An efficient factorization for the noisy MAX - CISIAD
... Dı́ez’s algorithm for the noisy MAX is very efficient for polytrees, but when the network has loops it has to be combined with local conditioning, a suboptimal propagation algorithm. Other algorithms, based on several factorizations of the conditional probability of the noisy MAX, are not as efficie ...
... Dı́ez’s algorithm for the noisy MAX is very efficient for polytrees, but when the network has loops it has to be combined with local conditioning, a suboptimal propagation algorithm. Other algorithms, based on several factorizations of the conditional probability of the noisy MAX, are not as efficie ...
1 HYBRID EXPERT SYSTEM OF ROUGH SET AND NEURAL
... significant input variables for evaluating an output goal. Two drawbacks of this method are: inefficient backward chaining mechanism and lack of explanation in inferential process. Glorfeld [3] presents a methodology to simplify network models by using a backward selection process to eliminate input ...
... significant input variables for evaluating an output goal. Two drawbacks of this method are: inefficient backward chaining mechanism and lack of explanation in inferential process. Glorfeld [3] presents a methodology to simplify network models by using a backward selection process to eliminate input ...
An information-theoretic approach to curiosity
... so far is lacking any notion of curiosity. Apart from the rate constraint, the agent is just maximizing the return, as defined based on external rewards received from the environment. In this section, we present a formalization of curiosity based on information-theoretic principles. Drawing on ideas ...
... so far is lacking any notion of curiosity. Apart from the rate constraint, the agent is just maximizing the return, as defined based on external rewards received from the environment. In this section, we present a formalization of curiosity based on information-theoretic principles. Drawing on ideas ...
beekman7_ppt_15
... The questions can be about anything—math, science, politics, sports, entertainment, art, human relationships, emotions, etc. As answers to the questions asked appear on the screen, the interrogator attempts to guess whether those answers were typed by the other person or generated by the computer ...
... The questions can be about anything—math, science, politics, sports, entertainment, art, human relationships, emotions, etc. As answers to the questions asked appear on the screen, the interrogator attempts to guess whether those answers were typed by the other person or generated by the computer ...
Inductive Logic Programming
... of first order logic [Van Laer and De Raedt, 2001]. By examining state-of-the-art inductive logic programming systems one can identify a methodology for realizing this [Van Laer and De Raedt, 2001]. It starts from an attribute-value learning problem and system of interest, and takes the following tw ...
... of first order logic [Van Laer and De Raedt, 2001]. By examining state-of-the-art inductive logic programming systems one can identify a methodology for realizing this [Van Laer and De Raedt, 2001]. It starts from an attribute-value learning problem and system of interest, and takes the following tw ...
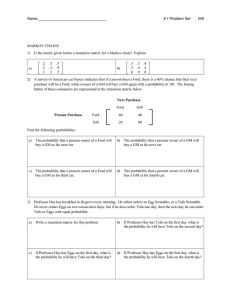
MARKOV CHAINS
... A survey of American car buyers indicates that if a person buys a Ford, there is a 60% chance that their next purchase will be a Ford, while owners of a GM will buy a GM again with a probability of .80. The buying habits of these consumers are represented in the transition matrix below. ...
... A survey of American car buyers indicates that if a person buys a Ford, there is a 60% chance that their next purchase will be a Ford, while owners of a GM will buy a GM again with a probability of .80. The buying habits of these consumers are represented in the transition matrix below. ...