Classification of Deforestation Factors Using Data Mining
... referred as Data mining [5]. Classification is one of the data mining task, the objective of the classification is to build a model in training data set to predict the class of future objects whose class label is not known [2][13]. There are lots of classification algorithms, for example, classifica ...
... referred as Data mining [5]. Classification is one of the data mining task, the objective of the classification is to build a model in training data set to predict the class of future objects whose class label is not known [2][13]. There are lots of classification algorithms, for example, classifica ...
Agent-Based Hybrid Intelligent Systems and Their Dynamic
... where d denotes the number of genes in subset s, and g j is the jth gene in subset s. ...
... where d denotes the number of genes in subset s, and g j is the jth gene in subset s. ...
Linear fit
... and the image of linear transformations helps to understand this situation and leads to an explicit formulas for the least square fit. Why do we care about non-consistent systems? Often we have to solve linear systems of equations with more constraints than variables. An example is when we try to fi ...
... and the image of linear transformations helps to understand this situation and leads to an explicit formulas for the least square fit. Why do we care about non-consistent systems? Often we have to solve linear systems of equations with more constraints than variables. An example is when we try to fi ...
Raymond J. Mooney Need for Probabilistic
... probability estimates are adjusted or smoothed. • Laplace smoothing using an m-estimate assumes that each feature is given a prior probability, p, that is assumed to have been previously observed in a “virtual” sample of size m. P( X i = xij | Y = yk ) = ...
... probability estimates are adjusted or smoothed. • Laplace smoothing using an m-estimate assumes that each feature is given a prior probability, p, that is assumed to have been previously observed in a “virtual” sample of size m. P( X i = xij | Y = yk ) = ...
[Part 1]
... where u(k) is the control input to the system at discrete time instant k, and x(k) is a state variable of the system at the same instant. ...
... where u(k) is the control input to the system at discrete time instant k, and x(k) is a state variable of the system at the same instant. ...
This Is a Publication of The American Association
... make it easier for other people to run comparative studies. They may show how bad your system is, but that is what science is all about. Kerschberg took an engineering view. He suggested taking some of the existing algorithms and seeing how they scale up on very large databases. It is not so importa ...
... make it easier for other people to run comparative studies. They may show how bad your system is, but that is what science is all about. Kerschberg took an engineering view. He suggested taking some of the existing algorithms and seeing how they scale up on very large databases. It is not so importa ...
A180 / SMA180 Cascadable Amplifier 10 to 500 MHz
... and/or prototype measurements. Commitment to develop is not guaranteed. Visit www.macomtech.com for additional data sheets and product information. PRELIMINARY: Data Sheets contain information regarding a product M/A-COM Technology Solutions has under development. Performance is based on engineering ...
... and/or prototype measurements. Commitment to develop is not guaranteed. Visit www.macomtech.com for additional data sheets and product information. PRELIMINARY: Data Sheets contain information regarding a product M/A-COM Technology Solutions has under development. Performance is based on engineering ...
lesson plan
... Introduction to Genetic Algorithms (GA) – Applications of GA in Machine Learning – Machine Learning Approach to Knowledge Acquisition. Objective : To impart knowledge on genetic algorithms and their applications. ...
... Introduction to Genetic Algorithms (GA) – Applications of GA in Machine Learning – Machine Learning Approach to Knowledge Acquisition. Objective : To impart knowledge on genetic algorithms and their applications. ...
Anomaly, Event, and Fraud Detection in Large Network
... Given the long list of applications and challenges they pose, abnormality detection is a very popular research topic. Not only the problems are mathematically interesting from a scientific point of view but, with their many applications in diverse fields, are also appealing from practitioners’ point ...
... Given the long list of applications and challenges they pose, abnormality detection is a very popular research topic. Not only the problems are mathematically interesting from a scientific point of view but, with their many applications in diverse fields, are also appealing from practitioners’ point ...
April 4, 2017 (20th Annual Tribal Environmental
... • More Result data in WQX than via any other single source • 17% of Result data in WQX flowed to WQX via AWQMS ...
... • More Result data in WQX than via any other single source • 17% of Result data in WQX flowed to WQX via AWQMS ...
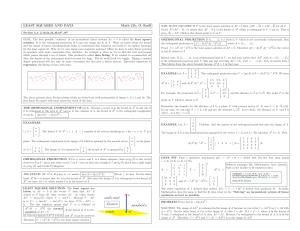
10.3: Limits and Continuity: Algebraic Approach
... A function is written in closed form if it is specified by combining constants, powers of x, exponential functions, radicals, logarithms, absolute values, trigonometric functions (and some other functions we do not encounter in this text) into a single mathematical formula by means of the usual arit ...
... A function is written in closed form if it is specified by combining constants, powers of x, exponential functions, radicals, logarithms, absolute values, trigonometric functions (and some other functions we do not encounter in this text) into a single mathematical formula by means of the usual arit ...








![[Part 1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008795794_1-80a9f1ca3e285d5b53c1894ae34bae80-300x300.png)