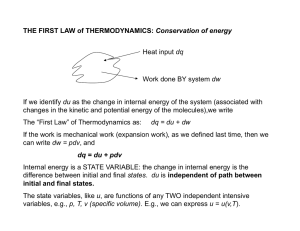
Chapter 6
... Identify each energy change as primarily heat or work, and determine whether Esys is positive or negative. a. One billiard ball (the system) hits another one, and stops rolling. b. A book (the system) is dropped on the floor c. A father pushes his daughter on the swing (the daughter & swing are the ...
... Identify each energy change as primarily heat or work, and determine whether Esys is positive or negative. a. One billiard ball (the system) hits another one, and stops rolling. b. A book (the system) is dropped on the floor c. A father pushes his daughter on the swing (the daughter & swing are the ...
Lecture 5: Heat transmission
... far wall by the more recently warmed air rising from the radiator below. In this way warm air moves to the other side of the room. Once on the other side of the room the air drops down both because it has cooled a little and because the air behind it continues to push on it. The air then continues t ...
... far wall by the more recently warmed air rising from the radiator below. In this way warm air moves to the other side of the room. Once on the other side of the room the air drops down both because it has cooled a little and because the air behind it continues to push on it. The air then continues t ...
Calorimetry - HCC Learning Web
... some final, equilibrium temperature. In this it is assumed that no heat is lost to, or gained from, the surroundings. Specific heat is defined as the quantity of heat (in calories or joules) that is required to raise the temperature of unit mass of a substance by one degree. In SI units, the units o ...
... some final, equilibrium temperature. In this it is assumed that no heat is lost to, or gained from, the surroundings. Specific heat is defined as the quantity of heat (in calories or joules) that is required to raise the temperature of unit mass of a substance by one degree. In SI units, the units o ...
Liquids
... when...a liquid evaporates, it takes energy from its surroundings that’s why alcohol feels cool to the skin. it’s also why we get cold when getting out of the shower ...
... when...a liquid evaporates, it takes energy from its surroundings that’s why alcohol feels cool to the skin. it’s also why we get cold when getting out of the shower ...
Thermal Conductivity
... Consider a conductive bar initially a room temperature. If one end of the bar is place on a fire, the temperature at that end will begin to rise making the molecules vibrate with larger amplitude. These molecules will cause their neighbors to vibrate with larger amplitude as well and so on until thi ...
... Consider a conductive bar initially a room temperature. If one end of the bar is place on a fire, the temperature at that end will begin to rise making the molecules vibrate with larger amplitude. These molecules will cause their neighbors to vibrate with larger amplitude as well and so on until thi ...
Find the resulting acceleration from a 300 N force that acts on an
... What that common temperature is depends on the amount of heat (i.e. thermal energy) in the system. Some of the factors that come into play are: How much (mass of) food there is. How much (mass of) your mouth is involved (see below). The initial temperature of the food. The "specific heat" of both th ...
... What that common temperature is depends on the amount of heat (i.e. thermal energy) in the system. Some of the factors that come into play are: How much (mass of) food there is. How much (mass of) your mouth is involved (see below). The initial temperature of the food. The "specific heat" of both th ...
Thermochemistry - thelapierres.com
... Potential energy of hiker 1 and hiker 2 is the same even though they took different paths. ...
... Potential energy of hiker 1 and hiker 2 is the same even though they took different paths. ...
A few sections on Green`s functions in 1D
... The continuity and jump conditions for Green function gives us the equations c1 u1 (ξ) − c2 u2 (ξ) = 0 c1 u�1 (ξ) − c2 u�2 (ξ) = −1. Using Kramer’s rule, the solution is ...
... The continuity and jump conditions for Green function gives us the equations c1 u1 (ξ) − c2 u2 (ξ) = 0 c1 u�1 (ξ) − c2 u�2 (ξ) = −1. Using Kramer’s rule, the solution is ...
Thermochemistry notes
... heat into or out of a system for chemical and physical processes. • Based on the fact that the heat released = the heat absorbed The device used to measure the absorption or release of heat in chemical or physical processes is called a “Calorimeter” ...
... heat into or out of a system for chemical and physical processes. • Based on the fact that the heat released = the heat absorbed The device used to measure the absorption or release of heat in chemical or physical processes is called a “Calorimeter” ...
Chapter 19 First Law of Thermodynamics 19.1 Specific Heat (I)
... which is the sum of all the kinds of energy in the system. The internal energy is a state function that depends on the equilibrium state of a system, whereas Q and W depend on the thermodynamic path between two equilibrium states. That is, Q and W are associated with processes. The heat absorbed by ...
... which is the sum of all the kinds of energy in the system. The internal energy is a state function that depends on the equilibrium state of a system, whereas Q and W depend on the thermodynamic path between two equilibrium states. That is, Q and W are associated with processes. The heat absorbed by ...
Determination of Heat of Combustion of Liquid
... The constant volume constraint means that pressure is not constant and neither is temperature making this an adiabatic process. The other type of heat of combustion is net heat of combustion. This is similar to gross heat of combustion but occurs at constant pressure rather than constant volume. The ...
... The constant volume constraint means that pressure is not constant and neither is temperature making this an adiabatic process. The other type of heat of combustion is net heat of combustion. This is similar to gross heat of combustion but occurs at constant pressure rather than constant volume. The ...
Heat equation

The heat equation is a parabolic partial differential equation that describes the distribution of heat (or variation in temperature) in a given region over time.