose tolerance tests to measure insulin sensitivity. Targeted profiling of 75 met ...
... Several other studies have shown that a branched chain amino acid signature is associated with insulin resistance. In a cross sectional study, a group of sedentary metabolic syndrome subjects underwent frequent oral glucose tolerance tests to measure insulin sensitivity. Targeted profiling of 75 met ...
Regulation of hepatic metabolism by AMPK - HAL
... metabolic enzymes, long-term effects have been clearly demonstrated on the expression of a number of gene sets. AMPK promotes the induction of the transcriptional mitochondrial gene program and the inhibition of lipogenesis gene expression by direct phosphorylation of transcription factors and co-ac ...
... metabolic enzymes, long-term effects have been clearly demonstrated on the expression of a number of gene sets. AMPK promotes the induction of the transcriptional mitochondrial gene program and the inhibition of lipogenesis gene expression by direct phosphorylation of transcription factors and co-ac ...
AMPK and mTOR: Antagonist ATP Sensors
... The body uses three energetic pathways to maintain cellular ATP levels, phosphocreatine, glycolysis, and oxidative phosphorylation. Two enzymes are responsible for maintaining ATP levels as soon as muscle contraction begins; more precisely as soon as the muscle starts using ATP at an accelerated rat ...
... The body uses three energetic pathways to maintain cellular ATP levels, phosphocreatine, glycolysis, and oxidative phosphorylation. Two enzymes are responsible for maintaining ATP levels as soon as muscle contraction begins; more precisely as soon as the muscle starts using ATP at an accelerated rat ...
Mechanisms of amino acid sensing in mTOR signaling pathway
... growth by phosphorylating S6K1 and 4EBP1. Rheb directly binds and activates mTOR kinase. GTP-bound active Rheb sequesters FKBP38 which otherwise binds and inhibits mTORC1. TSC1/2 heterodimer converts Rheb from GTP-bound active to GDP-bound inactive form. In Drosophila, TCTP was identified as Rheb GE ...
... growth by phosphorylating S6K1 and 4EBP1. Rheb directly binds and activates mTOR kinase. GTP-bound active Rheb sequesters FKBP38 which otherwise binds and inhibits mTORC1. TSC1/2 heterodimer converts Rheb from GTP-bound active to GDP-bound inactive form. In Drosophila, TCTP was identified as Rheb GE ...
mTORC kinase assays
... wash buffer 3 times. For mTORC1 kinase assay, add a wash with CHAPS wash buffer with 500mM NaCl to remove PRAS40. 5. The immunoprecipitates are washed once in kinase wash buffer. Resuspend the immunoprecipitates in kinase wash buffer and make 10-12 aliquots (~2.5 ul beads per reaction). Spin, and re ...
... wash buffer 3 times. For mTORC1 kinase assay, add a wash with CHAPS wash buffer with 500mM NaCl to remove PRAS40. 5. The immunoprecipitates are washed once in kinase wash buffer. Resuspend the immunoprecipitates in kinase wash buffer and make 10-12 aliquots (~2.5 ul beads per reaction). Spin, and re ...
Abstract Example
... Akt and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) are serine/threonine protein kinases with diverse physiological roles affecting a number of cellular processes. For instance, Akt has been shown to contribute to cardiac hypertrophy while AMPK is a stress related kinase involved in the control of cardiac e ...
... Akt and AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) are serine/threonine protein kinases with diverse physiological roles affecting a number of cellular processes. For instance, Akt has been shown to contribute to cardiac hypertrophy while AMPK is a stress related kinase involved in the control of cardiac e ...
Regulation of protein synthesis by insulin
... The phosphorylation of several sites in 4E–BP1 is controlled via the mTOR. mTOR is a protein kinase whose catalytic domain resembles lipid kinases such as PI3K. Some functions of mTOR are blocked by rapamycin, which also impairs the phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and blocks its release from eIF4E. mTOR s ...
... The phosphorylation of several sites in 4E–BP1 is controlled via the mTOR. mTOR is a protein kinase whose catalytic domain resembles lipid kinases such as PI3K. Some functions of mTOR are blocked by rapamycin, which also impairs the phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and blocks its release from eIF4E. mTOR s ...
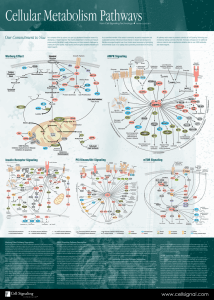
Cellular Metabolism Pathways
... Since its initial discovery as a proto-oncogene, the serine/threonine kinase Akt (also known as protein kinase B or PKB) has become a major focus of attention because of its critical regulatory role in diverse cellular processes, including cancer progression and insulin metabolism. The Akt cascade i ...
... Since its initial discovery as a proto-oncogene, the serine/threonine kinase Akt (also known as protein kinase B or PKB) has become a major focus of attention because of its critical regulatory role in diverse cellular processes, including cancer progression and insulin metabolism. The Akt cascade i ...
mTORC1 Activates SREBP-1c and Uncouples Lipogenesis From Gluconeogenesis Please share
... 17. Newgard CB, et al. (2009) A branched-chain amino acid-related metabolic signature that differentiates obese and lean humans and contributes to insulin resistance. Cell Metab 9:311–326. 18. Um SH, et al. (2004) Absence of S6K1 protects against age- and diet-induced obesity while enhancing insulin ...
... 17. Newgard CB, et al. (2009) A branched-chain amino acid-related metabolic signature that differentiates obese and lean humans and contributes to insulin resistance. Cell Metab 9:311–326. 18. Um SH, et al. (2004) Absence of S6K1 protects against age- and diet-induced obesity while enhancing insulin ...
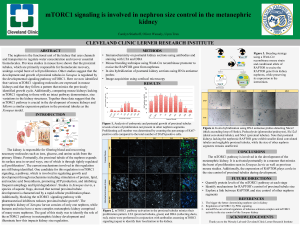
mTORC1 signaling is involved in nephron size control in the
... The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney that uses channels and transporters to regulate water concentration and recover essential biomolecules. Previous studies in mouse have shown that the proximal tubules, which are primarily responsible for biomolecule recovery, undergo a rapid burst of ...
... The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney that uses channels and transporters to regulate water concentration and recover essential biomolecules. Previous studies in mouse have shown that the proximal tubules, which are primarily responsible for biomolecule recovery, undergo a rapid burst of ...
Μάθημα φοιτητών Ιωάννινα - E
... A tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to a protein in a cell. It functions as an "on" or "off" switch in many cellular functions. Tyrosine kinases are a subclass of protein kinase. The phosphate group is attached to the amino acid tyrosine on the protein. Phosp ...
... A tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to a protein in a cell. It functions as an "on" or "off" switch in many cellular functions. Tyrosine kinases are a subclass of protein kinase. The phosphate group is attached to the amino acid tyrosine on the protein. Phosp ...
Dr. Bryan Ballif identifies phosphorylation sites on key proteins regulating cell growth and proliferation.
... However, determining precisely where a protein is phosphorylated, and understanding the effect of phosphorylation at a given amino acid requires exacting instrumentation and skilled analysis. Dr. Ballif, working with a colleague, Dr. Diane Fingar, from the University of Mich ...
... However, determining precisely where a protein is phosphorylated, and understanding the effect of phosphorylation at a given amino acid requires exacting instrumentation and skilled analysis. Dr. Ballif, working with a colleague, Dr. Diane Fingar, from the University of Mich ...
MTORC1

mTORC1, also known as mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 or mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1, is a protein complex that functions as a nutrient/energy/redox sensor and controls protein synthesis.mTOR Complex 1 (mTORC1) is composed of mTOR itself, regulatory-associated protein of mTOR (Raptor), mammalian lethal with SEC13 protein 8 (MLST8) and the recently identified PRAS40 and DEPTOR. This complex embodies the classic functions of mTOR, namely as a nutrient/energy/redox sensor and controller of protein synthesis. The activity of this complex is controlled by insulin, growth factors, amino acids (particularly leucine), and oxidative stress.The role of mTORC1 is to activate translation of proteins. In order for cells to grow and proliferate by manufacturing more proteins, the cells must ensure that they have the resources available for protein production. Thus, for protein production, and therefore mTORC1 activation, cells must have adequate energy resources, nutrient availability, oxygen abundance, and proper growth factors in order for mRNA translation to begin.