11. Pankaj Gupta and V.H. Allan, The Acyclic Bayesian Net
... Arcs in the parent nodes are transferred to the daughters, either directly or by reversing the order. For X, the parent relation between the nodes of a1 (or b2) are directly transferred from A (or B). Similarly for Y , the parent relations between the nodes of b1 (or a2) are directly transferred fro ...
... Arcs in the parent nodes are transferred to the daughters, either directly or by reversing the order. For X, the parent relation between the nodes of a1 (or b2) are directly transferred from A (or B). Similarly for Y , the parent relations between the nodes of b1 (or a2) are directly transferred fro ...
Chapter 4. Data Preprocessing Why preprocess the data? Data in
... Partition data set into clusters based on similarity, and store cluster representation (e.g., centroid and diameter) only Can be very effective if data is clustered but not if data is “smeared” Can have hierarchical clustering and be stored in multidimensional index tree structures There are ...
... Partition data set into clusters based on similarity, and store cluster representation (e.g., centroid and diameter) only Can be very effective if data is clustered but not if data is “smeared” Can have hierarchical clustering and be stored in multidimensional index tree structures There are ...
Decision support and Intelligent systems
... • DSS serve the management, operations, and planning levels of an organization and help to make decisions, which may be rapidly changing and not easily specified in advance. • DSS are used to collect data, analyze and shape the data that is collected, and make sound decisions or construct strategies ...
... • DSS serve the management, operations, and planning levels of an organization and help to make decisions, which may be rapidly changing and not easily specified in advance. • DSS are used to collect data, analyze and shape the data that is collected, and make sound decisions or construct strategies ...
The adversarial stochastic shortest path problem with unknown
... Note that our problem formulation implies that each path from the initial state to the terminal state consists of exactly L transitions. While this assumptions may seem restrictive, it is not: all loop-free state spaces (with varying path lengths) can easily be transformed to one that satisfies our ...
... Note that our problem formulation implies that each path from the initial state to the terminal state consists of exactly L transitions. While this assumptions may seem restrictive, it is not: all loop-free state spaces (with varying path lengths) can easily be transformed to one that satisfies our ...
methodology for elliott waves pattern recognition
... uses seven rules, which classify waves into groups depending on a ratio of heights of neighbouring waves. The rules use Fibonacci ratios with a deviation of 5%. The only possibility of searching is to check each monowave through the conditions and some experience of a researcher is expected as well. ...
... uses seven rules, which classify waves into groups depending on a ratio of heights of neighbouring waves. The rules use Fibonacci ratios with a deviation of 5%. The only possibility of searching is to check each monowave through the conditions and some experience of a researcher is expected as well. ...
g(n)
... • Definition. f(n) has the higher order growth then g(n), if the ratio f(n)/g(n) goes to infinity as n goes to infinity. • Note: both f(n) and g(n) are functions taking on positive values and they are increasing functions starting from a certain point. ...
... • Definition. f(n) has the higher order growth then g(n), if the ratio f(n)/g(n) goes to infinity as n goes to infinity. • Note: both f(n) and g(n) are functions taking on positive values and they are increasing functions starting from a certain point. ...
Position Vectors, Force along a Line
... If force F is directed along the AB, then it can be expressed as a Cartesian vector, knowing that it has the same direction as the position vector ( r ) which is directed from A to B. The direction can be expressed using the unit vector (u) u = (r / r) where, ( r ) is the vector and ( r ) is its mag ...
... If force F is directed along the AB, then it can be expressed as a Cartesian vector, knowing that it has the same direction as the position vector ( r ) which is directed from A to B. The direction can be expressed using the unit vector (u) u = (r / r) where, ( r ) is the vector and ( r ) is its mag ...
The Disposition Table: Make it Easy
... macros has been developed. Thereby, merely a composition of loops, a single-letter comparison of strings and a certain weight on similarity had been installed within the calculation. The calculation is a self-development and therefore it is possible to vary / proportion the emphasis of the same stri ...
... macros has been developed. Thereby, merely a composition of loops, a single-letter comparison of strings and a certain weight on similarity had been installed within the calculation. The calculation is a self-development and therefore it is possible to vary / proportion the emphasis of the same stri ...
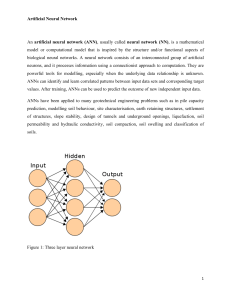
Artificial Neural Network An artificial neural network (ANN)
... Slope failures are complex natural phenomena that constitute a serious natural hazard in many countries. To prevent or mitigate the landslide damage, slope-stability analyses and stabilization require an understanding and evaluation of the processes that govern the behavior of the slopes. The factor ...
... Slope failures are complex natural phenomena that constitute a serious natural hazard in many countries. To prevent or mitigate the landslide damage, slope-stability analyses and stabilization require an understanding and evaluation of the processes that govern the behavior of the slopes. The factor ...
Chapter 6: The Normal Model
... In a Normal Probability Plot, the actual data values are plotted on one axis and each value’s theoretical z-score is plotted on the other axis. For example, in a data set with 100 values from a normal distribution, the smallest value should have a z-score of -2.58. If a data set closely follows a no ...
... In a Normal Probability Plot, the actual data values are plotted on one axis and each value’s theoretical z-score is plotted on the other axis. For example, in a data set with 100 values from a normal distribution, the smallest value should have a z-score of -2.58. If a data set closely follows a no ...
View PDF - CiteSeerX
... Feature selection is an effective technique in dealing with dimensionality reduction. For classification, it is used to find an “optimal” subset of relevant features such that the overall accuracy of classification is increased while the data size is reduced and the comprehensibility is improved. Fe ...
... Feature selection is an effective technique in dealing with dimensionality reduction. For classification, it is used to find an “optimal” subset of relevant features such that the overall accuracy of classification is increased while the data size is reduced and the comprehensibility is improved. Fe ...
Learning from Heterogeneous Sources via
... through the latent factor. There are mainly two differences between our work and the previous approaches. First, most of the previous works do not consider the vector-based features and the relational features simultaneously. Second and foremost, most of the previous works require the data sources t ...
... through the latent factor. There are mainly two differences between our work and the previous approaches. First, most of the previous works do not consider the vector-based features and the relational features simultaneously. Second and foremost, most of the previous works require the data sources t ...
SENSE in Chech Republik (SENSE_CENIA) - Eionet
... Content making SoER team wasn't aware that the result should be web presentation - change of approach needed, already written texts had to be rewrited ...
... Content making SoER team wasn't aware that the result should be web presentation - change of approach needed, already written texts had to be rewrited ...
+ p - Fizyka UMK
... • Rules may expose limitations of black box solutions. • Only relevant features are used in rules. • Rules may sometimes be more accurate than NN and other CI methods. • Overfitting is easy to control, rules usually have small number of parameters. • Rules forever !? A logical rule about logical rul ...
... • Rules may expose limitations of black box solutions. • Only relevant features are used in rules. • Rules may sometimes be more accurate than NN and other CI methods. • Overfitting is easy to control, rules usually have small number of parameters. • Rules forever !? A logical rule about logical rul ...
Document
... table for the premisses and the conclusion. A conclusion is invalid if we can find a counterexample case: a case in which both premisses are true, but the conclusion is false. ...
... table for the premisses and the conclusion. A conclusion is invalid if we can find a counterexample case: a case in which both premisses are true, but the conclusion is false. ...
Example: Amplifier Distortion
... For the BJT to remain in active mode, vCE (t ) must remain greater than 0.7 V for all time t (or equivalently vCB (t ) > 0.0 ). From an earlier handout, we know that VE = 5.05 V . The large capacitor on the emitter keeps this voltage constant with respect to time. Therefore, the voltage vCE (t ) wil ...
... For the BJT to remain in active mode, vCE (t ) must remain greater than 0.7 V for all time t (or equivalently vCB (t ) > 0.0 ). From an earlier handout, we know that VE = 5.05 V . The large capacitor on the emitter keeps this voltage constant with respect to time. Therefore, the voltage vCE (t ) wil ...
ObjectRecognition - CIS @ Temple University
... environment, while considering real life applications of Object Recognition/Navigation in Artificial Intelligence. Included in the project will be a simulation program demonstrating how Artificial Intelligence functions within the Object Recognition/Navigation environment. I’m thinking along the lin ...
... environment, while considering real life applications of Object Recognition/Navigation in Artificial Intelligence. Included in the project will be a simulation program demonstrating how Artificial Intelligence functions within the Object Recognition/Navigation environment. I’m thinking along the lin ...