Electromagnet - SuccessTutor
... • When an electric current (a.c.) from the mains flows through the coil, the soft iron hammer is magnetized with south pole and north pole alternately at the frequency equal to that of the mains. Thus the hammer is set into vibration at the same frequency. • Use T = 1/f, hence the time is obtained. ...
... • When an electric current (a.c.) from the mains flows through the coil, the soft iron hammer is magnetized with south pole and north pole alternately at the frequency equal to that of the mains. Thus the hammer is set into vibration at the same frequency. • Use T = 1/f, hence the time is obtained. ...
KidWind Kit Inventory List:
... The number of electrons in the outermost orbit of a conducting atom is a critical clue as to why some elements are good conductors. What are the characteristics of these conductor atom’s outer orbits that make them good conductors? ...
... The number of electrons in the outermost orbit of a conducting atom is a critical clue as to why some elements are good conductors. What are the characteristics of these conductor atom’s outer orbits that make them good conductors? ...
Discussion 11
... A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. A method to detect a magnetic field is to scatter iron filings and observe their pattern. An electromagnet is a wire coil in which the magnetic Iron filings that have oriented field is produced by the flow of an electric current. in th ...
... A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. A method to detect a magnetic field is to scatter iron filings and observe their pattern. An electromagnet is a wire coil in which the magnetic Iron filings that have oriented field is produced by the flow of an electric current. in th ...
02461-05.8 Physical Properties of Elect Circuits
... There are three basic components of an electrical circuit: voltage, current, and resistance. Voltage is a measure of the pressure of an electromotive force. In agricultural settings, the pressure or source of alternating current is usually the power company and voltage is carried over power transmis ...
... There are three basic components of an electrical circuit: voltage, current, and resistance. Voltage is a measure of the pressure of an electromotive force. In agricultural settings, the pressure or source of alternating current is usually the power company and voltage is carried over power transmis ...
Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
... The current as seen from points A and B (in the plane of paper and on the axis of the coil) is anti clockwise and clockwise respectively. The magnetic field lines point from B to A. The N-pole of the resultant magnet is on the face close to (a) A (b) B (c) A if the current is small, and B if the cur ...
... The current as seen from points A and B (in the plane of paper and on the axis of the coil) is anti clockwise and clockwise respectively. The magnetic field lines point from B to A. The N-pole of the resultant magnet is on the face close to (a) A (b) B (c) A if the current is small, and B if the cur ...
Physics 12 Electromagnetic Induction
... coil is connected directly to a galvanometer (a device for measuring current). When the switch is closed there is a current in the primary circuit, causing the entire iron ring to become magnetized. This sudden increase in magnetic field strength causes a current to be induced momentarily in the sec ...
... coil is connected directly to a galvanometer (a device for measuring current). When the switch is closed there is a current in the primary circuit, causing the entire iron ring to become magnetized. This sudden increase in magnetic field strength causes a current to be induced momentarily in the sec ...
Lecture 10 - UConn Physics
... – What is the relation between the magnitudes of the forces on the two protons? ...
... – What is the relation between the magnitudes of the forces on the two protons? ...
Magnetism
... to do with it? In magnetized material, all or most of the magnetic fields are arranged in the same direction. A material that keeps its magnetism is called a permanent magnet. ...
... to do with it? In magnetized material, all or most of the magnetic fields are arranged in the same direction. A material that keeps its magnetism is called a permanent magnet. ...
HOTS Questions with Answers Magnetic Effects of Electric
... 1. Why does a current carrying conductor kept in a magnetic field experience force? On what factors does the direction of this force depend? Name and state the rule used for determination of direction of this force. Answer: Force on a conductor carrying current in a magnetic field :A.M. Ampere sugge ...
... 1. Why does a current carrying conductor kept in a magnetic field experience force? On what factors does the direction of this force depend? Name and state the rule used for determination of direction of this force. Answer: Force on a conductor carrying current in a magnetic field :A.M. Ampere sugge ...
Chapter 30.
... CT-3- Consider two parallel wires carrying currents I1 and I2 respectively. The wires are a small distance a apart. Which of the following (is) are true: A. If I1 = 2I2 and the directions of the currents are in the same direction, then the attractive force on the wire carrying I2 is 2 times that on ...
... CT-3- Consider two parallel wires carrying currents I1 and I2 respectively. The wires are a small distance a apart. Which of the following (is) are true: A. If I1 = 2I2 and the directions of the currents are in the same direction, then the attractive force on the wire carrying I2 is 2 times that on ...
intake structures uptake 316(b) regulations
... Many electrical workers have heard the expression, “It’s not the voltage that will kill you, it’s the current”. This is a true statement. It’s important to understand how much, or in reality, how little current it takes to affect the human body. Approximately, 10% of occupational deaths each year ar ...
... Many electrical workers have heard the expression, “It’s not the voltage that will kill you, it’s the current”. This is a true statement. It’s important to understand how much, or in reality, how little current it takes to affect the human body. Approximately, 10% of occupational deaths each year ar ...
3-phase short-circuit current (Isc) at any point within a LV installation
... In general, this fault-current contribution may be ignored. However, if the total power of motors running simultaneously is higher than 25% of the total power o Their total contribution can be estimated from the formula: Iscm = 3.5 In from each motor i.e. 3.5m In for m similar motors operating concu ...
... In general, this fault-current contribution may be ignored. However, if the total power of motors running simultaneously is higher than 25% of the total power o Their total contribution can be estimated from the formula: Iscm = 3.5 In from each motor i.e. 3.5m In for m similar motors operating concu ...
Motors and Generators Lab - University of Michigan SharePoint Portal
... 1. Motors use the magnetic force on a current-carrying wire to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. 2. Generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. 3. Electric motors also function as generators by converting mechanical energy (work done to rotate the shaft) into electri ...
... 1. Motors use the magnetic force on a current-carrying wire to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. 2. Generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. 3. Electric motors also function as generators by converting mechanical energy (work done to rotate the shaft) into electri ...
Faraday
... •How can there be an EMF in the wire in this case? •Charges aren’t moving, so it can’t be magnetic fields •Electric fields must be produced by the changing B-field! •The EMF is caused by an electric field that points around the loop dB E W q F ds q E d s E ...
... •How can there be an EMF in the wire in this case? •Charges aren’t moving, so it can’t be magnetic fields •Electric fields must be produced by the changing B-field! •The EMF is caused by an electric field that points around the loop dB E W q F ds q E d s E ...
Ch. 18 sec.8,9 - Physics-YISS
... • We place this point charge at the center of the imaginary spherical surface of radius r, called the Gaussian surface. • A = 4πr^2 so the equation can be written as ...
... • We place this point charge at the center of the imaginary spherical surface of radius r, called the Gaussian surface. • A = 4πr^2 so the equation can be written as ...
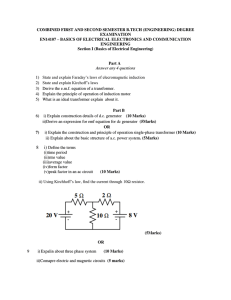
COMBINED FIRST AND SECOND SEMESTER B.TECH
... iii)RMS value:-Root Mean Square value.It is the capability of a sine wav in terms of heating power iv) Form factor:FF=RMS value/ Average value For a sin wave form factor is 1.11 v)Time period:-It is the time taken to complete one cycle ii) ...
... iii)RMS value:-Root Mean Square value.It is the capability of a sine wav in terms of heating power iv) Form factor:FF=RMS value/ Average value For a sin wave form factor is 1.11 v)Time period:-It is the time taken to complete one cycle ii) ...
Skin effect
Skin effect is the tendency of an alternating electric current (AC) to become distributed within a conductor such that the current density is largest near the surface of the conductor, and decreases with greater depths in the conductor. The electric current flows mainly at the ""skin"" of the conductor, between the outer surface and a level called the skin depth. The skin effect causes the effective resistance of the conductor to increase at higher frequencies where the skin depth is smaller, thus reducing the effective cross-section of the conductor. The skin effect is due to opposing eddy currents induced by the changing magnetic field resulting from the alternating current. At 60 Hz in copper, the skin depth is about 8.5 mm. At high frequencies the skin depth becomes much smaller. Increased AC resistance due to the skin effect can be mitigated by using specially woven litz wire. Because the interior of a large conductor carries so little of the current, tubular conductors such as pipe can be used to save weight and cost.