Topic 2 Chapter 2: Simple Probability Samples
... • Often results will be similar to an SRS. • If there is a cyclic pattern in the list, results can be very bad. (Safeguard: do two or more systematic samples with different values of k.) • If there is a natural ordering in the list related to the outcome, the results can be better than an SRS. • Sys ...
... • Often results will be similar to an SRS. • If there is a cyclic pattern in the list, results can be very bad. (Safeguard: do two or more systematic samples with different values of k.) • If there is a natural ordering in the list related to the outcome, the results can be better than an SRS. • Sys ...
File - Glorybeth Becker
... 6. Which of the following statements regarding the sampling distribution of sample means is incorrect? A. The sampling distribution is approximately normal when the population is normal or the sample size is large. B. The mean of the sampling distribution is the mean of the population. C. The standa ...
... 6. Which of the following statements regarding the sampling distribution of sample means is incorrect? A. The sampling distribution is approximately normal when the population is normal or the sample size is large. B. The mean of the sampling distribution is the mean of the population. C. The standa ...
Document
... The population is first divided into groups of elements called strata. Each element in the population belongs to one and only one stratum. Best results are obtained when the elements within each stratum are as much alike as possible (i.e. homogeneous group). A simple random sample is taken from each ...
... The population is first divided into groups of elements called strata. Each element in the population belongs to one and only one stratum. Best results are obtained when the elements within each stratum are as much alike as possible (i.e. homogeneous group). A simple random sample is taken from each ...
x - Cameron University
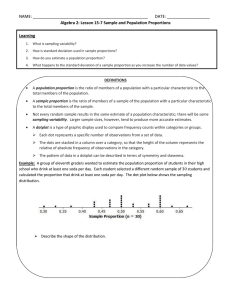
... When the expected value of a point estimator is equal to the population parameter, the point estimator is said to be unbiased. The absolute value of the difference between an unbiased point estimate and the corresponding population parameter is called the sampling error. Sampling error is the ...
... When the expected value of a point estimator is equal to the population parameter, the point estimator is said to be unbiased. The absolute value of the difference between an unbiased point estimate and the corresponding population parameter is called the sampling error. Sampling error is the ...
CHOOSING AMONG THE VARIOUS TYPES OF INTERNET SURVEYS
... to generate than probability samples, and thus are usually less costly. However, statistical inference is much more problematic with convenience samples. For example, in a survey about the environment, respondents who have an active interest in environmental issues may be more likely to self-select ...
... to generate than probability samples, and thus are usually less costly. However, statistical inference is much more problematic with convenience samples. For example, in a survey about the environment, respondents who have an active interest in environmental issues may be more likely to self-select ...
Inference about Mean (σ Unknown)
... mean is normal if condi>ons are sa>sfied. For many years, it was thought that when σ was unknown, this was s>ll the case. However, because of the increased variability introduced by not knowing σ, the sampling distribu>on for a sample mean with unknown σ is not normal. This was discovered by W ...
... mean is normal if condi>ons are sa>sfied. For many years, it was thought that when σ was unknown, this was s>ll the case. However, because of the increased variability introduced by not knowing σ, the sampling distribu>on for a sample mean with unknown σ is not normal. This was discovered by W ...
Sampling (statistics)
In statistics, quality assurance, and survey methodology, sampling is concerned with the selection of a subset of individuals from within a statistical population to estimate characteristics of the whole population. Each observation measures one or more properties (such as weight, location, color) of observable bodies distinguished as independent objects or individuals. In survey sampling, weights can be applied to the data to adjust for the sample design, particularly stratified sampling. Results from probability theory and statistical theory are employed to guide practice. In business and medical research, sampling is widely used for gathering information about a population .The sampling process comprises several stages: Defining the population of concern Specifying a sampling frame, a set of items or events possible to measure Specifying a sampling method for selecting items or events from the frame Determining the sample size Implementing the sampling plan Sampling and data collecting Data which can be selected↑ ↑