The Rise of Sumer
... and social structure ; the stage of cultural development at which writing and the keeping of written records is attained ...
... and social structure ; the stage of cultural development at which writing and the keeping of written records is attained ...
Powerpoint link
... • Built walls to protect the cities from invaders • Traded for resources needed w/ other cities – Traded grain and cloth for wood, metal and tools ...
... • Built walls to protect the cities from invaders • Traded for resources needed w/ other cities – Traded grain and cloth for wood, metal and tools ...
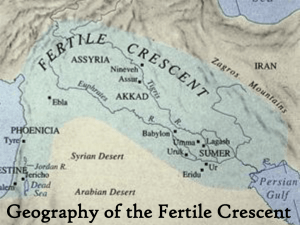
Fertile Crescent
... • Sumerians were great inventors, they invented irrigation systems, wheeled vehicles, the potter’s wheel, and sailboats. • The invention of the wheel greatly helped trade as they could now use horse powered carts to move goods, and helped in battle with the use of war chariots. The wheel also helpe ...
... • Sumerians were great inventors, they invented irrigation systems, wheeled vehicles, the potter’s wheel, and sailboats. • The invention of the wheel greatly helped trade as they could now use horse powered carts to move goods, and helped in battle with the use of war chariots. The wheel also helpe ...
Mesopotamia - White Plains Public Schools
... - About 2350 B.C., a conqueror named Sargon defeated the city-states of Sumer ...
... - About 2350 B.C., a conqueror named Sargon defeated the city-states of Sumer ...
Sumeria and the Fertile Crescent
... Ziggurats were built to honor the gods (or chief god of their city-state) and offered sacrifices to them there ...
... Ziggurats were built to honor the gods (or chief god of their city-state) and offered sacrifices to them there ...
Mesopotamia and the Fertile Crescent
... Ur was one of the earliest and largest cities of ancient Mesopotamia. This great trading center and port was home to roughly 30,000 people. Located on the Euphrates Ricer near the Persian Gulf, Ur carried on a rich trade with merchants from distant lands like India. ...
... Ur was one of the earliest and largest cities of ancient Mesopotamia. This great trading center and port was home to roughly 30,000 people. Located on the Euphrates Ricer near the Persian Gulf, Ur carried on a rich trade with merchants from distant lands like India. ...
Mesopotamia and Ancient Egypt
... Around 4500 B.C., people began settling in this area. Farming Revolution-People could produce their own food and not have to travel to get it. 12 month calendar was used based on the phases of the moon. With a steady food supply, the population ...
... Around 4500 B.C., people began settling in this area. Farming Revolution-People could produce their own food and not have to travel to get it. 12 month calendar was used based on the phases of the moon. With a steady food supply, the population ...
T H E T Y N D A L E H O U S E B U L L E T I N
... The excavation, between the wars, of such sites as Mari (1933-39), Alalakh (1936-39), and Nuzi (1925-31), has thrown considerable light on the time of Abraham and the patriarchs, and the post-war excavations are constantly adding to the picture. Cuneiform tablets from Mari and Alalakh, dating from t ...
... The excavation, between the wars, of such sites as Mari (1933-39), Alalakh (1936-39), and Nuzi (1925-31), has thrown considerable light on the time of Abraham and the patriarchs, and the post-war excavations are constantly adding to the picture. Cuneiform tablets from Mari and Alalakh, dating from t ...
Mesopotamia
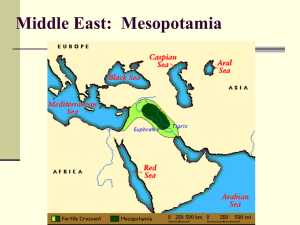
... (The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers) BUT = land between the rivers was inhospitable. Sudden flooding could cause death. It was in this area that humans first gave up their nomadic lifestyle and settled down into permanent settlements. ...
... (The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers) BUT = land between the rivers was inhospitable. Sudden flooding could cause death. It was in this area that humans first gave up their nomadic lifestyle and settled down into permanent settlements. ...
Akkadian Empire

The Akkadian Empire /əˈkeɪdiən/ was an ancient Semitic empire centered in the city of Akkad /ˈækæd/ and its surrounding region, also called Akkad in ancient Mesopotamia. The empire united all the indigenous Akkadian-speaking Semites and the Sumerian speakers under one rule. The Akkadian Empire controlled Mesopotamia, the Levant, and parts of Iran.During the 3rd millennium BC, there developed a very intimate cultural symbiosis between the Sumerians and the Semitic Akkadians, which included widespread bilingualism. Akkadian gradually replaced Sumerian as a spoken language somewhere between the 3rd and the 2nd millennia BC (the exact dating being a matter of debate).The Akkadian Empire reached its political peak between the 24th and 22nd centuries BC, following the conquests by its founder Sargon of Akkad (2334–2279 BC). Under Sargon and his successors, Akkadian language was briefly imposed on neighboring conquered states such as Elam. Akkad is sometimes regarded as the first empire in history, though there are earlier Sumerian claimants.After the fall of the Akkadian Empire, the Akkadian people of Mesopotamia eventually coalesced into two major Akkadian speaking nations: Assyria in the north, and, a few centuries later, Babylonia in the south.