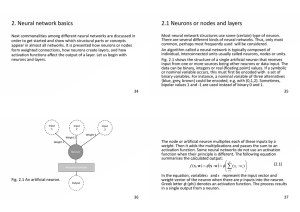
2. Neural network basics 2.1 Neurons or nodes and layers
... Most neural network structures use some (certain) type of neuron. There are several different kinds of neural networks. Thus, only most common, perhaps most frequently used will be considered. An algorithm called a neural network is typically composed of individual, interconnected units usually call ...
... Most neural network structures use some (certain) type of neuron. There are several different kinds of neural networks. Thus, only most common, perhaps most frequently used will be considered. An algorithm called a neural network is typically composed of individual, interconnected units usually call ...
nips2.frame - /marty/papers/drotdil
... receptive field. Regions of maximum weights in direction-speed subspace tended to vary smoothly across x-y space such that opposite ends of the receptive field were sensitive to opposite directions. This picture obtained with full and medium-sized partial field training examples, breaking down only ...
... receptive field. Regions of maximum weights in direction-speed subspace tended to vary smoothly across x-y space such that opposite ends of the receptive field were sensitive to opposite directions. This picture obtained with full and medium-sized partial field training examples, breaking down only ...
Machine Learning
... learning beginning with topics, machine learning ibm analytics - machine learning infuse continuous intelligence into your enterprise using machine learning dramatically improve the productivity of your data science team, machine learning gartner it glossary - advanced machine learning algorithms ar ...
... learning beginning with topics, machine learning ibm analytics - machine learning infuse continuous intelligence into your enterprise using machine learning dramatically improve the productivity of your data science team, machine learning gartner it glossary - advanced machine learning algorithms ar ...
MS PowerPoint 97/2000 format
... If every undirected path from a node in X to a node in Y is d-separated by E, then X and Y are conditionally independent given E. – D-separate A set of node E d-separates two sets of nodes X and Y if every undirected path from a node in X to a node in Y is blocked given E. ...
... If every undirected path from a node in X to a node in Y is d-separated by E, then X and Y are conditionally independent given E. – D-separate A set of node E d-separates two sets of nodes X and Y if every undirected path from a node in X to a node in Y is blocked given E. ...
- Amazon Web Services
... Most text mining requires data resources as well as source code. The need for data resources does not fit well 17 into the open source paradigm. ...
... Most text mining requires data resources as well as source code. The need for data resources does not fit well 17 into the open source paradigm. ...
Artificial Intelligence
... • El Niños tend to happen once every 10 years • The chance of a split jet stream given an El Niño event is 0.5 • The chance of a split jet stream without an El Niño is 0.1 • The chance that there will be a wet winter in the SW, given a split jet stream, is 0.5 while it is 0.1 when there is not a spl ...
... • El Niños tend to happen once every 10 years • The chance of a split jet stream given an El Niño event is 0.5 • The chance of a split jet stream without an El Niño is 0.1 • The chance that there will be a wet winter in the SW, given a split jet stream, is 0.5 while it is 0.1 when there is not a spl ...
15-451 Homework 1 Jan 20, 2008
... 1. Given a fair 6-sided die: (a) What is the probability that X (the outcome) is 1? (b) What is the probability that X is even? (c) What is the probability that X ≥ 5? 2. Given two independent, fair 6-sided dice: (a) What is the probability that X1 = 1 and X2 = 1? (b) What is the probability that X1 ...
... 1. Given a fair 6-sided die: (a) What is the probability that X (the outcome) is 1? (b) What is the probability that X is even? (c) What is the probability that X ≥ 5? 2. Given two independent, fair 6-sided dice: (a) What is the probability that X1 = 1 and X2 = 1? (b) What is the probability that X1 ...
Use of AI in the Logistics Sector : Case Study of Improving
... The big data collected by work systems consists of several different types of data such as numerical quantities, times, and product codes, along with text and symbols. So, for all this data to be entered into an analytical system, it must be tagged in advance by experts with knowledge of the industr ...
... The big data collected by work systems consists of several different types of data such as numerical quantities, times, and product codes, along with text and symbols. So, for all this data to be entered into an analytical system, it must be tagged in advance by experts with knowledge of the industr ...
Algorithms
... A program is a formal representation of an algorithm, which can be executed by a computer A process is the activity of executing an algorithm (or equivalently, a program) ...
... A program is a formal representation of an algorithm, which can be executed by a computer A process is the activity of executing an algorithm (or equivalently, a program) ...
A Behavior Based Intrusion Detection System Using Machine
... Primarily, the human factors in information security breaches were researched, and two major questions came up at this stage. What types of human factors cause what kind of information security breaches? The purpose of asking this question is to identify information security breaches and human facto ...
... Primarily, the human factors in information security breaches were researched, and two major questions came up at this stage. What types of human factors cause what kind of information security breaches? The purpose of asking this question is to identify information security breaches and human facto ...