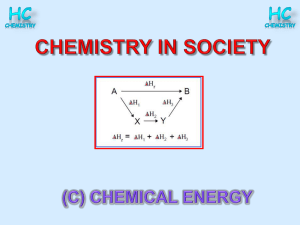
Specific Heat and Enthalpy Practice
... c. Calculate the heat released from the food in kJ. ANS: 5.43 kJ 2. 5.00 g of copper was heated from 20.0C to 80.0C. a. How much energy was used to heat the Cu? ANS: 116 J 3. If a 3.15 g ring is heated using 10.0 J, it’s temperature rises by 17.9C. Calculate the specific heat capacity of the ring ...
... c. Calculate the heat released from the food in kJ. ANS: 5.43 kJ 2. 5.00 g of copper was heated from 20.0C to 80.0C. a. How much energy was used to heat the Cu? ANS: 116 J 3. If a 3.15 g ring is heated using 10.0 J, it’s temperature rises by 17.9C. Calculate the specific heat capacity of the ring ...
Chapter 15
... or isovolumetric. If we want the gas to return to its original state without changing temperature, we must trace a curve from point C to A along an isotherm. Note that an isotherm on a PV diagram is not a straight line. The work done during the process ABCA is the area enclosed by the graph, since W ...
... or isovolumetric. If we want the gas to return to its original state without changing temperature, we must trace a curve from point C to A along an isotherm. Note that an isotherm on a PV diagram is not a straight line. The work done during the process ABCA is the area enclosed by the graph, since W ...
MME 4713 Polymers D4-DSC
... at a specific rate, usually something like 10oC per minute. The computer makes absolutely sure that the heating rate stays exactly the same throughout the experiment. But more importantly, it makes sure that the two separate pans, with their two separate heaters, heat at the same rate as each other. ...
... at a specific rate, usually something like 10oC per minute. The computer makes absolutely sure that the heating rate stays exactly the same throughout the experiment. But more importantly, it makes sure that the two separate pans, with their two separate heaters, heat at the same rate as each other. ...
Name: SOLUTIONS Physics 240, Exam #1 Sept. 24 2015 (4:15
... (b.) In the example of the Japanese bees killing the hornet by surrounding it, from the chapter on the first law of thermodynamics, how did they accomplish that? Which equation was primarily used to demonstrate the fact? Would the property in (a.) prolong its life? (c.) In the kinetic theory chapter ...
... (b.) In the example of the Japanese bees killing the hornet by surrounding it, from the chapter on the first law of thermodynamics, how did they accomplish that? Which equation was primarily used to demonstrate the fact? Would the property in (a.) prolong its life? (c.) In the kinetic theory chapter ...
Lecture Slides - School of Chemical Sciences
... The macroscopic description of a system of ~1023 particles may involve only a few variables! “Simple systems”: Macroscopically homogeneous, isotropic, uncharged, large enough that surface effects can be neglected, not acted upon by electric, magnetic, or gravitational fields. Only those few part ...
... The macroscopic description of a system of ~1023 particles may involve only a few variables! “Simple systems”: Macroscopically homogeneous, isotropic, uncharged, large enough that surface effects can be neglected, not acted upon by electric, magnetic, or gravitational fields. Only those few part ...
A Micro-Insulation Concept for MEMS Applications
... Small scale, thermally driven power sources will require appropriate insulation to achieve sufficiently high thermal conversion efficiencies. This paper presents a microinsulation design, which was developed for a thermionic microbattery, which converts the decay heat from radioactive isotopes direc ...
... Small scale, thermally driven power sources will require appropriate insulation to achieve sufficiently high thermal conversion efficiencies. This paper presents a microinsulation design, which was developed for a thermionic microbattery, which converts the decay heat from radioactive isotopes direc ...
Lecture 1
... words the change in entropy adds to zero over the entire cycle. The net entropy change per cycle: S SL SH 0 (In a Carnot engine there are two reversible energy transfers as heat, and thus two changes in the entropy of the working substance - one at temperature TH and one at TL.) Entropy as ...
... words the change in entropy adds to zero over the entire cycle. The net entropy change per cycle: S SL SH 0 (In a Carnot engine there are two reversible energy transfers as heat, and thus two changes in the entropy of the working substance - one at temperature TH and one at TL.) Entropy as ...
Chapter 15
... or isovolumetric. If we want the gas to return to its original state without changing temperature, we must trace a curve from point C to A along an isotherm. Note that an isotherm on a PV diagram is not a straight line. The work done during the process ABCA is the area enclosed by the graph, since W ...
... or isovolumetric. If we want the gas to return to its original state without changing temperature, we must trace a curve from point C to A along an isotherm. Note that an isotherm on a PV diagram is not a straight line. The work done during the process ABCA is the area enclosed by the graph, since W ...
Chapter 15 THERMODYNAMICS
... or isovolumetric. If we want the gas to return to its original state without changing temperature, we must trace a curve from point C to A along an isotherm. Note that an isotherm on a PV diagram is not a straight line. The work done during the process ABCA is the area enclosed by the graph, since W ...
... or isovolumetric. If we want the gas to return to its original state without changing temperature, we must trace a curve from point C to A along an isotherm. Note that an isotherm on a PV diagram is not a straight line. The work done during the process ABCA is the area enclosed by the graph, since W ...
Dynamically Incompressible Flow
... incompressible. Dynamic incompressibility differs from incompressibility ( ρ = constant ) by the fact that the density of the gas is considered as being approximately constant ( ρ ≈ constant ) . This small change in equal to approximately equal sign has a large bearing on the results. From this assu ...
... incompressible. Dynamic incompressibility differs from incompressibility ( ρ = constant ) by the fact that the density of the gas is considered as being approximately constant ( ρ ≈ constant ) . This small change in equal to approximately equal sign has a large bearing on the results. From this assu ...
Heat equation

The heat equation is a parabolic partial differential equation that describes the distribution of heat (or variation in temperature) in a given region over time.