Discrete time Fourier transform and its Properties
... DTFT is unstable which means that for a bounded 'x[n]' it gives an unbounded output. We saw its time shifting & frequency shifting properties & also time scaling & frequency scaling. Convolution Property for an LSI system is given as, if 'x[n]' is the input to a system with transfer function 'h[n] t ...
... DTFT is unstable which means that for a bounded 'x[n]' it gives an unbounded output. We saw its time shifting & frequency shifting properties & also time scaling & frequency scaling. Convolution Property for an LSI system is given as, if 'x[n]' is the input to a system with transfer function 'h[n] t ...
Smoothness of Densities on Compact Lie Groups
... In the second part of our paper we turn our attention to measures with smooth densities. A key element of our approach is the important insight of b of the group G can be parameterised Hermann Weyl that the unitary dual G b to investigation by the space of highest weights. This effectively opens up G ...
... In the second part of our paper we turn our attention to measures with smooth densities. A key element of our approach is the important insight of b of the group G can be parameterised Hermann Weyl that the unitary dual G b to investigation by the space of highest weights. This effectively opens up G ...
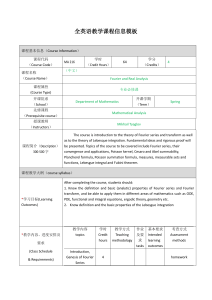
Document
... You can use the ztrans() function which is part of the symbolic toolbox. It evaluates signals x[n]u[n], i.e. for non-negative values of n. syms k n w z ztrans(2^n) % returns z/(z-2) ztrans(0.5^n) % returns z/(z-0.5) ztrans(sin(k*n),w) ...
... You can use the ztrans() function which is part of the symbolic toolbox. It evaluates signals x[n]u[n], i.e. for non-negative values of n. syms k n w z ztrans(2^n) % returns z/(z-2) ztrans(0.5^n) % returns z/(z-0.5) ztrans(sin(k*n),w) ...
Lecture05_waves_and_discontinuities
... sample contained no energy above the Nyquist frequency. To reproduce the original time series a(t) from its samples ak=a(kt) we can use Shannon's theorem, which states that if the signal contains no power above frequency N/2Hz, it can be reconstructed from N measurements. ...
... sample contained no energy above the Nyquist frequency. To reproduce the original time series a(t) from its samples ak=a(kt) we can use Shannon's theorem, which states that if the signal contains no power above frequency N/2Hz, it can be reconstructed from N measurements. ...
PDF file - UC Davis Mathematics
... 4) Compare the speed of the decay of the Fourier coefficients of this function with these different values of σ; 5) Compare these decays with those of Problems 3 and 4. Which decays faster? Why? 6) Do they agree with the discretized version of the Fourier transform formula of Problem 3 of HW #1 (wit ...
... 4) Compare the speed of the decay of the Fourier coefficients of this function with these different values of σ; 5) Compare these decays with those of Problems 3 and 4. Which decays faster? Why? 6) Do they agree with the discretized version of the Fourier transform formula of Problem 3 of HW #1 (wit ...
PPT - Jung Y. Huang
... DFT propagation. Note that this step occurs only after we have multiplied the field by a quadratic phase factor: ...
... DFT propagation. Note that this step occurs only after we have multiplied the field by a quadratic phase factor: ...
2. HARMONIC ANALYSIS ON COMPACT
... maximal compact subgroups of real reductive Lie groups. But much of the early material makes no use of the Lie group structure, so I’ll work without it for as long as possible. Thanks to Ben Harris (2007) for correcting a number of slips of the keyboard and the mind. You may wonder where in real lif ...
... maximal compact subgroups of real reductive Lie groups. But much of the early material makes no use of the Lie group structure, so I’ll work without it for as long as possible. Thanks to Ben Harris (2007) for correcting a number of slips of the keyboard and the mind. You may wonder where in real lif ...
Introduction to Tomography - Engineering School Class Web Sites
... Idea: use the projection data to get slices of the Fourier transform of the object image. Then, calculate the object image ...
... Idea: use the projection data to get slices of the Fourier transform of the object image. Then, calculate the object image ...
Midterm 2: Solutions Math 118A, Fall 2013 1. [25%] Find all
... • In summary, the solution of the IBVP is given by (2), where λn is given in (1), and bn is given in (3). • (b) This problem describes the flow of heat in a rod with a heat source whose strength is proportional to the temperature u. Both endpoints of the rod are held at a fixed temperature 0, and th ...
... • In summary, the solution of the IBVP is given by (2), where λn is given in (1), and bn is given in (3). • (b) This problem describes the flow of heat in a rod with a heat source whose strength is proportional to the temperature u. Both endpoints of the rod are held at a fixed temperature 0, and th ...
Tyaglov_Fourier_and_Real_Analysis_Syllabus_Form
... The course is introduction to the theory of Fourier series and transform as well as to the theory of Lebesque integration. Fundamental ideas and rigorous proof will be presented. Topics of the course to be covered include Fourier series, their convergence and applications, Poisson kernel, Cesaro and ...
... The course is introduction to the theory of Fourier series and transform as well as to the theory of Lebesque integration. Fundamental ideas and rigorous proof will be presented. Topics of the course to be covered include Fourier series, their convergence and applications, Poisson kernel, Cesaro and ...
Functional analysis exercises 02
... ball of some positive radius, at 0, in Cn . Show that V violates the conclusion of the Baire category theorem, so is not complete-metrizable. Here Cauchy sequences {xn } are those such that, given a neighborhood N of 0, there is no such that xm − xn ∈ N for all m, n ≥ no . Show that Cauchy sequences ...
... ball of some positive radius, at 0, in Cn . Show that V violates the conclusion of the Baire category theorem, so is not complete-metrizable. Here Cauchy sequences {xn } are those such that, given a neighborhood N of 0, there is no such that xm − xn ∈ N for all m, n ≥ no . Show that Cauchy sequences ...
Paley-Wiener theorems
... since x → (ξ → e−ixξ ϕ(ξ) extends to a continuous smooth-function-valued function on the stereographicprojection one-point compactification of R, and Gelfand-Pettis applies. Thus, as expected, u b is integration against x → u(ξ → e−ixξ ). The smooth-function-valued function z → (ξ → e−izξ ) is holom ...
... since x → (ξ → e−ixξ ϕ(ξ) extends to a continuous smooth-function-valued function on the stereographicprojection one-point compactification of R, and Gelfand-Pettis applies. Thus, as expected, u b is integration against x → u(ξ → e−ixξ ). The smooth-function-valued function z → (ξ → e−izξ ) is holom ...
Fourier Series
... It is important to establish simple criteria which determine when a Fourier series converges. In this section we will develop conditions on f(x) that enable us to determine the sum of the Fourier series. One quite useful method to analyse the convergence properties is to express the partial sums of ...
... It is important to establish simple criteria which determine when a Fourier series converges. In this section we will develop conditions on f(x) that enable us to determine the sum of the Fourier series. One quite useful method to analyse the convergence properties is to express the partial sums of ...
solution of heat equation on a semi infinite line using
... rod which is insulated. For finding the solution we have derived the Fourier cosine transform for the I-function of one variable and then this transform is used to solve a boundary value problem for finding the temperature distribution near the end of the long rod which is insulated over the interva ...
... rod which is insulated. For finding the solution we have derived the Fourier cosine transform for the I-function of one variable and then this transform is used to solve a boundary value problem for finding the temperature distribution near the end of the long rod which is insulated over the interva ...
Homework 5 - UMass Math
... 3. Compute y = F8 c by the three steps of the Fast Fourier Transform, for each of c = (1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0) and c = (0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1). ...
... 3. Compute y = F8 c by the three steps of the Fast Fourier Transform, for each of c = (1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0) and c = (0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1). ...
Transport Equations: An Attempt of Analytical Solution and Application
... Initial condition: c(x,y,0)=f(x,y). ...
... Initial condition: c(x,y,0)=f(x,y). ...






![Midterm 2: Solutions Math 118A, Fall 2013 1. [25%] Find all](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014992809_1-16ed3d3489ed8ac8ee652c44f479db24-300x300.png)