Biological Constraints on Signal Integration in - q
... Dept. of Molecular Biology, Princeton University,E-mail: [email protected] ...
... Dept. of Molecular Biology, Princeton University,E-mail: [email protected] ...
File
... listening to soothing music. Let Xbe the number of puzzles completed successfully by a subject. The psychologist found that X had the following probability distribution: Value of X Probability ...
... listening to soothing music. Let Xbe the number of puzzles completed successfully by a subject. The psychologist found that X had the following probability distribution: Value of X Probability ...
DGRC Overview slides - Computer Science, Columbia University
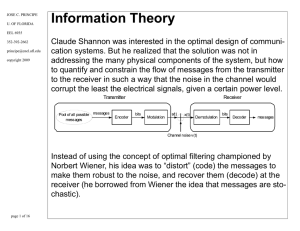
... Special subproblems: Ontology browsing, ontology merging, understanding PDF, … Support for existing “reports” In-memory data manipulation and analysis ...
... Special subproblems: Ontology browsing, ontology merging, understanding PDF, … Support for existing “reports” In-memory data manipulation and analysis ...