PDF
... Dirtiness, Bumps and Other_Faults. The models include C5.0 decision tree (C5.0 DT) with boosting, Multi Perceptron Neural Network (MLPNN) with pruning and logistic regression (LR) with step forward. DTs focus on conveying the relationship among the rules that expressed the results. They have express ...
... Dirtiness, Bumps and Other_Faults. The models include C5.0 decision tree (C5.0 DT) with boosting, Multi Perceptron Neural Network (MLPNN) with pruning and logistic regression (LR) with step forward. DTs focus on conveying the relationship among the rules that expressed the results. They have express ...
Unit 3 Topics
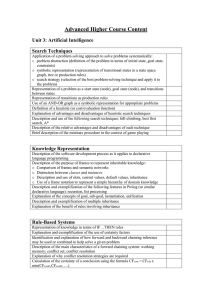
... o symbolic representation (representation of transitional states in a state space graph, tree or production rules) o search strategy (selection of the best problem-solving technique and apply it to the problem) Representation of a problem as a start state (node), goal state (node), and transitions b ...
... o symbolic representation (representation of transitional states in a state space graph, tree or production rules) o search strategy (selection of the best problem-solving technique and apply it to the problem) Representation of a problem as a start state (node), goal state (node), and transitions b ...
hw6soln
... [8pts. 2 for each line] b. calculate and tabulate Id, Vov, gm, ro, Cgs, and Cgd for all devices [18pts – ½ pt for each entry in the table above] c. calculate the 1st and 2nd stage gain, and the overall gain for both differential and common mode signals. [5 pts. 2 each for 1st and 2nd, 1 for overall] ...
... [8pts. 2 for each line] b. calculate and tabulate Id, Vov, gm, ro, Cgs, and Cgd for all devices [18pts – ½ pt for each entry in the table above] c. calculate the 1st and 2nd stage gain, and the overall gain for both differential and common mode signals. [5 pts. 2 each for 1st and 2nd, 1 for overall] ...
Contextually Supervised Source Separation with Application to
... bases are represented and assigned to different signal components and 2) how the algorithm infers the activation of the different bases given the aggregate signal. For example, PLCA typically uses pre-defined basis functions (commonly Fourier or Wavelet bases), with a probabilistic model for how sou ...
... bases are represented and assigned to different signal components and 2) how the algorithm infers the activation of the different bases given the aggregate signal. For example, PLCA typically uses pre-defined basis functions (commonly Fourier or Wavelet bases), with a probabilistic model for how sou ...
Genetic Algorithm and their applicability in Medical Diagnostic
... represented classification and feature extraction for high dimensionally pattern using genetic algorithm by their research work. ...
... represented classification and feature extraction for high dimensionally pattern using genetic algorithm by their research work. ...
Drs._Communication OL Win14
... Your individual speeches must also have an introduction and conclusion tailored to your particular speech (as in the problem main point or the solution main point) In these introductions you DO NOT need an adaptation statement since the relevance of the topic will be made known to us in the general ...
... Your individual speeches must also have an introduction and conclusion tailored to your particular speech (as in the problem main point or the solution main point) In these introductions you DO NOT need an adaptation statement since the relevance of the topic will be made known to us in the general ...
9th Grade Chapter 1 - 2 Review Worksheet 1. Classify each function
... Identify the input value, the output value, the y-intercept, and the rate of change for each function. 10. A hot air balloon at 130 feet begins to ascend. It ascends at a rate of 160.5 feet per minute. The function represents the height of the balloon as it ascends. ...
... Identify the input value, the output value, the y-intercept, and the rate of change for each function. 10. A hot air balloon at 130 feet begins to ascend. It ascends at a rate of 160.5 feet per minute. The function represents the height of the balloon as it ascends. ...
Streaming String Transducers - the Department of Computer and
... Checking Equivalence of SSTs S and S’ (4) Propagate classification of variables consistently. Add a counter to check assumption about lengths When S adds symbols to L vars & to left in M vars, increment; When S’ adds symbols to L vars & to left of M vars, decrement ...
... Checking Equivalence of SSTs S and S’ (4) Propagate classification of variables consistently. Add a counter to check assumption about lengths When S adds symbols to L vars & to left in M vars, increment; When S’ adds symbols to L vars & to left of M vars, decrement ...
Sparrow2011
... notation that a positive score corresponds to an increase in the number of satisfied clauses if the variable were to be flipped. The behaviour of S PARROW differs from G N OVELTY+ when there are no (penalized) promising variables. S PARROW replaces the WALK SAT-based component in G N OVELTY+ with a ...
... notation that a positive score corresponds to an increase in the number of satisfied clauses if the variable were to be flipped. The behaviour of S PARROW differs from G N OVELTY+ when there are no (penalized) promising variables. S PARROW replaces the WALK SAT-based component in G N OVELTY+ with a ...