
Part IV - TTU Physics
... • At high temperatures, all crystalline solids have a specific heat of 6 cal/K per mole; they require 6 calories per mole to raise their temperature 1 K. • This agreement between observation and classical theory breaks down if T is low. Experiments show that at room temperature & below the specific ...
... • At high temperatures, all crystalline solids have a specific heat of 6 cal/K per mole; they require 6 calories per mole to raise their temperature 1 K. • This agreement between observation and classical theory breaks down if T is low. Experiments show that at room temperature & below the specific ...
Dose uniformity of ferromagnetic seed implants in tissue with
... (viii) Multifilament PdNi seed (3) inserted in a plastic catheter filled up with water: this implant is similar to the previous one, but the catheter is filled up with water to reduce the influence of the intermediate air layer. (ix) Multifilament PdNi seed (4) inserted in a metallic needle: the cat ...
... (viii) Multifilament PdNi seed (3) inserted in a plastic catheter filled up with water: this implant is similar to the previous one, but the catheter is filled up with water to reduce the influence of the intermediate air layer. (ix) Multifilament PdNi seed (4) inserted in a metallic needle: the cat ...
Explanatory Metaphors
... on the science of climate change. It explains the basic mechanism of climate change in simple terms that are easily grasped and remembered. Heat-Trapping Blanket: Climate change is caused, in part, by the man-made blanket of carbon dioxide that is building up around the Earth and trapping in heat. T ...
... on the science of climate change. It explains the basic mechanism of climate change in simple terms that are easily grasped and remembered. Heat-Trapping Blanket: Climate change is caused, in part, by the man-made blanket of carbon dioxide that is building up around the Earth and trapping in heat. T ...
Regulation
... • 3. Origin of disturbance/disease in regulated system • 4. History of regulated systems and their description • 5. Different types of governors (automated regulators) • 6. Regulation of cardiac output and blood pressure • heart • vessels • kidney regulator ...
... • 3. Origin of disturbance/disease in regulated system • 4. History of regulated systems and their description • 5. Different types of governors (automated regulators) • 6. Regulation of cardiac output and blood pressure • heart • vessels • kidney regulator ...
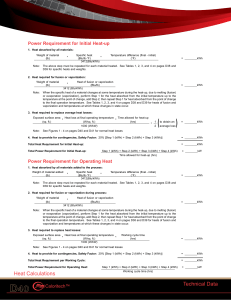
Technical Data Heat Calculations
... When the specific heat of a material changes at some temperature during the heat-up, due to melting (fusion) or evaporation (vaporization), perform Step 1 for the heat absorbed from the initial temperature up to the temperature at the point of change, add Step 2, then repeat Step 1 for heat absorbed ...
... When the specific heat of a material changes at some temperature during the heat-up, due to melting (fusion) or evaporation (vaporization), perform Step 1 for the heat absorbed from the initial temperature up to the temperature at the point of change, add Step 2, then repeat Step 1 for heat absorbed ...
Air Mass Modification over the Eastem Gulf of Mexico as a Function
... eastern Gulf of Mexico during a typical February is comprised of distinctly different wind regimes at the sea surface. For instance, cold fronts frequently cross the Gulf in the winter. These "northers" bring cold dry air over the Gulf in their wake as described in DiMego et al. (1976), for instance ...
... eastern Gulf of Mexico during a typical February is comprised of distinctly different wind regimes at the sea surface. For instance, cold fronts frequently cross the Gulf in the winter. These "northers" bring cold dry air over the Gulf in their wake as described in DiMego et al. (1976), for instance ...
972649 Quasi-Isothermal Expansion Engines for Liquid Nitrogen
... enabled the range of the vehicle to be increased by 50% over that of using each fuel source separately. Scavenging heat from engine friction and vehicle braking was also proposed. Even though many researchers have investigated the energy storage potential of cryogens and have developed several means ...
... enabled the range of the vehicle to be increased by 50% over that of using each fuel source separately. Scavenging heat from engine friction and vehicle braking was also proposed. Even though many researchers have investigated the energy storage potential of cryogens and have developed several means ...
Energy Transfer Technologies Energy Transfer Technologies
... In order to protect themselves from the intense heat, firefighters wear special protective clothing. The clothing uses special materials that prevent heat transfer. At the same time, firefighters use water to increase heat transfer. When water is sprayed over flames, the liquid water quickly heats a ...
... In order to protect themselves from the intense heat, firefighters wear special protective clothing. The clothing uses special materials that prevent heat transfer. At the same time, firefighters use water to increase heat transfer. When water is sprayed over flames, the liquid water quickly heats a ...
The Greenhouse Effect - mc
... 100% of the heat lost from the Earth's atmosphere to space is lost by radiation. However, at the temperatures found in the Earth's atmosphere, monatomic and diatomic gas molecules are not able to radiate energy - specifically, Nitrogen (N2), Oxygen (O2), and Argon (Ar) have no way to lose heat. (Con ...
... 100% of the heat lost from the Earth's atmosphere to space is lost by radiation. However, at the temperatures found in the Earth's atmosphere, monatomic and diatomic gas molecules are not able to radiate energy - specifically, Nitrogen (N2), Oxygen (O2), and Argon (Ar) have no way to lose heat. (Con ...
Standard Method of Test for Thermal Conductivity of Rock
... Further detail depends on the application of the results. 10.1.3 A detailed listing of the equipment actually used for the test shall be included in the report. The name, model number, and basic specifications of each major piece shall be listed. 10.1.4 If the actual equipment or procedure has varie ...
... Further detail depends on the application of the results. 10.1.3 A detailed listing of the equipment actually used for the test shall be included in the report. The name, model number, and basic specifications of each major piece shall be listed. 10.1.4 If the actual equipment or procedure has varie ...
Document
... system - the part of the universe being studied and observed surroundings - everything else in the universe open system - a system that can exchange matter and energy with the surroundings eg. an open beaker of water a candle burning closed system - allows energy transfer but is closed to the flow o ...
... system - the part of the universe being studied and observed surroundings - everything else in the universe open system - a system that can exchange matter and energy with the surroundings eg. an open beaker of water a candle burning closed system - allows energy transfer but is closed to the flow o ...
Lecture No.8 8.1 Modes of heat loss
... warm air is blown from unit heaters that have self contained fireboxes. These heaters consist of three functional parts. Fuel is combusted in a firebox to provide heat. The heat is initially contained in the exhaust, which rises through the inside of a set of thin walled metal tubes on it way to the ...
... warm air is blown from unit heaters that have self contained fireboxes. These heaters consist of three functional parts. Fuel is combusted in a firebox to provide heat. The heat is initially contained in the exhaust, which rises through the inside of a set of thin walled metal tubes on it way to the ...
6. Magnetic Cooling - Particle Physics
... To get some idea of the relative magnitudes, we look at the unit for electronic dipole moment (Bohr magneton) and the unit for nuclear dipole moment (nuclear magneton): Bohr magneton, µB = 9.27 × 10−24 J/T Nuclear magneton, µn = 5.05 × 10−27 J/T The nuclear magneton is nearly 2000 times smaller. Thi ...
... To get some idea of the relative magnitudes, we look at the unit for electronic dipole moment (Bohr magneton) and the unit for nuclear dipole moment (nuclear magneton): Bohr magneton, µB = 9.27 × 10−24 J/T Nuclear magneton, µn = 5.05 × 10−27 J/T The nuclear magneton is nearly 2000 times smaller. Thi ...
Simulation of Biomechanical and Chemical Transport in
... N is the number of flow channels, C is specific heat, Kt is thermal conductivity and Kp is pressure conductivity; In converting to dimensionless concentration units as above, specific heat must be eliminated from the calculations by similar means, and Qg must be set to zero (internal heat generation ...
... N is the number of flow channels, C is specific heat, Kt is thermal conductivity and Kp is pressure conductivity; In converting to dimensionless concentration units as above, specific heat must be eliminated from the calculations by similar means, and Qg must be set to zero (internal heat generation ...
An Overview of Body Systems
... 2) Make up 50-63 of the pounds of the weight in a 125pound adult’s weight 3) Attach to bones b. Functions 1) Contract and relax to cause movement by pulling on the bones 2) Stabilize body position 3) Generate heat 4. Nervous System a. Composed of the brain, spinal cord, nerves and special sense orga ...
... 2) Make up 50-63 of the pounds of the weight in a 125pound adult’s weight 3) Attach to bones b. Functions 1) Contract and relax to cause movement by pulling on the bones 2) Stabilize body position 3) Generate heat 4. Nervous System a. Composed of the brain, spinal cord, nerves and special sense orga ...
Energy
... 1. All gases have a pressure of exactly 1 atm. 2. Pure substances are in the form that they normally exist in at 25oC and 1 atm pressure. 3. All solutions have a concentration of exactly ...
... 1. All gases have a pressure of exactly 1 atm. 2. Pure substances are in the form that they normally exist in at 25oC and 1 atm pressure. 3. All solutions have a concentration of exactly ...
worksheet
... 5. B (5 choices) 4.3 – The transfer of energy as heat can be controlled (pgs. 116–121). 6. Heat moves from __________ to __________. a. cold/hot b. Heat moves both ways. ...
... 5. B (5 choices) 4.3 – The transfer of energy as heat can be controlled (pgs. 116–121). 6. Heat moves from __________ to __________. a. cold/hot b. Heat moves both ways. ...
Chapter 19
... from 10.0 L to 2.0 L. (In this process, some heat flows out of the gas and the temperature drops.) Heat is then added to the gas, holding the volume constant, and the pressure and temperature are allowed to rise (line DA) until the temperature reaches its original value (TA = TB). Calculate (a) the ...
... from 10.0 L to 2.0 L. (In this process, some heat flows out of the gas and the temperature drops.) Heat is then added to the gas, holding the volume constant, and the pressure and temperature are allowed to rise (line DA) until the temperature reaches its original value (TA = TB). Calculate (a) the ...
BTD QUESTION BANK[1].
... 3.5 bar according to a law PVn = Constant .The fluid is then heated reversibly at constant volume until the pressure is 4 bar ,The specific volume is then 0.5 m3 /Kg .A reversible expansion according to a law PV2 constant ,restore the fluid to its initial state .Sketch the cycle on P-V- diagram and ...
... 3.5 bar according to a law PVn = Constant .The fluid is then heated reversibly at constant volume until the pressure is 4 bar ,The specific volume is then 0.5 m3 /Kg .A reversible expansion according to a law PV2 constant ,restore the fluid to its initial state .Sketch the cycle on P-V- diagram and ...
Chapter 13 Energy, Heat, and Chemical Change
... distance in Euclidean space (measured along a straight line, “as the crow flies”) is determined entirely by the positions of the two endpoints. There is one and only one possible value. See the sketch in (e). 6. The first law of thermodynamics requires that energy be conserved-specifically, that any ...
... distance in Euclidean space (measured along a straight line, “as the crow flies”) is determined entirely by the positions of the two endpoints. There is one and only one possible value. See the sketch in (e). 6. The first law of thermodynamics requires that energy be conserved-specifically, that any ...
Ch 2 - HCC Learning Web
... base units by factors of ten • The unit analysis method is a tool to convert between units of a given value to units asked for in the answer • A percent expresses the amount of a single quantity compared to an entire sample • Volume of a solid = l × w × t; it is often reported in cm3 • Volume by dis ...
... base units by factors of ten • The unit analysis method is a tool to convert between units of a given value to units asked for in the answer • A percent expresses the amount of a single quantity compared to an entire sample • Volume of a solid = l × w × t; it is often reported in cm3 • Volume by dis ...
Film Cooling Characteristics of a Single Round Hole at
... disadvantage of this method is that the coating is nonrenewable, so the method is restricted to high heat fluxes of short duration, such as re-entering space vehicles. In transpiration, the surface is porous and a secondary fluid enters the boundary layers through the porous wall. A disadvantage to ...
... disadvantage of this method is that the coating is nonrenewable, so the method is restricted to high heat fluxes of short duration, such as re-entering space vehicles. In transpiration, the surface is porous and a secondary fluid enters the boundary layers through the porous wall. A disadvantage to ...
Full text in PDF form
... The Braysson cycle is a hybrid power cycle based on a conventional Brayton cycle for the high tempe rature heat addition while adopting the Ericsson cycle for the low temperature heat rejection as proposed and investigated by Frost et al. [1] using the first law of thermodynamics. Very recently, som ...
... The Braysson cycle is a hybrid power cycle based on a conventional Brayton cycle for the high tempe rature heat addition while adopting the Ericsson cycle for the low temperature heat rejection as proposed and investigated by Frost et al. [1] using the first law of thermodynamics. Very recently, som ...
closed system
... gases. Radiation is the only mode which transmits energy through a vacuum and is likely to be the dominant mode of heat transfer from surfaces at high temperatures (>103 K). Heat conduction in a solid is governed by Fourier’s law and the thermal conductivity of the material. Convective heat transfer ...
... gases. Radiation is the only mode which transmits energy through a vacuum and is likely to be the dominant mode of heat transfer from surfaces at high temperatures (>103 K). Heat conduction in a solid is governed by Fourier’s law and the thermal conductivity of the material. Convective heat transfer ...
Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia is elevated body temperature due to failed thermoregulation that occurs when a body produces or absorbs more heat than it dissipates. Extreme temperature elevation then becomes a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment to prevent disability or death.The most common causes include heat stroke and adverse reactions to drugs. The former is an acute temperature elevation caused by exposure to excessive heat, or combination of heat and humidity, that overwhelms the heat-regulating mechanisms. The latter is a relatively rare side effect of many drugs, particularly those that affect the central nervous system. Malignant hyperthermia is a rare complication of some types of general anesthesia.Hyperthermia differs from fever in that the body's temperature set point remains unchanged. The opposite is hypothermia, which occurs when the temperature drops below that required to maintain normal metabolism.

















![BTD QUESTION BANK[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009330461_1-f5de3108f7a7a17ebe3a8cbd391865db-300x300.png)




