Introduction to Remote Sensing of Biomass
... extending from gamma rays (highest frequency & shortest wavelength) to radio waves (lowest frequency & longest wavelength) and including visible light. ...
... extending from gamma rays (highest frequency & shortest wavelength) to radio waves (lowest frequency & longest wavelength) and including visible light. ...
lecture-1 Introduction - Centre of Studies In Resources
... Most widely used remote sensors: human eyes • Motivation for remote sensing systems • Collection (eye), transmission (optic nerve) and storage (brain) • Cannot distribute the data though ...
... Most widely used remote sensors: human eyes • Motivation for remote sensing systems • Collection (eye), transmission (optic nerve) and storage (brain) • Cannot distribute the data though ...
Thermal Infrared Remote Sensing
... Minimal Definition The noncontact recording of information from the ultraviolet, visible, infrared, and microwave regions of the electromagnetic spectrum by means of instruments such as cameras, scanners, lasers, linear arrays, and/or area arrays located on platforms such as aircraft or spacecraft, ...
... Minimal Definition The noncontact recording of information from the ultraviolet, visible, infrared, and microwave regions of the electromagnetic spectrum by means of instruments such as cameras, scanners, lasers, linear arrays, and/or area arrays located on platforms such as aircraft or spacecraft, ...
Document
... observations between sensors of the same family on different satellite platforms. and hence with inter-calibration of sensors for climate monitoring, operational weather and environmental applications. This includes also the consistency over time which means over generations of one sensor family ...
... observations between sensors of the same family on different satellite platforms. and hence with inter-calibration of sensors for climate monitoring, operational weather and environmental applications. This includes also the consistency over time which means over generations of one sensor family ...
ert 245:geomatic engineering remote sensing: energy sources
... Cameras and film are used. Photography provides the best spatial resolution but less flexibility in spectral data collection and image enhancement. Spatial resolution is dependent on altitude, focal length of lenses, and the types of film used. Spectral resolution is limited to visible and near ...
... Cameras and film are used. Photography provides the best spatial resolution but less flexibility in spectral data collection and image enhancement. Spatial resolution is dependent on altitude, focal length of lenses, and the types of film used. Spectral resolution is limited to visible and near ...
IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth
... have been widely used for remote sensing image and data analysis. However, in the abovementioned scenario, with sensor technology being advanced very quickly, pattern recognition techniques have been modified and improved to address the new methodological challenges defined by the new data available ...
... have been widely used for remote sensing image and data analysis. However, in the abovementioned scenario, with sensor technology being advanced very quickly, pattern recognition techniques have been modified and improved to address the new methodological challenges defined by the new data available ...
THE USE OF OPTICAL SENSORS TO ESTIMATE PASTURE QUALITY
... limited number of wavebands used to describe a limited number of features such as nitrogen [10] and biomass variation, and leaf area index [11] while hyperspectral sensors such as the ASD Field Spec® Pro offer fine spectral resolution with numerous and contiguous wavebands across the electromagnetic ...
... limited number of wavebands used to describe a limited number of features such as nitrogen [10] and biomass variation, and leaf area index [11] while hyperspectral sensors such as the ASD Field Spec® Pro offer fine spectral resolution with numerous and contiguous wavebands across the electromagnetic ...
Document
... RADAR (Radio Detection And Ranging) • -The concept of active microwave or RADAR is that an energy pulse is sent out from an antenna and the return signal (if any) is recorded. In essence this is similar to a camera flash. In this respect reflectance (specular and diffuse) become very important as t ...
... RADAR (Radio Detection And Ranging) • -The concept of active microwave or RADAR is that an energy pulse is sent out from an antenna and the return signal (if any) is recorded. In essence this is similar to a camera flash. In this respect reflectance (specular and diffuse) become very important as t ...
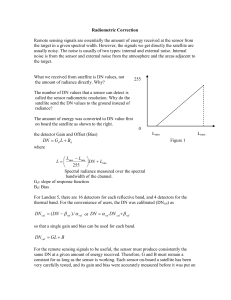
The essence of radiometric correction
... the satellite. This is called pre-launch calibration. However, nothing is perfect, after the sensors is launched, the sensor gain and bias may change. In remote sensing, we called it sensor degradation. To trace the change of sensors on board, on-board calibration is needed. Landsat 5: on-board the ...
... the satellite. This is called pre-launch calibration. However, nothing is perfect, after the sensors is launched, the sensor gain and bias may change. In remote sensing, we called it sensor degradation. To trace the change of sensors on board, on-board calibration is needed. Landsat 5: on-board the ...
Remote Sensing
... heart is synthetic aperture radar (SAR) – microwave instrument that sends pulsed signals to earth and processes the received reflected pulses. ...
... heart is synthetic aperture radar (SAR) – microwave instrument that sends pulsed signals to earth and processes the received reflected pulses. ...
Remote Sensing fundamentals Slide Notes
... Some objects emit and absorb radiation better than others. A blackbody is an object that absorbs all the electromagnetic energy that falls on the object, no matter what the wavelength of the radiation. The wavelength is the distance from wavecrest to wavecrest. Electromagnetic radiation can be descr ...
... Some objects emit and absorb radiation better than others. A blackbody is an object that absorbs all the electromagnetic energy that falls on the object, no matter what the wavelength of the radiation. The wavelength is the distance from wavecrest to wavecrest. Electromagnetic radiation can be descr ...