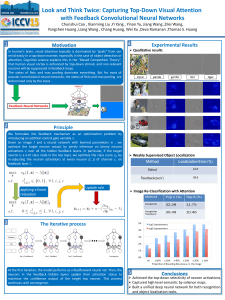
Difficulty (part of the hypothesis)
... Unconscious processing of visual saliency Ryota Kanai, Vincent Walsh ...
... Unconscious processing of visual saliency Ryota Kanai, Vincent Walsh ...
Integrating Top-Down and Bottom
... When the network is operated with disabled feedback projections between the two areas, noise in the bottom-up input is somewhat reduced due to the threshold process of action potential initiation. However, this reduction is local to each neuron and unspecific. Therefore, the amount of noise in the a ...
... When the network is operated with disabled feedback projections between the two areas, noise in the bottom-up input is somewhat reduced due to the threshold process of action potential initiation. However, this reduction is local to each neuron and unspecific. Therefore, the amount of noise in the a ...
Sensation & Perception
... 4. Image coming through activates photoreceptors in the retina called rods and cones (process information for darkness and color). 5. The rods and cones set off chemical reactions they form a synapse with bipolar cells which change light energy into neural impulses. 6. These neural impulses go to th ...
... 4. Image coming through activates photoreceptors in the retina called rods and cones (process information for darkness and color). 5. The rods and cones set off chemical reactions they form a synapse with bipolar cells which change light energy into neural impulses. 6. These neural impulses go to th ...
feedback-poster
... Chunshui Cao , Xianming Liu ,Yi Yang , Yinan Yu, Jiang Wang ,Zilei Wang, Yongzhen Huang ,Liang Wang , Chang Huang, Wei Xu ,Deva Ramanan ,Thomas S. Huang ...
... Chunshui Cao , Xianming Liu ,Yi Yang , Yinan Yu, Jiang Wang ,Zilei Wang, Yongzhen Huang ,Liang Wang , Chang Huang, Wei Xu ,Deva Ramanan ,Thomas S. Huang ...
The Top-down and Bottom-up Approaches to Studying Motor Learning
... The Top-down and Bottom-up Approaches to Studying Motor Learning VINCENT C.K. CHEUNG McGovern Institute for Brain Research, and Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, MIT Previous studies have demonstrated the critical role of motor cortical plasticity during both acquisition of new motor skill ...
... The Top-down and Bottom-up Approaches to Studying Motor Learning VINCENT C.K. CHEUNG McGovern Institute for Brain Research, and Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, MIT Previous studies have demonstrated the critical role of motor cortical plasticity during both acquisition of new motor skill ...
Readings
... We prefer to avoid head movements to select information sources. Why fatigued drivers fail to turn their head and look behind them. This understanding is important to designing alarms and displays 2. Selective Attention Selective attention is necessary for perception. The selection of which ch ...
... We prefer to avoid head movements to select information sources. Why fatigued drivers fail to turn their head and look behind them. This understanding is important to designing alarms and displays 2. Selective Attention Selective attention is necessary for perception. The selection of which ch ...
bcs513_lecture_week9_class1
... What is attention? Obligatory William James quote: "Everyone knows what attention is. It is the taking possession by the mind in clear and vivid form, of one out of what seem several simultaneously possible objects or trains of thought...It implies withdrawal from some things in order to deal effec ...
... What is attention? Obligatory William James quote: "Everyone knows what attention is. It is the taking possession by the mind in clear and vivid form, of one out of what seem several simultaneously possible objects or trains of thought...It implies withdrawal from some things in order to deal effec ...
Neural Coalition and Main Theorem
... the brain’s low-latency processing of sensory information. Without it, bottom-up delay would accumulate too fast to allow for the number of coalitions needed to achieve the sophisticated distinctions of which the brain is capable. ...
... the brain’s low-latency processing of sensory information. Without it, bottom-up delay would accumulate too fast to allow for the number of coalitions needed to achieve the sophisticated distinctions of which the brain is capable. ...
Cognitive Science and the Emergence of Symbolic Thought
... – The brain has adapted in order to make it easy to learn language – “front heavy” ...
... – The brain has adapted in order to make it easy to learn language – “front heavy” ...
What we*ll sense and perceive* in this chapter:
... and interpreting sensory information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events.” The brain makes sense out of the input from sensory organs. ...
... and interpreting sensory information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events.” The brain makes sense out of the input from sensory organs. ...
MIND: The Cognitive Side of Mind and Brain
... assess aspects of perception, attention, and memory. Models of mental structures and processes of human perception, attention, memory, etc. based on data obtained from solid experimental procedures ...
... assess aspects of perception, attention, and memory. Models of mental structures and processes of human perception, attention, memory, etc. based on data obtained from solid experimental procedures ...
Slide ()
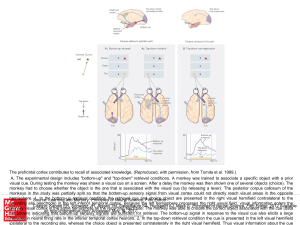
... A. The experimental design includes "bottom-up" and "top-down" retrieval conditions. A monkey was trained to associate a specific object with a prior visual cue. During testing the monkey was shown a visual cue on a screen. After a delay the monkey was then shown one of several objects (choice). The ...
... A. The experimental design includes "bottom-up" and "top-down" retrieval conditions. A monkey was trained to associate a specific object with a prior visual cue. During testing the monkey was shown a visual cue on a screen. After a delay the monkey was then shown one of several objects (choice). The ...
Slide ()
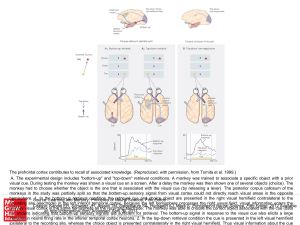
... A. The experimental design includes "bottom-up" and "top-down" retrieval conditions. A monkey was trained to associate a specific object with a prior visual cue. During testing the monkey was shown a visual cue on a screen. After a delay the monkey was then shown one of several objects (choice). The ...
... A. The experimental design includes "bottom-up" and "top-down" retrieval conditions. A monkey was trained to associate a specific object with a prior visual cue. During testing the monkey was shown a visual cue on a screen. After a delay the monkey was then shown one of several objects (choice). The ...
My artistic practice is about memorizing the number π to ten
... My artistic practice is about memorizing the number π to ten thousand digits. Although I have already accomplished that, I still make mistakes and need regular upkeep. Thus one approach I take aims to make the regular practice of π more effective and meaningful. To that end I create software or simp ...
... My artistic practice is about memorizing the number π to ten thousand digits. Although I have already accomplished that, I still make mistakes and need regular upkeep. Thus one approach I take aims to make the regular practice of π more effective and meaningful. To that end I create software or simp ...
Top-Down Processing in Neurocognitive Networks
... nervous system, united in a common task.” Higher Cortical Functions in Man, 1962 ...
... nervous system, united in a common task.” Higher Cortical Functions in Man, 1962 ...
Theoretical Basis for this Curriculum
... reader decoded orthographic input and then linked words into sentences, sentences into paragraphs. The 'bottom-up' skills are especially crucial at the lower levels of EAP. Smith (1971) and Goodman (1967) helped to integrate the field of cognitive psychology into the field of reading, with the top-d ...
... reader decoded orthographic input and then linked words into sentences, sentences into paragraphs. The 'bottom-up' skills are especially crucial at the lower levels of EAP. Smith (1971) and Goodman (1967) helped to integrate the field of cognitive psychology into the field of reading, with the top-d ...
Lab 2 slides
... Bias Weights » Why do we have them? » Why are some higher than others in the transform project? ...
... Bias Weights » Why do we have them? » Why are some higher than others in the transform project? ...