A Proposed `Megathrust Megaswath` OBS Deployment In
... earthquake processes that would help us better understand historical seismicity, crustal deformation, and crustal structure. It spans the M8.2 1938, M7.3 1948, ~M8.6 1946, and the M8.6 1957 megathrust ruptures, the Shumagin seismic gap, and it likely includes much of a region that ruptured during th ...
... earthquake processes that would help us better understand historical seismicity, crustal deformation, and crustal structure. It spans the M8.2 1938, M7.3 1948, ~M8.6 1946, and the M8.6 1957 megathrust ruptures, the Shumagin seismic gap, and it likely includes much of a region that ruptured during th ...
Lessons learned from the Tohoku earthquake / tsunami and
... geophysical measurements started before 2001 detected huge (30 to 50 m) seafloor displacements. By using these geodetic data, as well as seismological and tsunami data, numerous source models have been proposed. The seismic moment is approximately 4 x 1022 Nm (corresponding to Mw 9.0). Another commo ...
... geophysical measurements started before 2001 detected huge (30 to 50 m) seafloor displacements. By using these geodetic data, as well as seismological and tsunami data, numerous source models have been proposed. The seismic moment is approximately 4 x 1022 Nm (corresponding to Mw 9.0). Another commo ...
THE CASE FOR AN ADVANCED NATIONAL EARTHQUAKE
... significant earthquakes has been assessed. Three generations of seismic hazard maps have been produced at roughly 15-year intervals (1953, 1970, 1985; see Fig. 2), and a fourth generation is now justified (Basham, 1995). The GSC initially released a suite of new seismic hazard maps for trial use in ...
... significant earthquakes has been assessed. Three generations of seismic hazard maps have been produced at roughly 15-year intervals (1953, 1970, 1985; see Fig. 2), and a fourth generation is now justified (Basham, 1995). The GSC initially released a suite of new seismic hazard maps for trial use in ...
Wood-Frame Construction in Past Earthquakes
... Figure 1 Damaged two-story building with weak first storey; San Fernando Earthquake, 1971. Edgecumbe Earthquake, New Zealand, 1987 This event on the North Island consisted of a main shock of Magnitude 6.3, preceded by 7 minutes by a Magnitude 5.2 fore-shock, and followed by four aftershocks with Ma ...
... Figure 1 Damaged two-story building with weak first storey; San Fernando Earthquake, 1971. Edgecumbe Earthquake, New Zealand, 1987 This event on the North Island consisted of a main shock of Magnitude 6.3, preceded by 7 minutes by a Magnitude 5.2 fore-shock, and followed by four aftershocks with Ma ...
Fault, earthquake, elastic strain, focus, interact
... is directly above the focus, which means it is the shortest straight-line distance from the focus of the earthquake to the surface. Even though P- and S- waves move out from the focus in all directions, each type of wave moves at the same speed. Because they have to travel the shortest distance to ...
... is directly above the focus, which means it is the shortest straight-line distance from the focus of the earthquake to the surface. Even though P- and S- waves move out from the focus in all directions, each type of wave moves at the same speed. Because they have to travel the shortest distance to ...
Performance of Seismically Isolated Buildings at March 11, 2011
... performance of seismic isolation has become clear every time experiencing a large earthquake. However, since the seismic isolation techniques is still a new technology, it is necessary to consider the benefits of technology from various perspectives. From the investigation of 17 seismically isolated ...
... performance of seismic isolation has become clear every time experiencing a large earthquake. However, since the seismic isolation techniques is still a new technology, it is necessary to consider the benefits of technology from various perspectives. From the investigation of 17 seismically isolated ...
Pessimism - cloudfront.net
... Defending you conclusions: 9. Why is it necessary to use data from seismographs from three separate locations to find the epicenter of an earthquake: (Explain Table 3) ...
... Defending you conclusions: 9. Why is it necessary to use data from seismographs from three separate locations to find the epicenter of an earthquake: (Explain Table 3) ...
Earthquake Lab The goal of this portion of the lab is to learn how reco
... P-waves travel between 6 and 13 km/s. Swaves are slower and travel between 3.5 and 7.5 km/s. In most regions, study of numerous earthquakes with well-known epicenter locations results in an empirical S-P curve, such as the one shown to the right. ...
... P-waves travel between 6 and 13 km/s. Swaves are slower and travel between 3.5 and 7.5 km/s. In most regions, study of numerous earthquakes with well-known epicenter locations results in an empirical S-P curve, such as the one shown to the right. ...
Name Determining Earthquake Probabilities
... Sketch in a best-‐fit line to the data and extend it to cover the magnitude ranges for which you do not have data. ...
... Sketch in a best-‐fit line to the data and extend it to cover the magnitude ranges for which you do not have data. ...
Unit 1 student handout
... Sketch in a best-fit line to the data and extend it to cover the magnitude ranges for which you do not have data. ...
... Sketch in a best-fit line to the data and extend it to cover the magnitude ranges for which you do not have data. ...
Final Notice Regarding the Impact of the Great East Japan
... Final Notice Regarding the Impact of the Great East Japan Earthquake on Meiji Group We at Meiji Holdings Co., Ltd. would like to express our deepest sympathies to all those who have suffered from the Great East Japan Earthquake. We have issued a series of notices regarding the earthquake damages of ...
... Final Notice Regarding the Impact of the Great East Japan Earthquake on Meiji Group We at Meiji Holdings Co., Ltd. would like to express our deepest sympathies to all those who have suffered from the Great East Japan Earthquake. We have issued a series of notices regarding the earthquake damages of ...
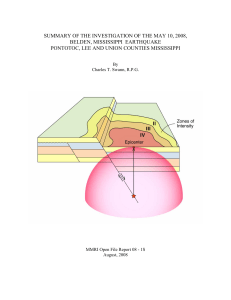
summary of the investigation of the may 10, 2008, belden
... are more subjective than magnitude values, requires interpretation by the analyst, and typically vary with distance from the epicenter. The intensity grade within an earthquake=s felt area is usually higher surrounding the epicenter (although exceptions have been noted) indicating more severe vibrat ...
... are more subjective than magnitude values, requires interpretation by the analyst, and typically vary with distance from the epicenter. The intensity grade within an earthquake=s felt area is usually higher surrounding the epicenter (although exceptions have been noted) indicating more severe vibrat ...
Earthquake Disaster Mitigation Research in Japan and International
... 1. Occurrence of a large earthquake is often a rare event for one country and accumulation of knowledge and experiences is usually slow if it is closed within the country. 2. An effective way to overcome such a problem is to collaborate with other countries facing the same problem and share knowl ...
... 1. Occurrence of a large earthquake is often a rare event for one country and accumulation of knowledge and experiences is usually slow if it is closed within the country. 2. An effective way to overcome such a problem is to collaborate with other countries facing the same problem and share knowl ...
Virtual Earthquake Name Date Objective: To use an on
... 27. Go to the following web site: http://earthquake.usgs.gov -- you will see a map under the heading “Latest Earthquakes”. Click on the map. Use the tool in the upper right corner of the map to zoom out until you can see a world map. Note the legend at the bottom of the screen. How do you distinguis ...
... 27. Go to the following web site: http://earthquake.usgs.gov -- you will see a map under the heading “Latest Earthquakes”. Click on the map. Use the tool in the upper right corner of the map to zoom out until you can see a world map. Note the legend at the bottom of the screen. How do you distinguis ...
LESSON
... Original content Copyright © by Holt McDougal. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt McDougal Algebra 2 ...
... Original content Copyright © by Holt McDougal. Additions and changes to the original content are the responsibility of the instructor. Holt McDougal Algebra 2 ...
URSI-Türkiye-2006 Bildirilerinin Yazım Kuralları
... It is well known that ionosphere plays a unique role in the Earth's environment because of strong coupling processes to regions below and above it [1]. There are many reports of possible links between ionospheric phenomena and events, e.g., earthquakes, volcanic explosions and severe weather, solar ...
... It is well known that ionosphere plays a unique role in the Earth's environment because of strong coupling processes to regions below and above it [1]. There are many reports of possible links between ionospheric phenomena and events, e.g., earthquakes, volcanic explosions and severe weather, solar ...
PDF
... encountered with a lot of destruction due to Earthquake. Similarly, Bhutan has been by the earthquake several times, until 21st September 2009, when earthquake of magnitude 6.1 has occurred in eastern Bhutan around 2:53:05pm local time. According to the Situation report: Earthquakes in Bhutan, India ...
... encountered with a lot of destruction due to Earthquake. Similarly, Bhutan has been by the earthquake several times, until 21st September 2009, when earthquake of magnitude 6.1 has occurred in eastern Bhutan around 2:53:05pm local time. According to the Situation report: Earthquakes in Bhutan, India ...
Keep It Up - Siemens Science Day
... experienced as minor bumps before the more destructive surface waves strike. ...
... experienced as minor bumps before the more destructive surface waves strike. ...
preparing a data base for estimating seismic damage on buildings
... After the main earthquake, a series of following tremors were registered in the area. Their magnitudes ranged from 1.0 to 4.4 degrees of the Richter scale. Those quakes of 2 degrees and below were only detected by instruments and could not be felt. During the interval of time until 1pm on November 9 ...
... After the main earthquake, a series of following tremors were registered in the area. Their magnitudes ranged from 1.0 to 4.4 degrees of the Richter scale. Those quakes of 2 degrees and below were only detected by instruments and could not be felt. During the interval of time until 1pm on November 9 ...
Constraints On The Rupture Mechanism Of The 2001 Bhuj
... latitude, in the region, which flooded in the pre-earthquake periods. Thus we suggest that this uplift prevented the flooded water to migrate to the north in the previously low-lying areas. The uplift has also led in shifting the southern limit of the waste salt land. Coseismic subsidence coincides ...
... latitude, in the region, which flooded in the pre-earthquake periods. Thus we suggest that this uplift prevented the flooded water to migrate to the north in the previously low-lying areas. The uplift has also led in shifting the southern limit of the waste salt land. Coseismic subsidence coincides ...
Earth Science Regents
... As you may recall, we use travel time graphs (Page 11 ESRT’s) to show how long it takes each type of seismic wave to travel a distance, measured on Earth’s surface. The difference between the S-wave arrival time and the Pwave arrival time corresponds to the distance of the seismograph from the focus ...
... As you may recall, we use travel time graphs (Page 11 ESRT’s) to show how long it takes each type of seismic wave to travel a distance, measured on Earth’s surface. The difference between the S-wave arrival time and the Pwave arrival time corresponds to the distance of the seismograph from the focus ...
Review for Exam 3
... 11. What factors determine the seismic intensity of a particular event at a given location? 12. Why do insurance companies use the Modified Mecalli intensity scale instead of a magnitude scale in classifying earthquakes? 13. Describe how a tsunami is generated by an earthquake. 14. Describe the two ...
... 11. What factors determine the seismic intensity of a particular event at a given location? 12. Why do insurance companies use the Modified Mecalli intensity scale instead of a magnitude scale in classifying earthquakes? 13. Describe how a tsunami is generated by an earthquake. 14. Describe the two ...
Kanamori layout.indd MH.indd
... Figure 1 | Comparison of rupture area and magnitude. Use of very longperiod (> 200 s) waves removed the saturation problem of the old surfacewave magnitude, M, which saturates above 8 and gives approximately the same values for great earthquakes regardless of the size of the rupture area inferred ma ...
... Figure 1 | Comparison of rupture area and magnitude. Use of very longperiod (> 200 s) waves removed the saturation problem of the old surfacewave magnitude, M, which saturates above 8 and gives approximately the same values for great earthquakes regardless of the size of the rupture area inferred ma ...
Structural Damage in Mexico City
... The predominant two-second period in the ground motion recorded at the SCT site on the lake bed (Beck and Hall, 1986) suggests that structures with fundamental periods of elastic ...
... The predominant two-second period in the ground motion recorded at the SCT site on the lake bed (Beck and Hall, 1986) suggests that structures with fundamental periods of elastic ...
Effect of structural irregularities and short columns on
... buildings were heavily damaged or collapsed due to short column failures during the earthquakes. Since this kind of damage to reinforced concrete (RC) framed buildings is frequently encountered. short column incidents are seperately investigated. Further. architectural based damage to buildings are ...
... buildings were heavily damaged or collapsed due to short column failures during the earthquakes. Since this kind of damage to reinforced concrete (RC) framed buildings is frequently encountered. short column incidents are seperately investigated. Further. architectural based damage to buildings are ...
2010 Canterbury earthquake
The 2010 Canterbury earthquake (also known as the Christchurch earthquake or Darfield earthquake) struck the South Island of New Zealand with a moment magnitude of 7.1 at 4:35 a.m. local time on 4 September, and had a maximum perceived intensity of X (Extreme) on the Mercalli Intensity Scale. Some damaging aftershocks followed the main event, the strongest of which was a magnitude 6.3 shock that occurred on 22 February 2011. Because this aftershock was centred very close to Christchurch, it was much more destructive and resulted in the deaths of 185 people, and was felt from Invercargill to Wellington.The main shock caused widespread damage and several power outages, particularly in the city of Christchurch, New Zealand's second largest city. Two residents were seriously injured, one by a collapsing chimney and a second by flying glass. One person died of a heart attack suffered during the quake, although this could not be directly linked to the earthquake. Mass fatalities were avoided partly due to there being few houses of unreinforced construction, although this was also aided by the quake occurring during the night when most people were off the street.The earthquake's epicentre was 40 kilometres (25 mi) west of Christchurch, near the town of Darfield. The hypocentre was at a shallow depth of 10 km. A foreshock of roughly magnitude 5.8 hit five seconds before the main quake, and strong aftershocks have been reported, up to magnitude 6.3.The initial quake lasted about 40 seconds, and was felt widely across the South Island, and in the North Island as far north as New Plymouth. As the epicentre was on land away from the coast, no tsunami occurred.The National Crisis Management Centre in the basement of the Beehive in Wellington was activated, and Civil Defence declared a state of emergency for Christchurch, the Selwyn District, and the Waimakariri District, while Selwyn District, Waimakariri and Timaru activated their emergency operation centres. Initially, a curfew was established for parts of Christchurch Central City from 7:00 pm to 7:00 am in response to the earthquake. The New Zealand Army was deployed to the worst affected areas in Canterbury.Claims from the earthquake were confirmed at being between $2.75 and $3.5 billion NZD.