statistics
... area code isn’t necessarily better than living in the 310 area code, even though it is higher numerically. In cases like these, the numbers are just labels for different categories. ...
... area code isn’t necessarily better than living in the 310 area code, even though it is higher numerically. In cases like these, the numbers are just labels for different categories. ...
Artificial Intelligence - KDD
... How To Get an A in This Course A Story from Dr. Gerard G. L. Meyer, Johns Hopkins University Ask Questions Ask for (more) examples, another explanation, etc. if needed (“don’t be shy”) All students (especially remote students): post in class web board Unclear points – bring to class as we ...
... How To Get an A in This Course A Story from Dr. Gerard G. L. Meyer, Johns Hopkins University Ask Questions Ask for (more) examples, another explanation, etc. if needed (“don’t be shy”) All students (especially remote students): post in class web board Unclear points – bring to class as we ...
Working with Data Part 4
... the relationship between two variables. • Choose Analyze > Fit Y by X. • The icons on the bottom left indicate what type of statistical analysis can be performed based on the variable types for the X and Y variables. • Make BAD the Y,Response variable and LOAN and JOB the X,Factor variables. • Since ...
... the relationship between two variables. • Choose Analyze > Fit Y by X. • The icons on the bottom left indicate what type of statistical analysis can be performed based on the variable types for the X and Y variables. • Make BAD the Y,Response variable and LOAN and JOB the X,Factor variables. • Since ...
Solving Bayesian Networks by Weighted Model Counting
... Bacchus et al. 2003a), the creators of Cachet (Sang et al. 2004) built a system that scales to problems with thousands of variables by combining clause learning, formula-caching, and decomposition into connected components. Model-counting is complete for the complexity class #P, which also includes ...
... Bacchus et al. 2003a), the creators of Cachet (Sang et al. 2004) built a system that scales to problems with thousands of variables by combining clause learning, formula-caching, and decomposition into connected components. Model-counting is complete for the complexity class #P, which also includes ...
Introduction to Machine Learning
... set of meaningful sub-classes, called clusters Helps users understand the natural grouping or structure in a data set ...
... set of meaningful sub-classes, called clusters Helps users understand the natural grouping or structure in a data set ...
Algorithms examples Correctness and testing
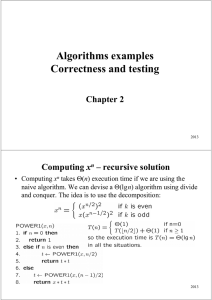
... is odd. Division by 2 is shift one position right. ...
... is odd. Division by 2 is shift one position right. ...
Covering the Aztec Diamond
... The problem (1) is known as the exact cover problem. In the case of the Aztec diamond pattern the system has 25 + 100 + 40 = 165 columns and 2945 rows. Knuth gives in [6] a backtracking algorithm to solve the Diophantine linear system (1). The abstract description of the algorithm is quite simple a ...
... The problem (1) is known as the exact cover problem. In the case of the Aztec diamond pattern the system has 25 + 100 + 40 = 165 columns and 2945 rows. Knuth gives in [6] a backtracking algorithm to solve the Diophantine linear system (1). The abstract description of the algorithm is quite simple a ...
as a PDF
... between a feed-forward and a recurrent neural network. With this recurrency, activity can be retained by the network over time. This provides a sort of memory within the network, enabling it to compute functions that are more complex than just simple reactive input-output mappings. This is a very im ...
... between a feed-forward and a recurrent neural network. With this recurrency, activity can be retained by the network over time. This provides a sort of memory within the network, enabling it to compute functions that are more complex than just simple reactive input-output mappings. This is a very im ...
ppt slides
... Replace the lowest one in the buffer if the input tuple is more than that. Takes O(n.K) time. Still low for a large n. ...
... Replace the lowest one in the buffer if the input tuple is more than that. Takes O(n.K) time. Still low for a large n. ...
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
... The problem–solving expertise component of an ICAI program contains the knowledge that system tries to impart to the student. This expertise is represented with techniques similar to those used in the knowledge base of an expert system. In fact, this component can be thought of as a specialized expe ...
... The problem–solving expertise component of an ICAI program contains the knowledge that system tries to impart to the student. This expertise is represented with techniques similar to those used in the knowledge base of an expert system. In fact, this component can be thought of as a specialized expe ...
Learning Bayesian Networks: Naïve and non
... Naïve Bayes is very popular, particularly in natural language processing and information retrieval where there are many features compared to the number of examples ...
... Naïve Bayes is very popular, particularly in natural language processing and information retrieval where there are many features compared to the number of examples ...