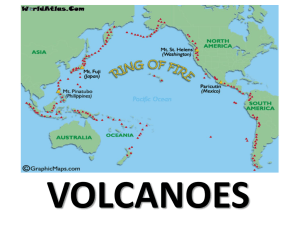
Homework04 n
... 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools and hardens within a volcano’s crater. 4. Pyroclastic materials that cool and solidify from lava ejected into the atmosphere are called _________. 5. When basaltic lava erupts beneath ...
... 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools and hardens within a volcano’s crater. 4. Pyroclastic materials that cool and solidify from lava ejected into the atmosphere are called _________. 5. When basaltic lava erupts beneath ...
6. Volcano PowerPoint
... The most recent eruption was in 1707-1708 0.8 cubic km of ash, blocks, and bombs were ejected during that eruption. (Greater than Mt. St. Helens and there were no fatalities). ...
... The most recent eruption was in 1707-1708 0.8 cubic km of ash, blocks, and bombs were ejected during that eruption. (Greater than Mt. St. Helens and there were no fatalities). ...
Volcanoes PPT - Van Buren Public Schools
... – Activity that occurs within a tectonic plate away from plate boundaries. • Most intraplate volcanism occurs where a mass of hotter than normal mantle material called a mantle plume rises toward the surface. • The activity forms localized volcanic regions called hot spots. • An example is the Hawai ...
... – Activity that occurs within a tectonic plate away from plate boundaries. • Most intraplate volcanism occurs where a mass of hotter than normal mantle material called a mantle plume rises toward the surface. • The activity forms localized volcanic regions called hot spots. • An example is the Hawai ...
Volcanoes
... Pre-eruption activities: Increase in earthquake activity under the cone increase in temperature of cone, melting of ice/snow in the crater swelling of the cone steam eruptions minor ash eruptions ...
... Pre-eruption activities: Increase in earthquake activity under the cone increase in temperature of cone, melting of ice/snow in the crater swelling of the cone steam eruptions minor ash eruptions ...
Volcanoes
... SO2 from an eruption forms tiny droplets of sulfuric acid in the upper atmosphere. The droplets significantly increase global albedo…..a negative radiative forcing that leads to cooling. Mt. Pinatubo (1991) released 22 million metric tons of SO2 and reduced the Earth’s average temperature by 0.5 deg ...
... SO2 from an eruption forms tiny droplets of sulfuric acid in the upper atmosphere. The droplets significantly increase global albedo…..a negative radiative forcing that leads to cooling. Mt. Pinatubo (1991) released 22 million metric tons of SO2 and reduced the Earth’s average temperature by 0.5 deg ...
Volcano Presentation 1
... Examples: Japan, most Pacific Islands, Caribbean Islands, west coast of North and South America. ...
... Examples: Japan, most Pacific Islands, Caribbean Islands, west coast of North and South America. ...
Volcanoes.
... Examples: Japan, most Pacific Islands, Caribbean Islands, west coast of North and South America. ...
... Examples: Japan, most Pacific Islands, Caribbean Islands, west coast of North and South America. ...
Volcanoes
... Pre-eruption activities: Increase in earthquake activity under the cone increase in temperature of cone, melting of ice/snow in the crater swelling of the cone steam eruptions minor ash eruptions ...
... Pre-eruption activities: Increase in earthquake activity under the cone increase in temperature of cone, melting of ice/snow in the crater swelling of the cone steam eruptions minor ash eruptions ...
Assignment #22A - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Crater Lake in Oregon - estimated that mt was 2000 meters higher before explosion that occurred 6600 years ago - eruptions occurring over 30-40 million years (refer to page 80, figure 4.4 how Crater Lake formed) - series of volcanos in western USA Cascade Mountain Range (page 81, figure 4.5) fatalit ...
... Crater Lake in Oregon - estimated that mt was 2000 meters higher before explosion that occurred 6600 years ago - eruptions occurring over 30-40 million years (refer to page 80, figure 4.4 how Crater Lake formed) - series of volcanos in western USA Cascade Mountain Range (page 81, figure 4.5) fatalit ...
Volcanoes - PrinceBwis
... more easily because gas dissolved in the magma bubbles • When the lava is thick and sticky the gas continues to store increasing pressure – When the pressure becomes so great an explosion takes place when the gas pushes the magma out with incredible force ...
... more easily because gas dissolved in the magma bubbles • When the lava is thick and sticky the gas continues to store increasing pressure – When the pressure becomes so great an explosion takes place when the gas pushes the magma out with incredible force ...
File - TAG Earth Science
... • When a volcano erupts, the dissolved gases (carbon dioxide and water vapor mainly) rush to the surface, carrying the magma with it, • At the surface the magma becomes lava. ...
... • When a volcano erupts, the dissolved gases (carbon dioxide and water vapor mainly) rush to the surface, carrying the magma with it, • At the surface the magma becomes lava. ...
File - Ms. D. Science CGPA
... Characteristics of a quiet eruption: A volcano erupts quietly if its magma is hot or low in silica. The gases in the magma bubble out gently. The lava oozes quietly from the vent and can flow for many kilometers. Characteristics of an explosive eruption: A volcano erupts explosively if its magma is ...
... Characteristics of a quiet eruption: A volcano erupts quietly if its magma is hot or low in silica. The gases in the magma bubble out gently. The lava oozes quietly from the vent and can flow for many kilometers. Characteristics of an explosive eruption: A volcano erupts explosively if its magma is ...
Volcanoes - Ms. Inden's Geography 12 Website | When one
... into a glacier, or possibly a cliff – this part of the lava cooled quicker, creating these columns • Look for columns like this on the highway toward Vancouver – south of Quesnel ...
... into a glacier, or possibly a cliff – this part of the lava cooled quicker, creating these columns • Look for columns like this on the highway toward Vancouver – south of Quesnel ...
Quiz # 1 Chapters 1 and 2
... 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools and hardens within a volcano’s crater. 4. Pyroclastic materials that cool and solidify from lava ejected into the atmosphere are called _________. 5. When basaltic lava erupts beneath ...
... 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools and hardens within a volcano’s crater. 4. Pyroclastic materials that cool and solidify from lava ejected into the atmosphere are called _________. 5. When basaltic lava erupts beneath ...
Practice04c
... 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools and hardens within a volcano’s crater. 4. Pyroclastic materials that cool and solidify from lava ejected into the atmosphere are called _________. 5. When basaltic lava erupts beneath ...
... 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools and hardens within a volcano’s crater. 4. Pyroclastic materials that cool and solidify from lava ejected into the atmosphere are called _________. 5. When basaltic lava erupts beneath ...
Homework for Volcanoes from Geology 1200
... 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools and hardens within a volcano’s crater. 4. Pyroclastic materials that cool and solidify from lava ejected into the atmosphere are called _________. 5. When basaltic lava erupts beneath ...
... 2. A flow of mud and pyroclastic material is called a ________. 3. A volcanic dome forms when rising ________ cools and hardens within a volcano’s crater. 4. Pyroclastic materials that cool and solidify from lava ejected into the atmosphere are called _________. 5. When basaltic lava erupts beneath ...
volcanoes - WISMYPScience
... A cloud of superheated gas, ash, and dust reaching speeds of 200 km/hr Races down mountain with temps. exceeding 300°C Large nuee ardentes may travel up to 100 km or more and will incinerate everything in its path Top: A nuee ardente roars down the slope of this Columbian volcano Bottom: Click on th ...
... A cloud of superheated gas, ash, and dust reaching speeds of 200 km/hr Races down mountain with temps. exceeding 300°C Large nuee ardentes may travel up to 100 km or more and will incinerate everything in its path Top: A nuee ardente roars down the slope of this Columbian volcano Bottom: Click on th ...
Volcanoes lesson 2
... collapse of an ancient volcano, posthumously named Mount Mazama. This volcano violently erupted approximately 7700 years ago. The basin was formed after the top 5000 feet of the volcano collapsed. Subsequent lava flows sealed the bottom, allowing the caldera to fill with approximately 4.6 trillion g ...
... collapse of an ancient volcano, posthumously named Mount Mazama. This volcano violently erupted approximately 7700 years ago. The basin was formed after the top 5000 feet of the volcano collapsed. Subsequent lava flows sealed the bottom, allowing the caldera to fill with approximately 4.6 trillion g ...
Volcanoes - 6th Grade Science with Mrs. Harlow
... are occurring around the world—on the ocean floor and on land. Nonexplosive eruptions are the most common type of eruption. These eruptions produce relatively calm flows of lava, such as those shown in Figure 1. Nonexplosive eruptions can release huge amounts of lava. ...
... are occurring around the world—on the ocean floor and on land. Nonexplosive eruptions are the most common type of eruption. These eruptions produce relatively calm flows of lava, such as those shown in Figure 1. Nonexplosive eruptions can release huge amounts of lava. ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... Volcanic eruptions Factors affecting magma viscosity • Temperature (hotter magmas are less viscous) • Chemical composition (silica content) - High silica – high viscosity (e.g., rhyolitic lava) - Low silica – more fluid (e.g., basaltic lava) • Dissolved gases (volatiles) - Mainly water vapor and c ...
... Volcanic eruptions Factors affecting magma viscosity • Temperature (hotter magmas are less viscous) • Chemical composition (silica content) - High silica – high viscosity (e.g., rhyolitic lava) - Low silica – more fluid (e.g., basaltic lava) • Dissolved gases (volatiles) - Mainly water vapor and c ...
Types of Volcanoes
... Volcanic eruptions Factors affecting magma viscosity • Temperature (hotter magmas are less viscous) • Chemical composition (silica content) - High silica – high viscosity (e.g., rhyolitic lava) - Low silica – more fluid (e.g., basaltic lava) • Dissolved gases (volatiles) - Mainly water vapor and c ...
... Volcanic eruptions Factors affecting magma viscosity • Temperature (hotter magmas are less viscous) • Chemical composition (silica content) - High silica – high viscosity (e.g., rhyolitic lava) - Low silica – more fluid (e.g., basaltic lava) • Dissolved gases (volatiles) - Mainly water vapor and c ...
Lascar (volcano)

Lascar, a stratovolcano, is the most active volcano of the northern Chilean Andes.